|
Bowral Hospital
Bowral () is the largest town in the Southern Highlands of New South Wales, Australia, about ninety minutes southwest of Sydney. It is the main business and entertainment precinct of the Wingecarribee Shire and Highlands. Bowral once served as a rural summer retreat for the gentry of Sydney, resulting in the establishment of a number of estates and manor houses in the district. Today, it is considered a "dormitory suburb" for commuter Sydneysiders, though it is 132 km away from the city centre. Bowral is often associated with the cricketer Sir Donald Bradman. Bowral is close to several other historic towns, being from Mittagong, from both Moss Vale and Berrima. The suburb of East Bowral and the village of Burradoo are nearby. History Bowral's colonial history extends back for approximately 200 years. During the pre-colonial era, the land was home to an Aboriginal tribe known as Tharawal (or Dharawal). The first European arrival was ex-convict John Wilson, who wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mittagong Parish, Camden
The Parish of Mittagong is a parish of the County of Camden in the Southern Highlands region of New South Wales. It includes the town of Bowral and the southern parts of Mittagong. Overview The Old Hume Highway is the boundary in the north, including the section which runs through Mittagong, so that the part of Mittagong south of the Old Hume highway is in Mittagong parish, with most of the northern portion in the Parish of Colo. The exception is Welby (formerly the village of Fitzroy) at which is almost cut off from the rest of the parish, located between the old and new Hume Highways. This is a rectangular portion of land with only one corner touching the main part of the parish, along the Gibbergunyah creek. The current Hume Highway runs somewhat to the north of the parish. The Southern Highlands railway line passes through the parish, including the stations of Burradoo, Bowral and Mittagong. The Nepean River is the boundary in the east. The Wingecarribee River is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sydneysiders
Sydney ( ) is the capital city of the state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Sydney Harbour and extends about towards the Blue Mountains to the west, Hawkesbury to the north, the Royal National Park to the south and Macarthur to the south-west. Sydney is made up of 658 suburbs, spread across 33 local government areas. Residents of the city are known as "Sydneysiders". The 2021 census recorded the population of Greater Sydney as 5,231,150, meaning the city is home to approximately 66% of the state's population. Estimated resident population, 30 June 2017. Nicknames of the city include the 'Emerald City' and the 'Harbour City'. Aboriginal Australians have inhabited the Greater Sydney region for at least 30,000 years, and Aboriginal engravings and cultural sites are common throughout Greater Sydney. The traditional custodians of the land on which modern Sydney stands are th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colony Of New South Wales
The Colony of New South Wales was a colony of the British Empire from 1788 to 1901, when it became a State of the Commonwealth of Australia. At its greatest extent, the colony of New South Wales included the present-day Australian states of New South Wales, Queensland, Victoria, Tasmania, and South Australia, the Northern Territory as well as New Zealand. The first "responsible" self-government of New South Wales was formed on 6 June 1856 with Sir Stuart Alexander Donaldson appointed by Governor Sir William Denison as its first Colonial Secretary. History Formation On 18 January 1788, the First Fleet led by Captain Arthur Phillip founded the first British settlement in Australian history as a penal colony. Having set sail on 13 May 1787, Captain Arthur Phillip assumed the role of governor of the settlement upon arrival. On 18 January 1788, the first ship of the First Fleet, HMS ''Supply'', with Phillip aboard, reached Botany Bay. However, Botany Bay was found to be unsuita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lachlan Macquarie
Major-general (United Kingdom), Major General Lachlan Macquarie, Companion of the Order of the Bath, CB (; gd, Lachann MacGuaire; 31 January 1762 – 1 July 1824) was a British Army officer and colonial administrator from Scotland. Macquarie served as the fifth Governor of New South Wales from 1810 to 1821, and had a leading role in the social, economic, and architectural development of the colony. He is considered by historians to have had a crucial influence on the transition of New South Wales from a penal colony to a free settlement and therefore to have played a major role in the shaping of Australian society in the early nineteenth century. Early life Lachlan Macquarie was born on the island of Ulva off the coast of the Isle of Mull in the Inner Hebrides, a chain of islands off the West Coast of Scotland. His father, Lachlan senior, worked as a carpenter and miller, and was a cousin of a Clan MacQuarrie chieftain. His mother, Margaret, was the sister of the influential Cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Throsby
Charles Throsby (1777 – 2 April 1828) was an English surgeon who, after he migrated to New South Wales in 1802, became an explorer, pioneer and parliamentarian. He opened up much new land beyond the Blue Mountains for colonial settlement. Early life Throsby was born in Glenfield near Leicester in England. He was engaged as a surgeon on the convict transport ''Coromandel'' carrying 136 male convicts from Portsmouth to Sydney. They departed Portsmouth 12 February 1802, and arrived in Sydney without calling in port on 13 June 1802, with no reported convict deaths under his care. Soon afterwards he joined the medical staff of the Colony, and in October 1802 he was appointed a magistrate and acting-surgeon at Castle Hill. In August 1804 he was transferred to Newcastle, and in April 1805 was made superintendent there. Towards the end of 1808 he was given a grant of 500 acres (2 km²) at Cabramatta, and in the following year resigned his position at Newcastle. In 181 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Oxley
John Joseph William Molesworth Oxley (1784 – 25 May 1828) was an explorer and surveyor of Australia in the early period of British colonisation. He served as Surveyor General of New South Wales and is perhaps best known for his two expeditions into the interior of New South Wales and his exploration of the Tweed River and the Brisbane River in what is now the state of Queensland. Early life John Oxley was born at Kirkham Abbey near Westow in Yorkshire, Great Britain. He was baptised at Bulmer on 6 July 1784, his parents recorded as John and Arabella Oxley. Naval career In 1799 (aged 15), he entered the Royal Navy as a midshipman on the . He travelled to Australia in October 1802 as master's mate of the naval vessel , which carried out coastal surveying (including the survey of Western Port), and this first stay in the Colonies would last for five years. In 1805, Oxley became acting lieutenant of the ''Buffalo'' and traveled to Van Diemen's Land the following yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hume And Hovell Expedition
The Hume and Hovell expedition was a journey of exploration undertaken in eastern Australia. In 1824 the Governor of New South Wales, Sir Thomas Brisbane, commissioned Hamilton Hume and former Royal Navy Captain William Hovell to lead an expedition to find new grazing land in the south of the colony, and also to find an answer to the mystery of where New South Wales's western rivers flowed. Surveyor General John Oxley asserted that no river could fall into the sea between Cape Otway and Spencer's Gulf, and that the country south of parallel of 34 degrees was ' uninhabitable and useless for all purposes of civilised men,' and for the time exploration in this direction was greatly discouraged. In 1824, newly appointed Sir Thomas Brisbane, who disbelieved this statement, offered to land a party of prisoners near Wilson's Promontory and grant them a free pardon, as well as a grant of land, to those who found their way overland to Sydney. Alexander Berry recommended the Governor to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Banks
Sir Joseph Banks, 1st Baronet, (19 June 1820) was an English naturalist, botanist, and patron of the natural sciences. Banks made his name on the 1766 natural-history expedition to Newfoundland and Labrador. He took part in Captain James Cook's first great voyage (1768–1771), visiting Brazil, Tahiti, and after 6 months in New Zealand, Australia, returning to immediate fame. He held the position of president of the Royal Society for over 41 years. He advised King George III on the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, and by sending botanists around the world to collect plants, he made Kew the world's leading botanical garden. He is credited for bringing 30,000 plant specimens home with him; amongst them, he was the first European to document 1,400. Banks advocated British settlement in New South Wales and the colonisation of Australia, as well as the establishment of Botany Bay as a place for the reception of convicts, and advised the British government on all Australian matte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Caley
George Caley (10 June 1770 – 23 May 1829) was an English botanist and explorer, active in Australia for the majority of his career. Early life Caley was born in Craven, Yorkshire, England, the son of a horse-dealer. He was educated at the Free Grammar School at Manchester for around four years and was then taken into his father's stables. According to a letter which was sent to William Withering on 15 June 1798, he started teaching himself botany after he coming across a volume of book about farriery which was written by William Gibson cause he became interested in the herbs mentioned in prescriptions. He started learning botany by studying Botanical arrangement (1787-92) by William Withering. He changed his job to that of a weaver in order to allow himself to spent more time with his associate in Manchester School of Botanists which consist of John Mellor, James Crowther, and John Dewhurst. This school was also attended by John Horsefield on 1808. In March 1795 he wrote t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Hunter (Royal Navy Officer)
Vice Admiral John Hunter (29 August 1737 – 13 March 1821) was an officer of the Royal Navy, who succeeded Arthur Phillip as the second Governor of New South Wales, serving from 1795 to 1800.J. J. Auchmuty,Hunter, John (1737–1821), ''Australian Dictionary of Biography'', Volume 1, MUP, 1966, pp 566–572. Retrieved 12 August 2009 Both a sailor and a scholar, he explored the Parramatta River as early as 1788, and was the first to surmise that Tasmania might be an island. As governor, he tried to combat serious abuses by the military in the face of powerful local interests led by John MacArthur. Hunter's name is commemorated in historic locations such as Hunter Valley and Hunter Street, Sydney. Family and early life John Hunter was born in Leith, Scotland, the son of William Hunter, a captain in the merchant service, and Helen, ''née'' Drummond, daughter of J. Drummond and niece of George Drummond, several-time lord provost of Edinburgh. As a boy Hunter was sent to live wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
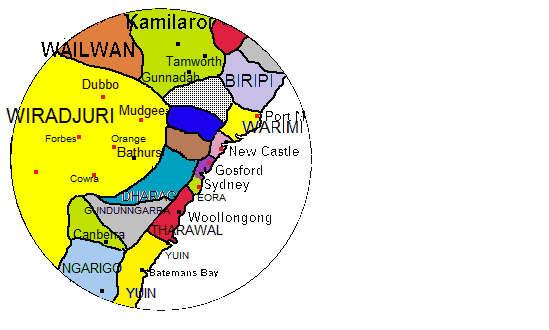
Dharawal
The Dharawal people, also spelt Tharawal and other variants, are an Aboriginal Australian people, identified by the Dharawal language. Traditionally, they lived as hunter–fisher–gatherers in family groups or clans with ties of kinship, scattered along the coastal area of what is now the Sydney basin in New South Wales. Etymology ''Dharawal'' means cabbage palm. Country According to ethnologist Norman Tindale, traditional Dharawal lands encompass some from the south of Sydney Harbour, through Georges River, Botany Bay, Port Hacking and south beyond the Shoalhaven River to the Beecroft Peninsula. Their inland extent reaches Campbelltown and Camden. Clans The Gweagal were also known as the "Fire Clan". They are said to be the first people to first make contact with Captain Cook. The artist Sydney Parkinson, one of the Endeavour's crew members, wrote in his journal that the indigenous people threatened them shouting words he transcribed as ''warra warra wai,'' which he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tharawal
The Dharawal people, also spelt Tharawal and other variants, are an Aboriginal Australian people, identified by the Dharawal language. Traditionally, they lived as hunter–fisher–gatherers in family groups or clans with ties of kinship, scattered along the coastal area of what is now the Sydney basin in New South Wales. Etymology ''Dharawal'' means cabbage palm. Country According to ethnologist Norman Tindale, traditional Dharawal lands encompass some from the south of Sydney Harbour, through Georges River, Botany Bay, Port Hacking and south beyond the Shoalhaven River to the Beecroft Peninsula. Their inland extent reaches Campbelltown and Camden. Clans The Gweagal were also known as the "Fire Clan". They are said to be the first people to first make contact with Captain Cook. The artist Sydney Parkinson, one of the Endeavour's crew members, wrote in his journal that the indigenous people threatened them shouting words he transcribed as ''warra warra wai,'' which he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




_-_geograph.org.uk_-_950933.jpg)