|
Bothriolepis2
''Bothriolepis'' (from el, βόθρος , 'trench' and el, λεπίς 'scale') was a widespread, abundant and diverse genus of antiarch placoderms that lived during the Middle to Late Devonian period of the Paleozoic Era. Historically, ''Bothriolepis'' resided in an array of paleo-environments spread across every paleocontinent, including near shore marine and freshwater settings. Most species of ''Bothriolepis'' were characterized as relatively small, benthic, freshwater detritivores (organisms that obtain nutrients by consuming decomposing plant/animal material), averaging around in length. However, the largest species, ''B. rex'', had an estimated bodylength of . Although expansive with over 60 species found worldwide, comparatively ''Bothriolepis'' is not unusually more diverse than most modern bottom dwelling species around today. Classification ''Bothriolepis'' is a genus placed within the placoderm order Antiarchi. The earliest antiarch placoderms first appeared in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant adaptive radiation of life on dry land occurred during the Devonian. Free-sporing vascular plants began to spread across dry land, forming extensive forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants appeared. The arthropod groups of myriapods, arachnids and hexapods also became well-established early in this period, after starting their expansion to land at least from the Ordovician period. Fish reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The placoderms began dominating al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bothriolepis Canadensis-001
''Bothriolepis'' (from el, βόθρος , 'trench' and el, λεπίς 'scale') was a widespread, abundant and diverse genus of antiarch placoderms that lived during the Middle to Late Devonian period of the Paleozoic Era. Historically, ''Bothriolepis'' resided in an array of paleo-environments spread across every paleocontinent, including near shore marine and freshwater settings. Most species of ''Bothriolepis'' were characterized as relatively small, benthic, freshwater detritivores (organisms that obtain nutrients by consuming decomposing plant/animal material), averaging around in length. However, the largest species, ''B. rex'', had an estimated bodylength of . Although expansive with over 60 species found worldwide, comparatively ''Bothriolepis'' is not unusually more diverse than most modern bottom dwelling species around today. Classification ''Bothriolepis'' is a genus placed within the placoderm order Antiarchi. The earliest antiarch placoderms first appeared in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
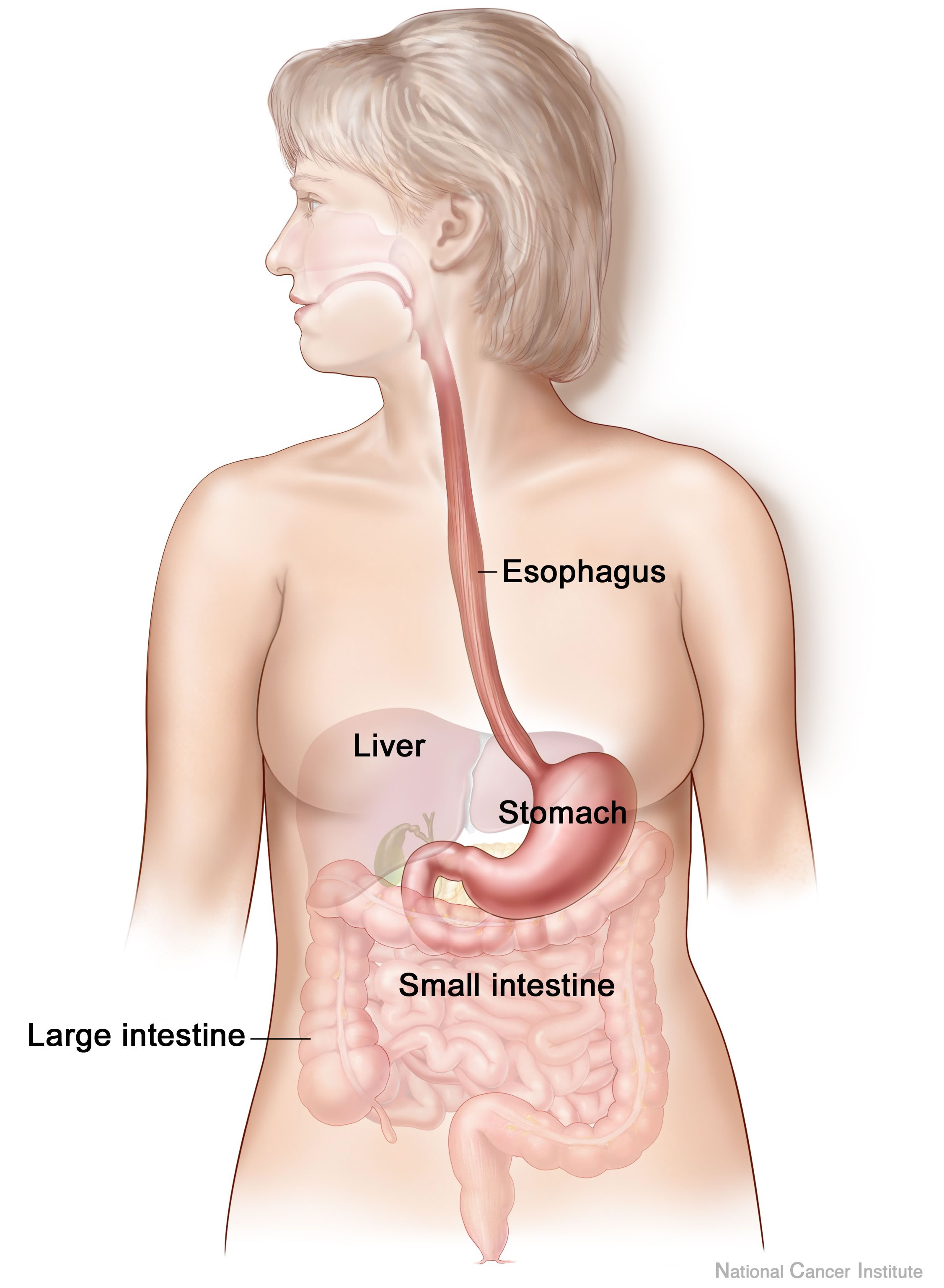
Alimentary System
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components, until they can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The process of digestion has three stages: the cephalic phase, the gastric phase, and the intestinal phase. The first stage, the cephalic phase of digestion, begins with secretions from gastric glands in response to the sight and smell of food. This stage includes the mechanical breakdown of food by chewing, and the chemical breakdown by digestive enzymes, that takes place in the mouth. Saliva contains the digestive enzymes amylase, and lingual lipase, secreted by the salivary and serous glands on the tongue. Chewing, in which the food is mixed with saliva, begins the mechanical process of digestion. This produces a bolus which is swallowed down the esophagus to enter t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PSM V82 D434 Restoration Of A Bothriolepsis Canadensis
PSM, an acronym, may refer to: Organizations * Sepaktakraw Association of Malaysia ( ms, Persatuan Sepaktakraw Malaysia; PSM), a national governing body in Malaysia. * Pakistan School Muscat, a Pakistani co-educational institute in Oman * Palestine Solidarity Movement, a student organization in the United States * Panhellenic Socialist Movement, a centre-left party in Greece * Parti Sosialis Malaysia, a socialist political party in Malaysia * PlayStation: The Official Magazine, a magazine originally known as PlayStation Magazine or PSM * Ponce School of Medicine, a post-graduate medical school located in Ponce, Puerto Rico * Power Systems Mfg, a subsidiary of Alstom, specializing in aftermarket gas turbine servicing for power generating industry. * ''Poznańska Spółdzielnia Mieszkaniowa'', a housing cooperative administering most of the Piątkowo district of Poznań, Poland * PSM3, a UK video game magazine specializing in Sony consoles * PSM Makassar, a football club that pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caudal Tail
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as seen in sharks. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the spine and are supported only by muscles. Their principal function is to help the fish swim. Fins located in different places on the fish serve different purposes such as moving forward, turning, keeping an upright position or stopping. Most fish use fins when swimming, flying fish use pectoral fins for gliding, and frogfish use them for crawling. Fins can also be used for other purposes; male sharks and mosquitofish use a modified fin to deliver sperm, thresher sharks use their caudal fin to stun prey, reef stonefish have spines in their dorsal fins that inject venom, anglerfish use the first spine of their dorsal fin like a fishing rod to lure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pectoral Fin
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as seen in sharks. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the spine and are supported only by muscles. Their principal function is to help the fish swim. Fins located in different places on the fish serve different purposes such as moving forward, turning, keeping an upright position or stopping. Most fish use fins when swimming, flying fish use pectoral fins for gliding, and frogfish use them for crawling. Fins can also be used for other purposes; male sharks and mosquitofish use a modified fin to deliver sperm, thresher sharks use their caudal fin to stun prey, reef stonefish have spines in their dorsal fins that inject venom, anglerfish use the first spine of their dorsal fin like a fishing rod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Origin Of Vertebrates Fig 016
Origin(s) or The Origin may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Comics and manga * ''Origin'' (comics), a Wolverine comic book mini-series published by Marvel Comics in 2002 * ''The Origin'' (Buffy comic), a 1999 ''Buffy the Vampire Slayer'' comic book series * Origins (''Judge Dredd'' story), a major ''Judge Dredd'' storyline running from 2006 through 2007 * ''Origin'' (manga), a 2016 manga by Boichi * '' Mobile Suit Gundam: The Origin'', a 2002 manga by Yoshikazu Yasuhiko * '' Wolverine: Origins'', a Marvel Comics series Films and television * ''Origin'' (TV series), 2018 science-fiction TV series * "Origin" (''Angel''), a fifth-season episode of ''Angel'' * '' Origin: Spirits of the Past'', a 2006 anime movie also known as ''Gin-iro no Kami no Agito'' * Origin (''Stargate''), the religion of the Ori * "Origin" (''Stargate SG-1''), a ninth-season episode of ''Stargate SG-1'' * '' X-Men Origins: Wolverine'', a 2009 superhero film, prequel to the ''X-Men'' film tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Morphology
The ''Journal of Morphology'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of anatomy and morphology featuring primary research articles, review articles, and meeting abstracts. The journal was established in 1887 by zoologists and morphologists Edward Phelps Allis and C. O. Whitman. The journal appeared regularly from 1887 onwards and made a financial loss. Allis provided the support necessary for the journal to continue appearing until, after a short gap, the journal underwent reorganization in 1907 when it was taken over by Wistar Institute in Philadelphia, as a more permanent solution to its financial problems. As of 2022, it is edited by J. Matthias Starck.''Am. Zool. (1979) 19 (4): 1251-1253.'' According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloaca
In animal anatomy, a cloaca ( ), plural cloacae ( or ), is the posterior orifice that serves as the only opening for the digestive, reproductive, and urinary tracts (if present) of many vertebrate animals. All amphibians, reptiles and birds, and a few mammals ( monotremes, tenrecs, golden moles, and marsupial moles), have this orifice, from which they excrete both urine and feces; this is in contrast to most placental mammals, which have two or three separate orifices for evacuation. Excretory openings with analogous purpose in some invertebrates are also sometimes referred to as cloacae. Mating through the cloaca is known as cloacal copulation, commonly referred to as cloacal kiss. The cloacal region is also often associated with a secretory organ, the cloacal gland, which has been implicated in the scent-marking behavior of some reptiles, marsupials, amphibians, and monotremes. Etymology The word is from the Latin verb ''cluo'', "(I) cleanse", thus the noun ''cloaca'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoracic
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the creature's body, each of which is in turn composed of multiple segments. The human thorax includes the thoracic cavity and the thoracic wall. It contains organs including the heart, lungs, and thymus gland, as well as muscles and various other internal structures. Many diseases may affect the chest, and one of the most common symptoms is chest pain. Etymology The word thorax comes from the Greek θώραξ ''thorax'' "breastplate, cuirass, corslet" via la, thorax. Plural: ''thoraces'' or ''thoraxes''. Human thorax Structure In humans and other hominids, the thorax is the chest region of the body between the neck and the abdomen, along with its internal organs and other contents. It is mostly protected and supported by the rib cage, spine, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notochord
In anatomy, the notochord is a flexible rod which is similar in structure to the stiffer cartilage. If a species has a notochord at any stage of its life cycle (along with 4 other features), it is, by definition, a chordate. The notochord consists of inner, vacuolated cells covered by fibrous and elastic sheaths, lies along the anteroposterior axis (''front to back''), is usually closer to the dorsal than the ventral surface of the embryo, and is composed of cells derived from the mesoderm. The most commonly cited functions of the notochord are: as a midline tissue that provides directional signals to surrounding tissue during development, as a skeletal (structural) element, and as a vertebral precursor. In lancelets the notochord persists throughout life as the main structural support of the body. In tunicates the notochord is present only in the larval stage, being completely absent in the adult animal. In these invertebrate chordates, the notochord is not vacuolated. In all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bothriolepis Canadensis 4343
''Bothriolepis'' (from el, βόθρος , 'trench' and el, λεπίς 'scale') was a widespread, abundant and diverse genus of antiarch placoderms that lived during the Middle to Late Devonian period of the Paleozoic Era. Historically, ''Bothriolepis'' resided in an array of paleo-environments spread across every paleocontinent, including near shore marine and freshwater settings. Most species of ''Bothriolepis'' were characterized as relatively small, benthic, freshwater detritivores (organisms that obtain nutrients by consuming decomposing plant/animal material), averaging around in length. However, the largest species, ''B. rex'', had an estimated bodylength of . Although expansive with over 60 species found worldwide, comparatively ''Bothriolepis'' is not unusually more diverse than most modern bottom dwelling species around today. Classification ''Bothriolepis'' is a genus placed within the placoderm order Antiarchi. The earliest antiarch placoderms first appeared in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)

