|
Bouchout Castle
Bouchout Castle ( nl, Kasteel van Bouchout, ; french: Château de Bouchout, ) is a castle in the Flemish town of Meise, Belgium. In the 12th century, this territory of the young Duchy of Brabant was strategically positioned between the County of Flanders and the Berthout family, lords of Grimbergen. Most likely, the first fortification was built by Wouter van Craaynem at the end of the Grimbergen Wars (1150–1170). Bouchout Castle is situated at aaltitude of 32meters. At about 1300, the Donjon tower of Bouchout Castle was erected by Daniel van Bouchout, a knight who fought gloriously at the Battle of Worringen. In the 15th and 16th century, Bouchout Castle was owned by the Van der Marck and van Sevenbergen sayd Transylvanus families. The castle fell into disrepair due to lack of maintenance, while the Spanish dominance and the iconoclastic fury further worsened its condition. The first major renovation was performed by Christoffel d'Assonville at about 1600. The rectangular m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
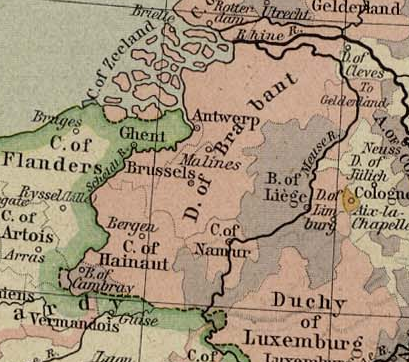
Duchy Of Brabant
The Duchy of Brabant was a State of the Holy Roman Empire established in 1183. It developed from the Landgraviate of Brabant and formed the heart of the historic Low Countries, part of the Burgundian Netherlands from 1430 and of the Habsburg Netherlands from 1482, until it was partitioned after the Dutch revolt. Present-day North Brabant (''Noord-Brabant'') was ceded to the Generality Lands of the Dutch Republic according to the 1648 Peace of Westphalia, while the reduced duchy remained part of the Habsburg Netherlands until it was conquered by French Revolutionary forces in 1794, which was recognized by treaty in 1797. Today all the duchy's former territories, apart from exclaves, are in Belgium except for the Dutch province of North Brabant. Geography The Duchy of Brabant (adjective: '' Brabantian'' or '' Brabantine'') was historically divided into four parts, each with its own capital. The four capitals were Leuven, Brussels, Antwerp and 's-Hertogenbosch. Before ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Botanic Garden Of Belgium
The Meise Botanic Garden ( nl, Plantentuin Meise, french: Jardin botanique de Meise), until 2014 called the National Botanic Garden of Belgium ( nl, Nationale Plantentuin van België, french: Jardin Botanique National de Belgique), is a botanical garden located in the grounds of Bouchout Castle in Meise, Flemish Brabant, just north of Brussels. It is one of the world's largest botanical gardens, with an extensive collection of living plants and a herbarium of about 4 million specimens. The current garden was established in 1958 after moving from central Brussels; the former site is now the Botanical Garden of Brussels. The Meise Botanic Garden contains about 18,000 plant species—about 6% of all the world's known plant species. Half are in greenhouses, the other half, including cultivated and indigenous plants, are outdoors. The ''Index Herbariorum'' code assigned to this botanic garden is BR, which is used when citing housed specimens. The botanic garden's mission statement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peace Of Münster
The Peace of Münster was a treaty between the Lords States General of the Seven United Netherlands and the Spanish Crown, the terms of which were agreed on 30 January 1648. The treaty, parallelly negotiated to but not part of the Peace of Westphalia, is a key event in Dutch history, marking the formal recognition of the independent Dutch Republic and the end of the Thirty Years' War and the Eighty Years' War. Background Negotiations Negotiations between began in 1641 in the towns of Münster and Osnabrück, in present-day Germany. With the initiation of Spanish-Dutch peace talks, Dutch trade with the Levant and the Iberian Peninsula began to flourish. Dutch merchants, benefiting from both the availability of relatively cheap shipping and the cessation of hostilities, soon dominated the markets that had been previously dominated by English traders. Dutch merchants would also benefit from the foreign upheavals of the English Civil War and gain on English trade in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas and achievements of classical antiquity. It occurred after the Crisis of the Late Middle Ages and was associated with great social change. In addition to the standard periodization, proponents of a "long Renaissance" may put its beginning in the 14th century and its end in the 17th century. The traditional view focuses more on the early modern aspects of the Renaissance and argues that it was a break from the past, but many historians today focus more on its medieval aspects and argue that it was an extension of the Middle Ages. However, the beginnings of the period – the early Renaissance of the 15th century and the Italian Proto-Renaissance from around 1250 or 1300 – overlap considerably with the Late Middle Ages, conventi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
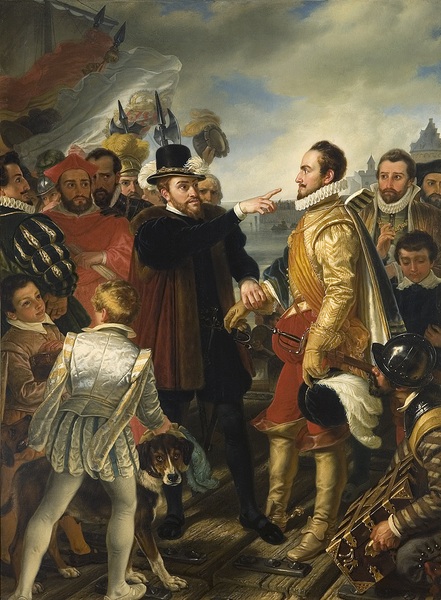
Willem Van Oranje
William the Silent (24 April 153310 July 1584), also known as William the Taciturn (translated from nl, Willem de Zwijger), or, more commonly in the Netherlands, William of Orange ( nl, Willem van Oranje), was the main leader of the Dutch Revolt against the Spanish Habsburgs that set off the Eighty Years' War (1568–1648) and resulted in the formal independence of the United Provinces in 1648. Born into the House of Nassau, he became Prince of Orange in 1544 and is thereby the founder of the Orange-Nassau branch and the ancestor of the monarchy of the Netherlands. In the Netherlands, he is also known as Father of the Fatherland (''Pater Patriae'') ( nl, Vader des Vaderlands). A wealthy nobleman, William originally served the Habsburgs as a member of the court of Margaret of Parma, governor of the Spanish Netherlands. Unhappy with the centralisation of political power away from the local estates and with the Spanish persecution of Dutch Protestants, William joined the Dutch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its predecessor states between 1492 and 1976. One of the largest empires in history, it was, in conjunction with the Portuguese Empire, the first to usher the European Age of Discovery and achieve a global scale, controlling vast portions of the Americas, territories in Western Europe], Africa, and various islands in Spanish East Indies, Asia and Oceania. It was one of the most powerful empires of the early modern period, becoming the first empire known as " the empire on which the sun never sets", and reached its maximum extent in the 18th century. An important element in the formation of Spain's empire was the dynastic union between Isabella I of Castile and Ferdinand II of Aragon in 1469, known as the Catholic Monarchs, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baesweiler
Baesweiler () is a municipality in the district of Aachen, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Geography Baesweiler is located approximately 20 km north-east of Aachen. Neighbouring municipalities * Geilenkirchen * Linnich * Aldenhoven * Alsdorf * Herzogenrath * Übach-Palenberg Division of the municipality The municipality has seven subdivisions since a local government reform in 1972 (populations as of January 2007): * Baesweiler (13,864 inhabitants) * Beggendorf (1,667 inhabitants) * Floverich (408 inhabitants) * Loverich (1,255 inhabitants) * Oidtweiler (2,731 inhabitants) * Puffendorf (441 inhabitants) * Setterich (7,794 inhabitants) History In 1371 a battle took place between the armies of Wenceslaus I, duke of Brabant on one hand, and Gulik and Gelre on the other. Wenceslaus, upon his capture, suffered a humiliating defeat. Population development * 1950: 13.268 * 1970: 24.223 * 1998: 26.731 * 2000: 27.434 * 2002: 27.604 * 2004: 27.933 * 2006: 28.160 * 2008: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margaret Of Brabant, Countess Of Flanders
Margaret of Brabant (9 February 1323 – 1380) was Countess of Flanders by marriage. She was the second daughter of Duke John III of Brabant and Mary of Évreux. She was the only child of Duke John to have children. In 1347 she married Louis II of Flanders, who was then sixteen years old and already count of Flanders. On 13 April 1350 their daughter, Margaret III, Countess of Flanders, was baptized. Through this daughter, their only surviving child, Brabant came under the influence of Burgundy when she married Philip the Bold Philip II the Bold (; ; 17 January 1342 – 27 April 1404) was Duke of Burgundy and ''jure uxoris'' Count of Flanders, Artois and Burgundy. He was the fourth and youngest son of King John II of France and Bonne of Luxembourg. Philip II was .... On 26 September 1371, Margaret and her mother-in-law, Margaret of France, countess of Artois, with their attendants, were guests of Philip the Bold, duke of Burgundy for supper in Lens. Soon afterwards, Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis II, Count Of Flanders
Louis II ( nl, Lodewijk van Male; french: Louis II de Flandre) (25 October 1330, Male – 30 January 1384, Lille), also known as Louis of Male, a member of the House of Dampierre, was Count of Flanders, Nevers and Rethel from 1346 as well as Count of Artois and Burgundy from 1382 until his death. Family Louis was the son of Count Louis I of Flanders, and Countess Margaret I of Burgundy, daughter of King Philip V of France. He was baptised by Bishop Pierre Roger (later Pope Clement VI). His father arranged his marriage with Margaret, daughter of Duke John III of Brabant, in the course of the rapprochement to the Imperial Duchy of Brabant. They had a daughter, Countess Margaret III of Flanders (1348–1405). Louis also had several illegitimate sons, three of whom were killed at the Battle of Nicopolis. Rule When his father was killed at the Battle of Crécy against the troops of King Edward III of England in 1346, he inherited the French counties of Flanders, Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John III, Duke Of Brabant
John III ( nl, Jan; 1300 – 5 December 1355) was Duke of Brabant, Lothier (1312–1355) and Limburg (1312–1347 then 1349–1355). He was the son of John II, Duke of Brabant, and Margaret of England. John and the towns of Brabant The early fourteenth century, an economic boom time for Brabant, marks the rise of the duchy's towns, which depended on English wool for their essential cloth industry. During John's minority, the major towns of Brabant had the authority to appoint councillors to direct a regency, under terms of the Charter of Kortenberg granted by his father in the year of his death (1312). By 1356 his daughter and son-in-law were forced to accept the famous Joyous Entry as a condition for their recognition, so powerful had the states of Brabant become. The marital alignment with France was tested and failed as early as 1316, when Louis X requested Brabant to cease trade with Flanders and to participate in a French attack; the councillors representing the towns found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joanna, Duchess Of Brabant
Joanna, Duchess of Brabant (24 June 1322 – 1 December 1406), also known as Jeanne, was a ruling Duchess (Duke) of Brabant from 1355 until her death. She was duchess of Brabant until the occupation of the duchy by her brother-in-law Louis II of Franders. Following her death, the rights to the duchy of Brabant went to her nephew Antoine. Life Joanna was born 24 June 1322, the daughter of John III, Duke of Brabant and Marie d'Évreux. Her first marriage, in 1334, was to William II, Count of Hainaut (1307–1345), who subsequently died in battle and their only son William died young, thus foiling the project of unifying their territories. Joanna's second marriage was to Wenceslaus of Luxemburg. The famous document, the foundation of the rule of law in Brabant called the '' Blijde Inkomst'' ("Joyous Entry"), was arrived at in January 1356, in order to assure Joanna and her consort peaceable entry into their capital and to settle the inheritance of the Duchy of Brabant on h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Godfrey III Of Leuven
Godfrey III ( nl, Godfried; c. 1142 – 21 August 1190) was count of Louvain (or Leuven), landgrave of Brabant, margrave of Antwerp, and duke of Lower Lorraine (as Godfrey VIII) from 1142 to his death. Origins He was the son of Godfrey II and Lutgarde of Sulzbach. He was still an infant at his succession (therefore called ''dux in cunis'') of which a few Brabantian vassals sought to take advantage to become independent of the duke (Wars of Grimbergen, 1141–1159). Career On 30 March 1147, Godfrey was present at the coronation of Henry Berengar, son of Conrad III of Germany, in Aachen. When Conrad left on Crusade, war began anew in 1148. Peace was elusive until the election of Conrad's successor, Frederick Barbarossa. By marriage to Margaret, daughter of Henry II of Limburg, Godfrey united two powerful and antagonistic houses in the region. In 1159 Godfrey ended the war with the Berthout, lords of Grimbergen, by burning their impressive castle at Grimbergen. In 1171, Godfrey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




