|
Borjomi Gorge
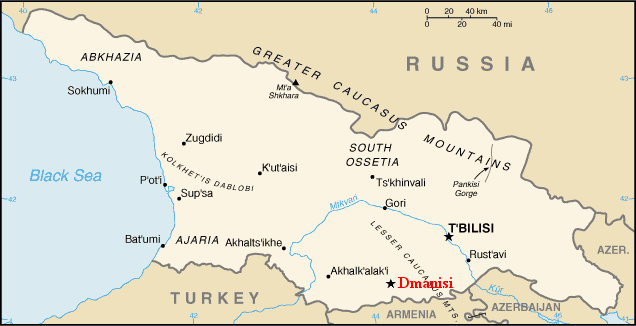
Borjomi Gorge ( ka, ბორჯომის ხეობა) is a picturesque canyon of the Kura River in central Georgia. The gorge was formed as a result of the Kura River cutting its path through the Lesser Caucasus Mountains where the Trialeti and Meskheti Ranges meet. A significant portion of the Borjomi Gorge is covered by mixed and coniferous forests made up of oak, maple, beech, spruce, fir, and pine. A large portion of the Borjomi-Kharagauli National Park lies within the gorge, as well as the towns of Likani and Borjomi itself. Georgia About Baku–Tbilisi–Ceyhan pipeline cuts through the portion of the gorge. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgia (country)
Georgia (, ; ) is a transcontinental country at the intersection of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is part of the Caucasus region, bounded by the Black Sea to the west, by Russia to the north and northeast, by Turkey to the southwest, by Armenia to the south, and by Azerbaijan to the southeast. The country covers an area of , and has a population of 3.7 million people. Tbilisi is its capital as well as its largest city, home to roughly a third of the Georgian population. During the classical era, several independent kingdoms became established in what is now Georgia, such as Colchis and Iberia. In the early 4th century, ethnic Georgians officially adopted Christianity, which contributed to the spiritual and political unification of the early Georgian states. In the Middle Ages, the unified Kingdom of Georgia emerged and reached its Golden Age during the reign of King David IV and Queen Tamar in the 12th and early 13th centuries. Thereafter, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caucasian Spruce
''Picea orientalis'', commonly known as the Oriental spruce or Caucasian spruce, is a species of spruce native to the Caucasus and adjacent northeast Turkey. Description It is a large coniferous evergreen tree growing to 30–45 m tall or 98–145 feet (exceptionally to 57 m), and with a trunk diameter of up to 1.5 m (exceptionally up to 4 m). The Caucasian Spruce can also be found in Northern Iran, though its numbers have decreased due to deforestation. The shoots are buff-brown and moderately pubescent (hairy). The leaves are needle-like, the shortest of any spruce, 6–8 mm long, rhombic in cross-section, dark green with inconspicuous stomatal lines. The cones are slender cylindric-conic, 5–9 cm long and 1.5 cm broad, red to purple when young, maturing dark brown 5–7 months after pollination, and have stiff, smoothly rounded scales. Cultivation It is a popular ornamental tree in large gardens, valued in northern Europe and the USA for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canyons And Gorges Of Georgia (country)
A canyon (from ; archaic British English spelling: ''cañon''), or gorge, is a deep cleft between escarpments or cliffs resulting from weathering and the erosive activity of a river over geologic time scales. Rivers have a natural tendency to cut through underlying surfaces, eventually wearing away rock layers as sediments are removed downstream. A river bed will gradually reach a baseline elevation, which is the same elevation as the body of water into which the river drains. The processes of weathering and erosion will form canyons when the river's headwaters and estuary are at significantly different elevations, particularly through regions where softer rock layers are intermingled with harder layers more resistant to weathering. A canyon may also refer to a rift between two mountain peaks, such as those in ranges including the Rocky Mountains, the Alps, the Himalayas or the Andes. Usually, a river or stream carves out such splits between mountains. Examples of mou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akhaltsikhe
Akhaltsikhe ( ka, ახალციხე ), formerly known as Lomsia ( ka, ლომსია), is a small city in Georgia's southwestern region (''mkhare'') of Samtskhe–Javakheti. It is situated on both banks of a small river Potskhovi (a left tributary of the Kura), which divides the city between the old city in the north and new in the south. The 9th-century Akhaltsikhe (Rabati) Castle, which was recently restored, is located in the old part of the city. It is one of the main attractions of the Samtskhe-Javakheti region, along with Vardzia, Vale, Okrostsikhe and Zarzma. Toponymy Akhaltsikhe is the Georgian name of the town, which literally means "new fortress". It is attested in Arabic sources as ''Akhiskha'' (and ''Akhsikhath''), in Persian as ''Akhesqeh'' (also spelled as ''Akheshkheh''), and in Turkish sources as ''Ahıska''. History The town is mentioned among the settlements conquered by general Habib ibn Maslama al-Fihri during the reign of Umayyad Caliph Mu' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russo-Turkish War (1828–29)
The Russo-Turkish wars (or Ottoman–Russian wars) were a series of twelve wars fought between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire between the 16th and 20th centuries. It was one of the longest series of military conflicts in European history. Except for the war of 1710–11 and the Crimean War, which is often treated as a separate event, the conflicts ended disastrously for the Ottoman Empire; conversely, they showcased the ascendancy of Russia as a European power after the modernization efforts of Peter the Great in the early 18th century. History Conflict begins (1568–1739) Before Peter the Great The first Russo-Turkish War (1568–1570) occurred after the conquest of Kazan and Astrakhan by the Russian tsar Ivan the Terrible. The Ottoman sultan Selim II tried to squeeze the Russians out of the lower Volga by sending a military expedition to Astrakhan in 1569. The Turkish expedition ended in disaster for the Ottoman army, which could not take Astrakhan and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baku–Tbilisi–Ceyhan Pipeline
The Baku–Tbilisi–Ceyhan (BTC) pipeline is a long crude oil pipeline from the Azeri–Chirag–Gunashli oil field in the Caspian Sea to the Mediterranean Sea. It connects Baku, the capital of Azerbaijan and Ceyhan, a port on the south-eastern Mediterranean coast of Turkey, via Tbilisi, the capital of Georgia. It is the second-longest oil pipeline in the former Soviet Union, after the Druzhba pipeline. The first oil that was pumped from the Baku end of the pipeline reached Ceyhan on 28 May 2006. History Planning The Caspian Sea lies above one of the world's largest collections of oil and gas fields. As the sea is landlocked, transporting oil to Western markets is complicated. During Soviet times, all transportation routes from the Caspian region were through Russia. The collapse of the Soviet Union inspired a search for new routes. Russia first insisted that the new pipeline should pass through its territory, then declined to participate. In the spring of 1992, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borjomi-Kharagauli National Park
The Borjomi-Kharagauli National Park (BKNP) ( ka, ბორჯომ-ხარაგაულის ეროვნული პარკი, ''borjom-kharagaulis erovnuli parki'') is a protected area in central Georgia, in Samtskhe-Javakheti situated in the Lesser Caucasus, southwest to the nation's capital of Tbilisi.Borjomi-Kharagauli in Georgia ''Protected Planet'' Its is that of the . One of the largest |
Scots Pine
''Pinus sylvestris'', the Scots pine (UK), Scotch pine (US) or Baltic pine, is a species of tree in the pine family Pinaceae that is native to Eurasia. It can readily be identified by its combination of fairly short, blue-green leaves and orange-red bark. Description ''Pinus sylvestris'' is an evergreen coniferous tree growing up to in height and in trunk diameter when mature, exceptionally over tall and in trunk diameter on very productive sites. The tallest on record is a tree over 210 years old tree growing in Estonia which stands at . The lifespan is normally 150–300 years, with the oldest recorded specimens in Lapland, Northern Finland over 760 years. The bark is thick, flaky and orange-red when young to scaly and gray-brown in maturity, sometimes retaining the former on the upper portion.Trees for LifeSpecies profile: Scots pine/ref> The habit of the mature tree is distinctive due to its long, bare and straight trunk topped by a rounded or flat-topped mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nordmann Fir
''Abies nordmanniana'', the Nordmann fir or Caucasian fir, is a fir indigenous to the mountains south and east of the Black Sea, in Turkey, Georgia and the Russian Caucasus. It occurs at altitudes of 900–2,200 m on mountains with precipitation of over 1,000 mm. The current distribution of the Nordmann fir is associated with the forest refugia that existed during the Ice Age at the eastern and southern Black Sea coast. In spite of currently suitable climate, the species is not found in areas of the Eastern Greater Caucasus, which are separated from the Black Sea Coast by more than 400–500 km. Description It is a large evergreen coniferous tree growing to 55–61 m tall and with a trunk diameter of up to 2 m. In the Western Caucasus Reserve, some specimens have been reported to be and even tall, the tallest trees in the Caucasus, Anatolia, the Russian Federation and the continent of Europe. The leaves are needle-like, flattened, 1.8–3.5 cm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oriental Beech
''Fagus orientalis'', commonly known as the Oriental beech, is a deciduous tree in the beech family Fagaceae. It is native to Eurasia, in Eastern Europe and Western Asia. Description ''Fagus orientalis'' is a large tree, capable of reaching heights of up to tall and trunk diameter, though more typically tall and up to trunk diameter. The leaves are alternate, simple, and entire or with a slightly crenate margin, long and broad, with 7–13 veins on each side of the leaf (6–7 veins in ''F. sylvatica''). The buds are long and slender, long and thick, but thicker, till , where the buds include flower buds. The flowers are small catkins which appear shortly after the leaves in spring. The seeds are small triangular nuts long and wide at the base; there are two nuts in each cupule, maturing in the autumn 5–6 months after pollination. The cupule differs from that of European Beech in having flattened, slightly leaf-like appendages at the base (slender, soft spines i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.jpg)

