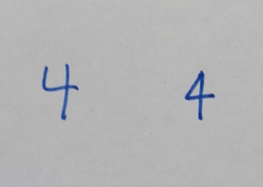|
Boyce V R
''Boyce v R'' is a 2004 Judicial Committee of the Privy Council (JCPC) case which upheld the law that sets out a mandatory sentence of death for murder in Barbados. The JCPC held in some cases, the law that makes capital punishment mandatory for murder will violate the prohibition on "inhuman or degrading punishment" in the Constitution of Barbados. (This principle is consistent with the 2002 JCPC cases of '' Hughes'', '' Fox'', and '' Reyes''.) However, because (1) the Constitution of Barbados disallows itself to act to invalidate laws that existed prior to the enactment of the constitution, and (2) the law in question pre-dated the constitution, the mandatory death provisions of the law could not be invalidated and must be upheld. In '' Matthew v S'', which was released on the same day, the JCPC applied the same principles to a similar law in Trinidad and Tobago. See also * Judiciary of Barbados * Attorney General of Barbados * Supreme Court of Judicature (Barbados) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judicial Committee Of The Privy Council
The Judicial Committee of the Privy Council (JCPC) is the highest court of appeal for the Crown Dependencies, the British Overseas Territories, some Commonwealth countries and a few institutions in the United Kingdom. Established on 14 August 1833 to hear appeals formerly heard by the King-in-Council, the Privy Council formerly acted as the court of last resort for the entire British Empire, other than for the United Kingdom itself.P. A. Howell, ''The Judicial Committee of the Privy Council, 1833–1876: Its Origins, Structure, and Development'', Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 1979 Formally a statutory committee of His Majesty's Most Honourable Privy Council, the Judicial Committee consists of senior judges who are Privy Councillors; they are predominantly Justices of the Supreme Court of the United Kingdom and senior judges from the Commonwealth of Nations. Although it is often simply referred to as the 'Privy Council', the Judicial Committee is only one cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judiciary Of Barbados
The Judiciary of Barbados is an independent branch of the Barbadian government, subject only to the Barbadian Constitution. It is headed by the Chief Justice of Barbados. Barbados is a common law jurisdiction, in which precedents from English law and British Commonwealth tradition may be taken into account. Structure There are three levels of courts in Barbados, structured as follows: *The magistrates' courts *The Supreme Court, made up of: **The High Court **The Court of Appeal ***Caribbean Court of Justice, which replaced the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council in 2005 in cases originating from Barbados. The Constitution places the Caribbean Court of Justice at the pinnacle of the Barbadian judicial system. The Court has two types of jurisdictions: appellate jurisdiction and original jurisdiction. In its appellate jurisdiction, the court serves as the final court of appeal from any decision given by the Court of Appeal of Barbados in civil and criminal matters. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prisoners Sentenced To Death By Barbados
A prisoner (also known as an inmate or detainee) is a person who is deprived of liberty against their will. This can be by confinement, captivity, or forcible restraint. The term applies particularly to serving a prison sentence in a prison. English law "Prisoner" is a legal term for a person who is imprisoned. In section 1 of the Prison Security Act 1992, the word "prisoner" means any person for the time being in a prison as a result of any requirement imposed by a court or otherwise that he be detained in legal custody. "Prisoner" was a legal term for a person prosecuted for felony. It was not applicable to a person prosecuted for misdemeanour. The abolition of the distinction between felony and misdemeanour by section 1 of the Criminal Law Act 1967 has rendered this distinction obsolete. Glanville Williams described as "invidious" the practice of using the term "prisoner" in reference to a person who had not been convicted. History The earliest evidence of the existe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judicial Committee Of The Privy Council Cases On Appeal From Barbados
The judiciary (also known as the judicial system, judicature, judicial branch, judiciative branch, and court or judiciary system) is the system of courts that adjudicates legal disputes/disagreements and interprets, defends, and applies the law in legal cases. Definition The judiciary is the system of courts that interprets, defends, and applies the law in the name of the state. The judiciary can also be thought of as the mechanism for the resolution of disputes. Under the doctrine of the separation of powers, the judiciary generally does not make statutory law (which is the responsibility of the legislature) or enforce law (which is the responsibility of the executive), but rather interprets, defends, and applies the law to the facts of each case. However, in some countries the judiciary does make common law. In many jurisdictions the judicial branch has the power to change laws through the process of judicial review. Courts with judicial review power may annul the laws ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Death Penalty Case Law
Death is the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain an organism. For organisms with a brain, death can also be defined as the irreversible cessation of functioning of the whole brain, including brainstem, and brain death is sometimes used as a legal definition of death. The remains of a former organism normally begin to decompose shortly after death. Death is an inevitable process that eventually occurs in almost all organisms. Death is generally applied to whole organisms; the similar process seen in individual components of an organism, such as cells or tissues, is necrosis. Something that is not considered an organism, such as a virus, can be physically destroyed but is not said to die. As of the early 21st century, over 150,000 humans die each day, with ageing being by far the most common cause of death. Many cultures and religions have the idea of an afterlife, and also may hold the idea of judgement of good and bad deeds in one's life (heave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2004 In Barbados
4 (four) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 3 and preceding 5. It is the smallest semiprime and composite number, and is considered unlucky in many East Asian cultures. In mathematics Four is the smallest composite number, its proper divisors being and . Four is the sum and product of two with itself: 2 + 2 = 4 = 2 x 2, the only number b such that a + a = b = a x a, which also makes four the smallest squared prime number p^. In Knuth's up-arrow notation, , and so forth, for any number of up arrows. By consequence, four is the only square one more than a prime number, specifically three. The sum of the first four prime numbers two + three + five + seven is the only sum of four consecutive prime numbers that yields an odd prime number, seventeen, which is the fourth super-prime. Four lies between the first proper pair of twin primes, three and five, which are the first two Fermat primes, like seventeen, which is the third. On the other han ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2004 In United Kingdom Case Law
4 (four) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 3 and preceding 5. It is the smallest semiprime and composite number, and is considered unlucky in many East Asian cultures. In mathematics Four is the smallest composite number, its proper divisors being and . Four is the sum and product of two with itself: 2 + 2 = 4 = 2 x 2, the only number b such that a + a = b = a x a, which also makes four the smallest squared prime number p^. In Knuth's up-arrow notation, , and so forth, for any number of up arrows. By consequence, four is the only square one more than a prime number, specifically three. The sum of the first four prime numbers two + three + five + seven is the only sum of four consecutive prime numbers that yields an odd prime number, seventeen, which is the fourth super-prime. Four lies between the first proper pair of twin primes, three and five, which are the first two Fermat primes, like seventeen, which is the third. On the other hand, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supreme Court Of Judicature (Barbados)
The Supreme Court of Judicature of Barbados is the highest judicial body in the country of Barbados. It is made up of the High Court and the Court of Appeals.Law Courts of Barbados - About the court Appeals from the Supreme Court can be further referred to the of the (CCJ). Functions The High Court consists of , |
Attorney General Of Barbados
The Attorney-General of Barbados is the primary legal advisor to the Government of Barbados. Legal basis According to Article 72 of the Constitution of Barbados, the Attorney-General holds ministerial rank in the government. He may, in the case of certain offences, give general or special directions to the Director of Public Prosecutions, which the latter must follow. List of attorneys-general *Robert Hooper c.1693 *Edward Chilton, 1698 to 1705 *Thomas Hodges, FRS ?1706 to ?1721 *Jonathan Blenman, 1726 to *Blenman 1728 to *Timothy Blenman, 1741 to *Henry Beckles, 1770 to 1772 *Robert Burnett *Anthony Chester *Robert Burnett Jones *John Beckles, 1807 to 1823 *Matthew Coulthurst, to 1824 *Samuel Hinds, 1824 to 1826 *Henry Edward Sharpe, 1826 to 1828 *John Paynter Musson, 1828 to 1831 *Henry Edward Sharpe, 1831 to c. 1838 *post of Attorney-General of Barbados vacant, c. 1838 to 1841 *Henry Edward Sharpe, 1841 to 1846 *John Sealy, 1846 to >1869 *Francis Fleming, 1878 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinidad And Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago (, ), officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean. Consisting of the main islands Trinidad and Tobago, and numerous much smaller islands, it is situated south of Grenada and off the coast of northeastern Venezuela. It shares maritime boundaries with Barbados to the northeast, Grenada to the northwest and Venezuela to the south and west. Trinidad and Tobago is generally considered to be part of the West Indies. The island country's capital is Port of Spain, while its largest and most populous city is San Fernando. The island of Trinidad was inhabited for centuries by Indigenous peoples before becoming a colony in the Spanish Empire, following the arrival of Christopher Columbus, in 1498. Spanish governor José María Chacón surrendered the island to a British fleet under the command of Sir Ralph Abercromby in 1797. Trinidad and Tobago were ceded to Britain in 1802 under the Treaty of Amiens as se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court Of Appeal Of Barbados
A court is any person or institution, often as a government institution, with the authority to adjudicate legal disputes between parties and carry out the administration of justice in civil, criminal, and administrative matters in accordance with the rule of law. In both common law and civil law legal systems, courts are the central means for dispute resolution, and it is generally understood that all people have an ability to bring their claims before a court. Similarly, the rights of those accused of a crime include the right to present a defense before a court. The system of courts that interprets and applies the law is collectively known as the judiciary. The place where a court sits is known as a venue. The room where court proceedings occur is known as a courtroom, and the building as a courthouse; court facilities range from simple and very small facilities in rural communities to large complex facilities in urban communities. The practical authority given ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matthew V S
''Matthew v S'' is a 2004 Judicial Committee of the Privy Council (JCPC) case which upheld the law that sets out a mandatory sentence of death for murder in Trinidad and Tobago. The JCPC held in some cases, the law that makes capital punishment mandatory for murder will violate the prohibition on "inhuman or degrading punishment" in the Constitution of Trinidad and Tobago. (This principle is consistent with the 2002 JCPC cases of '' Hughes'', ''Fox'', and '' Reyes''.) However, because (1) the Constitution of Trinidad and Tobago disallows itself to act to invalidate laws that existed prior to the enactment of the constitution, and (2) the law in question pre-dated the constitution, the mandatory death provisions of the law could not be invalidated and must be upheld. In '' Boyce v R'', which was released on the same day, the JCPC applied the same principles to a similar law in Barbados Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)