|
Bottleneck (network)
In a communication network, sometimes a max-min fairness of the network is desired, usually opposed to the basic first-come first-served policy. With max-min fairness, data flow between any two nodes is maximized, but only at the cost of ''more or equally expensive'' data flows. To put it another way, in case of network congestion any data flow is only impacted by smaller or equal flows. In such context, a bottleneck link for a given data flow is a link that is fully utilized (is ''saturated'') and of all the flows sharing this link, the given data flow achieves maximum data rate network-wide. Note that this definition is substantially different from a common meaning of a ''bottleneck''. Also note, that this definition does not forbid a single link to be a bottleneck for multiple flows. A data rate allocation is max-min fair if and only if a data flow between any two nodes has at least one bottleneck link. See also * Fairness measure * Max-min fairness In communication networks, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LEAD
Lead is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metals, heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale of mineral hardness#Intermediate hardness, soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is a shiny gray with a hint of blue. It tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable nuclide, stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is toxic, even in small amounts, especially to children. Lead is a relatively unreactive post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its amphoteric nature; lead and lead oxides react with acids and base (chemistry), bases, and it tends to form covalent bonds. Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2 oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
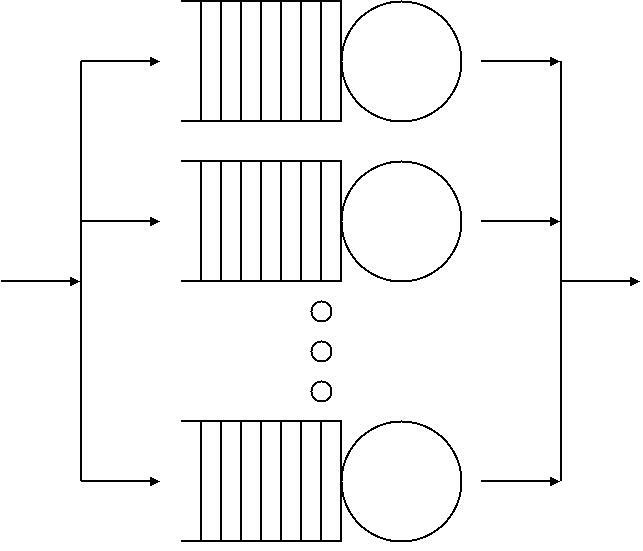
Communication Network
A telecommunications network is a group of nodes interconnected by telecommunications links that are used to exchange messages between the nodes. The links may use a variety of technologies based on the methodologies of circuit switching, message switching, or packet switching, to pass messages and signals. Multiple nodes may cooperate to pass the message from an originating node to the destination node, via multiple network hops. For this routing function, each node in the network is assigned a network address for identification and locating it on the network. The collection of addresses in the network is called the address space of the network. Examples of telecommunications networks include computer networks, the Internet, the public switched telephone network (PSTN), the global Telex network, the aeronautical ACARS network, and the wireless radio networks of cell phone telecommunication providers. Network structure In general, every telecommunications network conce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max-min Fairness
In communication networks, multiplexing and the division of scarce resources, max-min fairness is said to be achieved by an allocation if and only if the allocation is feasible and an attempt to increase the allocation of any participant necessarily results in the decrease in the allocation of some other participant with an equal or smaller allocation. In best-effort statistical multiplexing, a first-come first-served (FCFS) scheduling policy is often used. The advantage with max-min fairness over FCFS is that it results in traffic shaping, meaning that an ill-behaved flow, consisting of large data packets or bursts of many packets, will only punish itself and not other flows. Network congestion is consequently to some extent avoided. Fair queuing is an example of a max-min fair packet scheduling algorithm for statistical multiplexing and best-effort networks, since it gives scheduling priority to users that have achieved lowest data rate since they became active. In case of eq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First-come First-served
Queueing theory is the mathematical study of waiting lines, or queues. A queueing model is constructed so that queue lengths and waiting time can be predicted. Queueing theory is generally considered a branch of operations research because the results are often used when making business decisions about the resources needed to provide a service. Queueing theory has its origins in research by Agner Krarup Erlang when he created models to describe the system of Copenhagen Telephone Exchange company, a Danish company. The ideas have since seen applications including telecommunication, traffic engineering, computing and, particularly in industrial engineering, in the design of factories, shops, offices and hospitals, as well as in project management. Spelling The spelling "queueing" over "queuing" is typically encountered in the academic research field. In fact, one of the flagship journals of the field is ''Queueing Systems''. Single queueing nodes A queue, or queueing node ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Congestion
Network congestion in data networking and queueing theory is the reduced quality of service that occurs when a network node or link is carrying more data than it can handle. Typical effects include queueing delay, packet loss or the blocking of new connections. A consequence of congestion is that an incremental increase in offered load leads either only to a small increase or even a decrease in network throughput. Network protocols that use aggressive retransmissions to compensate for packet loss due to congestion can increase congestion, even after the initial load has been reduced to a level that would not normally have induced network congestion. Such networks exhibit two stable states under the same level of load. The stable state with low throughput is known as congestive collapse. Networks use congestion control and congestion avoidance techniques to try to avoid collapse. These include: exponential backoff in protocols such as CSMA/CA in 802.11 and the similar C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairness Measure
Fairness measures or metrics are used in network engineering to determine whether users or applications are receiving a fair share of system resources. There are several mathematical and conceptual definitions of fairness. TCP fairness Congestion control mechanisms for new network transmission protocols or peer-to-peer applications must interact well with TCP. TCP fairness requires that a new protocol receive a no larger share of the network than a comparable TCP flow. This is important as TCP is the dominant transport protocol on the Internet, and if new protocols acquire unfair capacity they tend to cause problems such as congestion collapse. This was the case with the first versions of RealMedia's streaming protocol: it was based on UDP and was widely blocked at organizational firewalls until a TCP-based version was developed. TCP throughput unfairness over WiFi is a critical problem and needs further investigations. Jain's fairness index Raj Jain's equation, :\mathcal (x ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max-min Fairness
In communication networks, multiplexing and the division of scarce resources, max-min fairness is said to be achieved by an allocation if and only if the allocation is feasible and an attempt to increase the allocation of any participant necessarily results in the decrease in the allocation of some other participant with an equal or smaller allocation. In best-effort statistical multiplexing, a first-come first-served (FCFS) scheduling policy is often used. The advantage with max-min fairness over FCFS is that it results in traffic shaping, meaning that an ill-behaved flow, consisting of large data packets or bursts of many packets, will only punish itself and not other flows. Network congestion is consequently to some extent avoided. Fair queuing is an example of a max-min fair packet scheduling algorithm for statistical multiplexing and best-effort networks, since it gives scheduling priority to users that have achieved lowest data rate since they became active. In case of eq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |