|
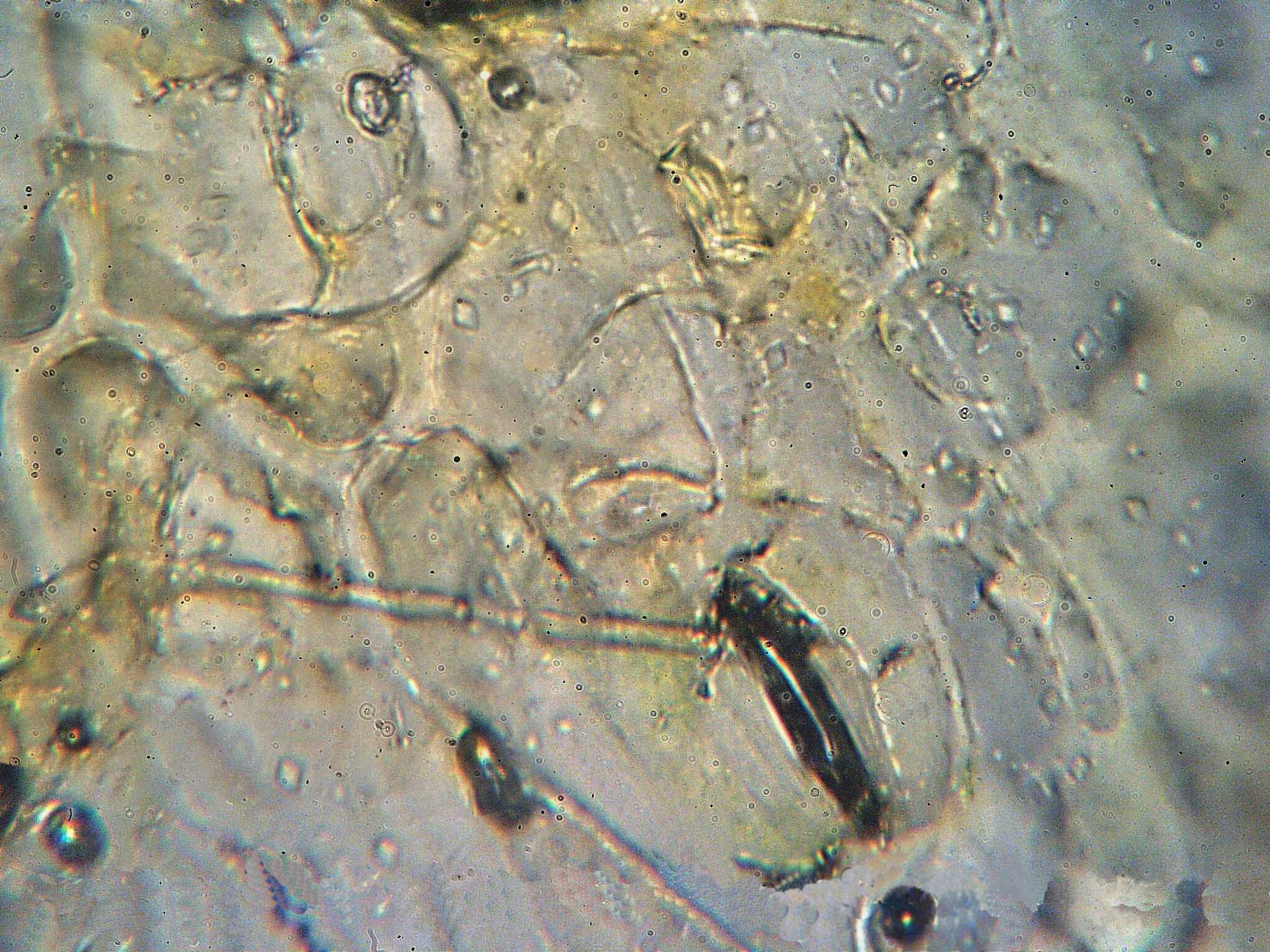
Botryorhiza
''Botryorhiza'' is a genus of rust fungi in the Chaconiaceae family. The genus is monotypic, containing the single species ''Botryorhiza hippocrateae'', which grows on ''Hippocratea ''Hippocratea'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Celastraceae, usually lianas, native to tropical and subtropical North America, South America and Africa. Species Currently accepted species include: *''Hippocratea myriantha'' Oliv. ...'' plants in Brazil and the Caribbean. References External links * {{Taxonbar, from=Q4948830, from2=Q10433821 Pucciniales Monotypic Basidiomycota genera Fungi of South America Taxa described in 1917 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaconiaceae
The Chaconiaceae are a family (biology), family of rust (fungus), rust fungi in the order Pucciniales. The family contains 8 genera and 75 species. Most species have a tropical distribution. ''Maravalia cryptostegiae'' has been used with success as a biocontrol agent against rubber vine in Australia. References External links * Pucciniales Basidiomycota families {{Basidiomycota-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basidiomycota
Basidiomycota () is one of two large divisions that, together with the Ascomycota, constitute the subkingdom Dikarya (often referred to as the "higher fungi") within the kingdom Fungi. Members are known as basidiomycetes. More specifically, Basidiomycota includes these groups: mushrooms, puffballs, stinkhorns, bracket fungi, other polypores, jelly fungi, boletes, chanterelles, earth stars, smuts, bunts, rusts, mirror yeasts, and ''Cryptococcus'', the human pathogenic yeast. Basidiomycota are filamentous fungi composed of hyphae (except for basidiomycota-yeast) and reproduce sexually via the formation of specialized club-shaped end cells called basidia that normally bear external meiospores (usually four). These specialized spores are called basidiospores. However, some Basidiomycota are obligate asexual reproducers. Basidiomycota that reproduce asexually (discussed below) can typically be recognized as members of this division by gross similarity to others, by the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pucciniomycetes
The Pucciniomycetes (formerly known as the Urediniomycetes) are a class of fungi in the Pucciniomycotina subdivision of the Basidiomycota. The class contains 5 orders, 21 families, 190 genera, and 8016 species. It includes several important plant pathogens causing forms of fungal rust. Characteristics Pucciniomycetes develop no basidiocarp, karyogamy occurs in a thick-walled resting spore (teliospore), and meiosis occurs upon germination of teliospore. They have simple septal pores without membrane caps and disc-like spindle pole bodies. Except for a few species, the basidia, when present, are transversally septate. Mannose is the major cell wall carbohydrate, glucose, fucose and rhamnose are the less prevalent neutral sugars and xylose Xylose ( grc, ξύλον, , "wood") is a sugar first isolated from wood, and named for it. Xylose is classified as a monosaccharide of the aldopentose type, which means that it contains five carbon atoms and includes an aldehyde f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pucciniales
Rusts are plant diseases caused by pathogenic fungi of the order Pucciniales (previously known as Uredinales). An estimated 168 rust genera and approximately 7,000 species, more than half of which belong to the genus ''Puccinia'', are currently accepted. Rust fungi are highly specialized plant pathogens with several unique features. Taken as a group, rust fungi are diverse and affect many kinds of plants. However, each species has a very narrow range of hosts and cannot be transmitted to non-host plants. In addition, most rust fungi cannot be grown easily in pure culture. A single species of rust fungi may be able to infect two different plant hosts in different stages of its life cycle, and may produce up to five morphologically and cytologically distinct spore-producing structures viz., spermogonia, aecia, uredinia, telia, and basidia in successive stages of reproduction. Each spore type is very host specific, and can typically infect only one kind of plant. Rust fungi are o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbert Hice Whetzel
Herbert Hice Whetzel (September 5, 1877 – November 30, 1944) was an American plant pathologist and mycologist. As a Professor of Plant Pathology, he led the first department of Plant Pathology at an American university and founded the Cornell Plant Pathology Herbarium (CUP). Personal Background and Education H.H. Whetzel was born near Avilla, Indiana, where he spent his boyhood on the family farm. A nature lover and collector from an early age, he taught school for 2 years after graduating high school, then earned a bachelor's degree at Wabash College. After graduating from Wabash College in 1902, he attended graduate school at Cornell University, where he studied under the prominent mycologist George F. Atkinson. In 1904 he married Lucy E. Baker. They had two children, Joseph and Gertrude; Lucy died in 1912. In 1914 he married Lucy's sister Bertha A. Baker, and they raised the children together in Ithaca, New York. Career While still working on his doctoral research, Whetze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edgar William Olive
Edgar is a commonly used English given name, from an Anglo-Saxon name ''Eadgar'' (composed of '' ead'' "rich, prosperous" and ''gar'' "spear"). Like most Anglo-Saxon names, it fell out of use by the later medieval period; it was, however, revived in the 18th century, and was popularised by its use for a character in Sir Walter Scott's ''The Bride of Lammermoor'' (1819). People with the given name * Edgar the Peaceful (942–975), king of England * Edgar the Ætheling (c. 1051 – c. 1126), last member of the Anglo-Saxon royal house of England * Edgar of Scotland (1074–1107), king of Scotland * Edgar Angara, Filipino lawyer * Edgar Barrier, American actor * Edgar Baumann, Paraguayan javelin thrower * Edgar Bergen, American actor, radio performer, ventriloquist * Edgar Berlanga, American boxer * Edgar H. Brown, American mathematician * Edgar Buchanan, American actor * Edgar Rice Burroughs, American author, creator of ''Tarzan'' * Edgar Cantero, Spanish author in Catalan, Spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rust (fungus)
Rusts are plant diseases caused by pathogenic fungi of the order Pucciniales (previously known as Uredinales). An estimated 168 rust genera and approximately 7,000 species, more than half of which belong to the genus ''Puccinia'', are currently accepted. Rust fungi are highly specialized plant pathogens with several unique features. Taken as a group, rust fungi are diverse and affect many kinds of plants. However, each species has a very narrow range of hosts and cannot be transmitted to non-host plants. In addition, most rust fungi cannot be grown easily in pure culture. A single species of rust fungi may be able to infect two different plant hosts in different stages of its life cycle, and may produce up to five morphologically and cytologically distinct spore-producing structures viz., spermogonia, aecia, uredinia, telia, and basidia in successive stages of reproduction. Each spore type is very host specific, and can typically infect only one kind of plant. Rust fungi are o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. In contrast, an oligotypic taxon contains more than one but only a very few subordinate taxa. Examples Just as the term ''monotypic'' is used to describe a taxon including only one subdivision, the contained taxon can also be referred to as monotypic within the higher-level taxon, e.g. a genus monotypic within a family. Some examples of monotypic groups are: Plants * In the order Amborellales, there is only one family, Amborellaceae and there is only one genus, '' Amborella'', and in this genus there is only one species, namely ''Amborella trichopoda. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocratea
''Hippocratea'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Celastraceae, usually lianas, native to tropical and subtropical North America, South America and Africa. Species Currently accepted species include: *''Hippocratea myriantha ''Hippocratea'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Celastraceae, usually lianas, native to tropical and subtropical North America, South America and Africa. Species Currently accepted species include: *''Hippocratea myriantha'' Oliv. ...'' Oliv. *'' Hippocratea pauciflora'' Rose *'' Hippocratea stuhlmanniana'' Loes. *'' Hippocratea vignei'' Hoyle *'' Hippocratea volubilis'' L. A large number of species names have been previously associated with ''Hippocratea''. *''Hippocratea acapulcensis'' Kunth *''Hippocratea acuminata'' Hoffmanns. ex Link *''Hippocratea acutiflora'' DC. *''Hippocratea adolphi-friderici'' Harms *''Hippocratea affinis'' De Wild. llegitimate/small> *''Hippocratea affinis'' Cambess. *''Hippocratea africana'' (Will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Basidiomycota Genera
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. In contrast, an oligotypic taxon contains more than one but only a very few subordinate taxa. Examples Just as the term ''monotypic'' is used to describe a taxon including only one subdivision, the contained taxon can also be referred to as monotypic within the higher-level taxon, e.g. a genus monotypic within a family. Some examples of monotypic groups are: Plants * In the order Amborellales, there is only one family, Amborellaceae and there is only one genus, ''Amborella'', and in this genus there is only one species, namely ''Amborella trichopoda.'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi Of South America
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true fungi' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |