|
Borophryne
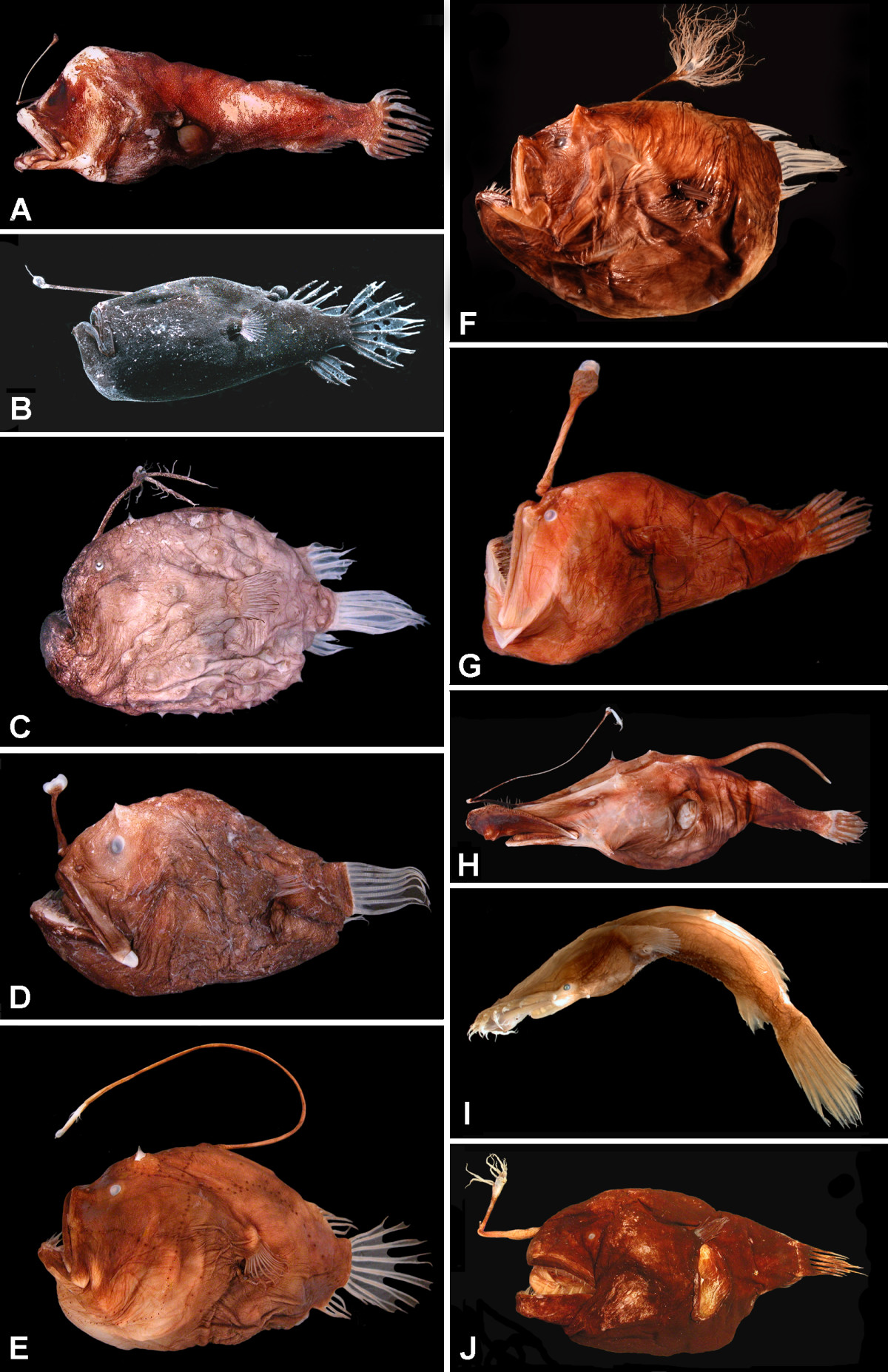
''Borophryne apogon'', the netdevil, or greedy seadevil, is a species of leftvent anglerfish known today from the waters of the eastern Pacific Ocean off the Central American coast. It is found at depths down to around . This species grows to a length of TL. A fossil specimen of this species has been found in the Los Angeles Basin dating back to the Late Miocene, some eight million years ago. Description A metamorphosed female ''Borophryne apogon'' is globose, and grows to a maximum length of about . The depth of the head is between 50% and 65% of the fish's standard length and the length of the head is between 50% and 60% of the standard length, with the lower jaw being four fifths of the length of the head. Three rows of long, sharp teeth line the jaws and there are up to four teeth on the roof of the mouth. The illicium on the snout is short and the esca on its tip is large with a branching terminal appendage and filaments on the side. There is a rounded protuberance on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leftvent
Leftvents are small, deep-sea lophiiform fish comprising the family Linophrynidae distributed throughout tropical to subtropical waters of all oceans. The name of the type genus '' Linophryne'' has been translated from the Greek to mean "toad that fishes with a net", an allusion to the fishes' impressive use of mimicry in luring prey. One of several families of anglerfishes, the Linophrynidae are not well studied, and only one species is given a common name: the netdevil, ''Borophryne apogon''. For this reason, the name "netdevil" can sometimes refer to any linophrynid. Description With roughly spherical to slightly elongated, gelatinous, and scaleless bodies and large triangular heads, leftvents possess a body plan typical of deep-sea anglerfish. In females only, long, sharp fang-like teeth line the jaws of a cavernous maw. An illicium (a modified dorsal spine; the "fishing rod") — and an esca (a bulbous, bioluminescent "fishing lure") are present, also in females only. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linophryne Indica
''Linophryne indica'', or headlight angler, is a leftvent anglerfish in the family Linophrynidae, found in the bathyal zone of the Pacific Ocean at depths below 1,000 m (3,300 ft). The female is significantly larger than the mature male. A fossil specimen of this species has been found in the Los Angeles Basin dating back to the Late Miocene, some eight million years ago. Description The mature female ''Linophryne indica'' has a laterally compressed, oval body. The head is broad and the large, oblique mouth extends behind the eye. The teeth are large and sharp, there being four longitudinal rows in the upper jaw and three in the lower jaw, as well as a single pair of vomerine teeth in the roof of the mouth. The sphenotic spines (above the eyes) are large and there is a prominent angulare spine. The illicium on the snout is short and broadens into the rather larger esca at its tip. This has a number of short filaments and a long trailing appendage. There is a barbel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglerfish
The anglerfish are fish of the teleost order Lophiiformes (). They are bony fish named for their characteristic mode of predation, in which a modified luminescent fin ray (the esca or illicium) acts as a lure for other fish. The luminescence comes from symbiotic bacteria, which are thought to be acquired from seawater, that dwell in and around the sea. Some anglerfish are notable for extreme sexual dimorphism and sexual symbiosis of the small male with the much larger female, seen in the suborder Ceratioidei, the deep sea anglerfish. In these species, males may be several orders of magnitude smaller than females. Anglerfish occur worldwide. Some are pelagic (dwelling away from the sea floor), while others are benthic (dwelling close to the sea floor). Some live in the deep sea (such as the Ceratiidae), while others on the continental shelf, such as the frogfishes and the Lophiidae (monkfish or goosefish). Pelagic forms are most often laterally compressed, whereas the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linophryne
''Linophryne'' (from el, λῐ́νον , 'fishing net' and el, φρῡ́νη , 'toad') is a genus of leftvents, commonly called the "bearded seadevils." Species There are currently 22 recognized species in this genus: * '' Linophryne algibarbata'' Waterman, 1939 * '' Linophryne andersoni'' Gon, 1992 * '' Linophryne arborifera'' Regan, 1925 * '' Linophryne arcturi'' Beebe, 1926 * '' Linophryne argyresca'' Regan & Trewavas, 1932 * '' Linophryne bicornis'' A. E. Parr, 1927 * '' Linophryne bipennata'' Bertelsen, 1982 * ''Linophryne brevibarbata'' Beebe, 1932 * '' Linophryne coronata'' A. E. Parr, 1927 * '' Linophryne densiramus'' S. Imai, 1941 (Thickbranch angler) * ''Linophryne escaramosa'' Bertelsen, 1982 * ''Linophryne indica'' A. B. Brauer, 1902 (Headlight angler) * ''Linophryne lucifer'' Collett, 1886 * ''Linophryne macrodon'' Regan, 1925 * ''Linophryne maderensis'' Maul, 1961 * ''Linophryne parini'' Bertelsen, 1980 * ''Linophryne pennibarbata'' Bertelsen, 1980 * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of California
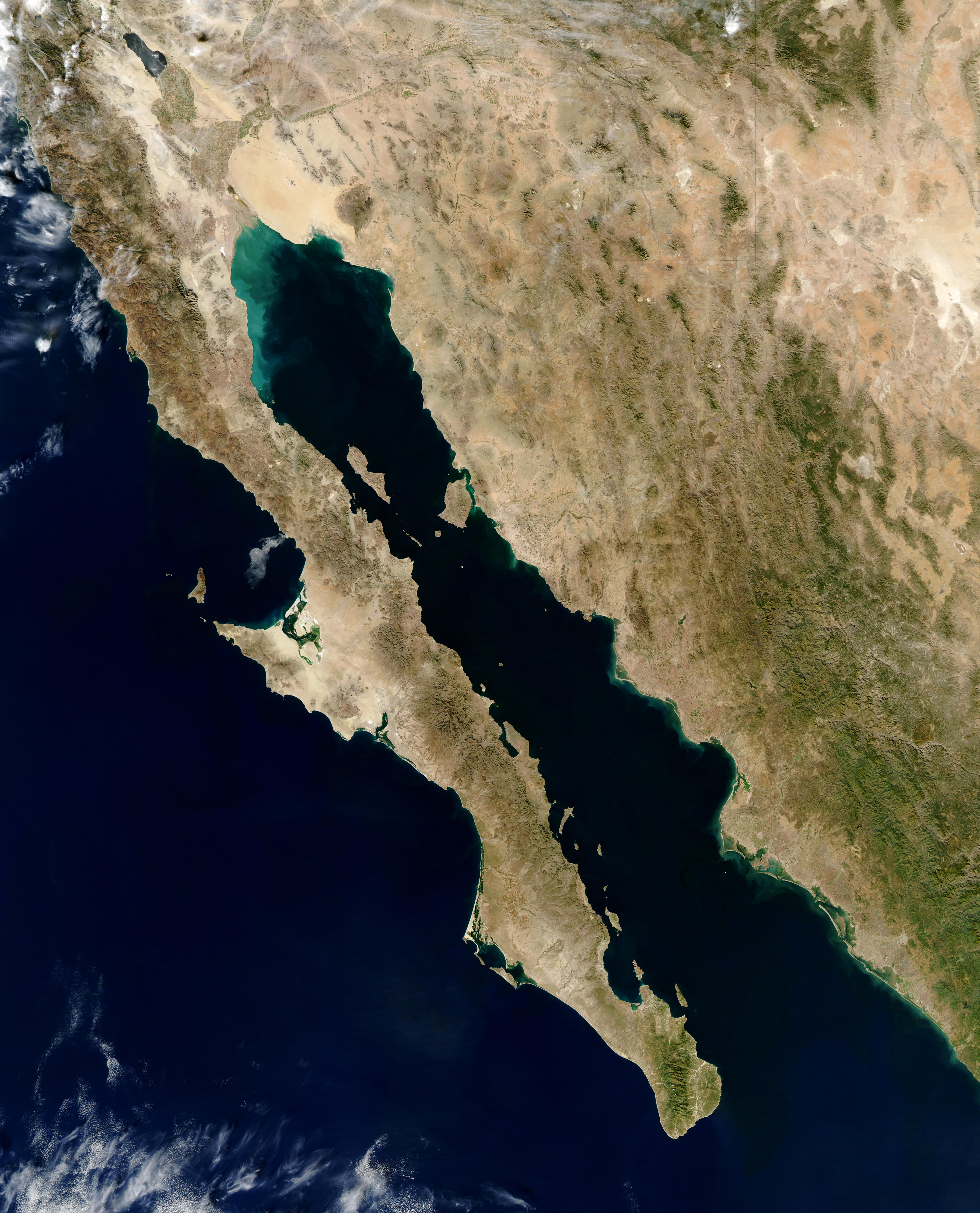
The Gulf of California ( es, Golfo de California), also known as the Sea of Cortés (''Mar de Cortés'') or Sea of Cortez, or less commonly as the Vermilion Sea (''Mar Bermejo''), is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean that separates the Baja California Peninsula from the Mexico, Mexican mainland. It is bordered by the states of Baja California, Baja California Sur, Sonora, and Sinaloa with a coastline of approximately . Rivers that flow into the Gulf of California include the Colorado River, Colorado, Fuerte River, Fuerte, Mayo River (Mexico), Mayo, Sinaloa River, Sinaloa, Sonora River, Sonora, and the Yaqui River, Yaqui. The surface of the gulf is about . Maximum depths exceed because of the complex geology, linked to plate tectonics. The gulf is thought to be one of the most diverse seas on Earth and is home to more than 5,000 species of micro-invertebrates. Parts of the Gulf of California are a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Geography History The marine expeditions of Fortún ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Charles Tate Regan
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the world's most populous megacities. Los Angeles is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Southern California. With a population of roughly 3.9 million residents within the city limits , Los Angeles is known for its Mediterranean climate, ethnic and cultural diversity, being the home of the Hollywood film industry, and its sprawling metropolitan area. The city of Los Angeles lies in a basin in Southern California adjacent to the Pacific Ocean in the west and extending through the Santa Monica Mountains and north into the San Fernando Valley, with the city bordering the San Gabriel Valley to it's east. It covers about , and is the county seat of Los Angeles County, which is the most populous county in the United States with an estim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathyal Zone
The bathypelagic zone or bathyal zone (from Greek βαθύς (bathýs), deep) is the part of the open ocean that extends from a depth of below the ocean surface. It lies between the mesopelagic above, and the abyssopelagic below. The bathypelagic is known as the midnight zone because of the lack of sunlight; this feature does not allow for photosynthesis-driven primary production, preventing growth of phytoplankton or aquatic plants. Although larger by volume than the photic zone, our knowledge of the bathypelagic zone remains limited by our ability to explore the deep ocean. Physical characteristics The bathypelagic zone is characterized by a nearly constant temperature of approximately and a salinity range of 33-35 g/kg. This region has little to no light, because sunlight does not reach this deep in the ocean and bioluminescence is limited. The hydrostatic pressure in this zone ranges 100-400 atmospheres (atm), due to the increase of 1 atm for every 10 m depth. It is bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Panama
The Gulf of Panama ( es, Golfo de Panamá) is a gulf of the Pacific Ocean off the southern coast of Panama, where most of eastern Panama's southern shores adjoin it. The Gulf has a maximum width of , a maximum depth of and the size of . The Panama Canal connects the Gulf of Panama with the Caribbean Sea, thus linking the Pacific and Atlantic oceans. The Panamanian capital Panama City is the main urban centre on the gulf shore. The Gulf itself also contains a few minor gulfs, with Panama Bay to the north, Gulf of Parita to the west and Gulf of San Miguel to the east. The gulf has a few islands and on the coast there are a few important ports, like Panama City, La Palma and Chitrè. The Pearl Islands archipelago is a group of over two hundred islands situated to the east in the gulf. Panama’s largest river, Tuira, flows south into the Gulf of San Miguel. Tourism Tourism is a very large part of the Panamanian economy, and much of it revolves around the Panama Bay. The most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |