|
Borel Resummation
In mathematics, Borel summation is a summation method for divergent series, introduced by . It is particularly useful for summing divergent asymptotic series, and in some sense gives the best possible sum for such series. There are several variations of this method that are also called Borel summation, and a generalization of it called Mittag-Leffler summation. Definition There are (at least) three slightly different methods called Borel summation. They differ in which series they can sum, but are consistent, meaning that if two of the methods sum the same series they give the same answer. Throughout let denote a formal power series :A(z) = \sum_^\infty a_kz^k, and define the Borel transform of to be its equivalent exponential series :\mathcalA(t) \equiv \sum_^\infty \fract^k. Borel's exponential summation method Let denote the partial sum :A_n(z) = \sum_^n a_k z^k. A weak form of Borel's summation method defines the Borel sum of to be : \lim_ e^\sum_^\infty \frac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Émile Borel
Félix Édouard Justin Émile Borel (; 7 January 1871 – 3 February 1956) was a French mathematician and politician. As a mathematician, he was known for his founding work in the areas of measure theory and probability. Biography Borel was born in Saint-Affrique, Aveyron, the son of a Protestant pastor. He studied at the Collège Sainte-Barbe and Lycée Louis-le-Grand before applying to both the École normale supérieure and the École Polytechnique. He qualified in the first position for both and chose to attend the former institution in 1889. That year he also won the concours général, an annual national mathematics competition. After graduating in 1892, he placed first in the agrégation, a competitive civil service examination leading to the position of professeur agrégé. His thesis, published in 1893, was titled ''Sur quelques points de la théorie des fonctions'' ("On some points in the theory of functions"). That year, Borel started a four-year stint as a lectu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
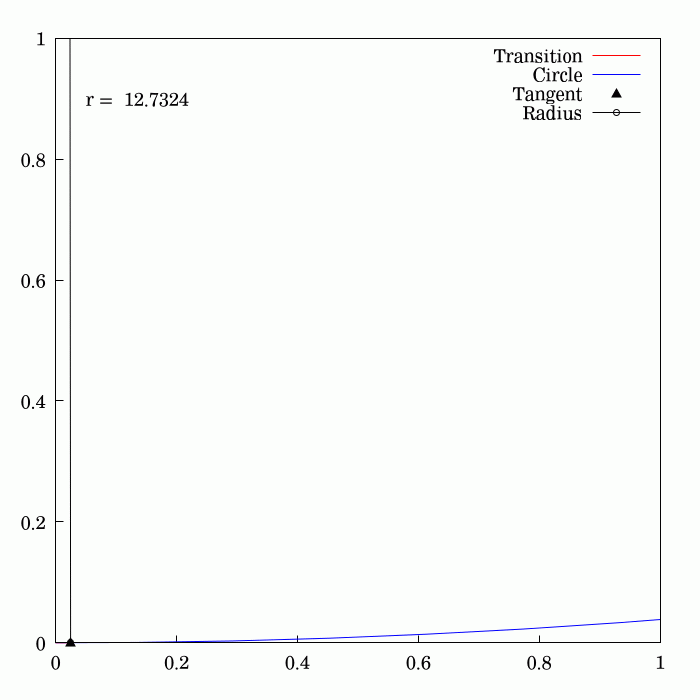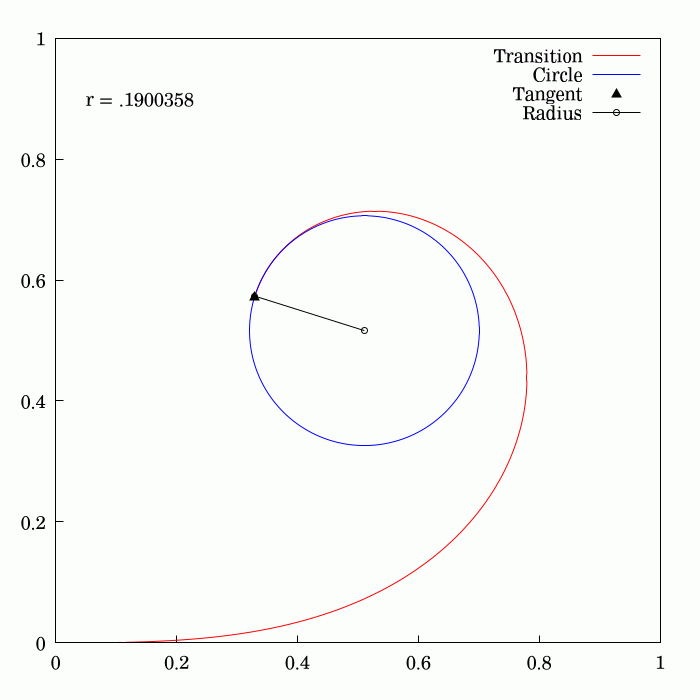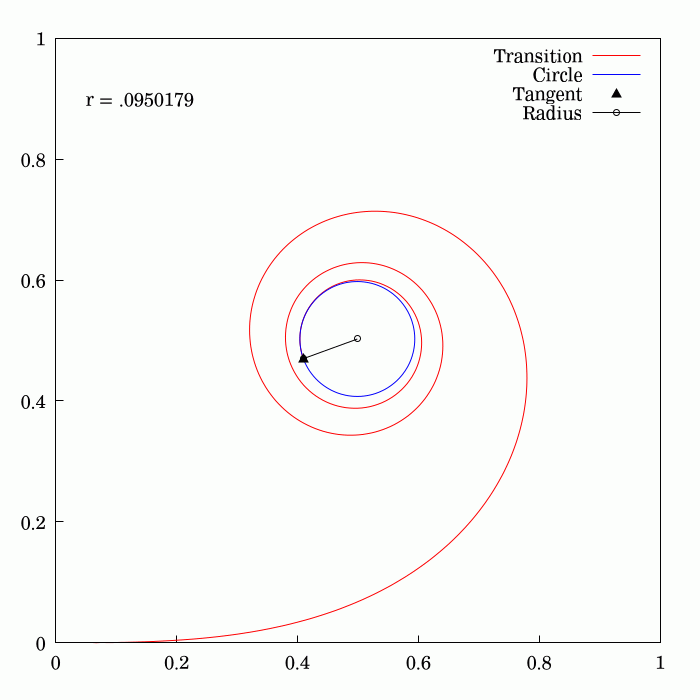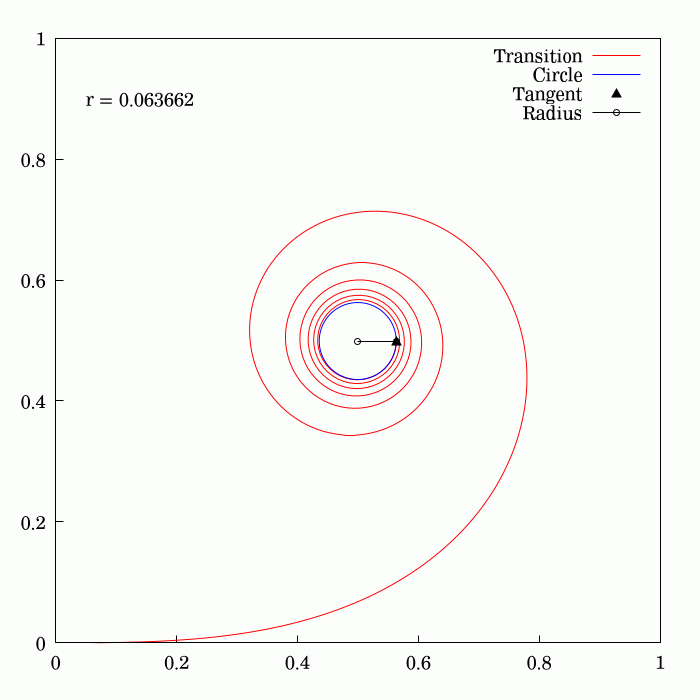
Fresnel Integral
250px, Plots of and . The maximum of is about . If the integrands of and were defined using instead of , then the image would be scaled vertically and horizontally (see below). The Fresnel integrals and are two transcendental functions named after Augustin-Jean Fresnel that are used in optics and are closely related to the error function (). They arise in the description of near-field Fresnel diffraction phenomena and are defined through the following integral representations: S(x) = \int_0^x \sin\left(t^2\right)\,dt, \quad C(x) = \int_0^x \cos\left(t^2\right)\,dt. The simultaneous parametric plot of and is the Euler spiral (also known as the Cornu spiral or clothoid). Definition 250px, Fresnel integrals with arguments instead of converge to instead of . The Fresnel integrals admit the following power series expansions that converge for all : \begin S(x) &= \int_0^x \sin\left(t^2\right)\,dt = \sum_^(-1)^n \frac, \\ C(x) &= \int_0^x \cos\left(t^2\right)\,dt = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exponential Type
In complex analysis, a branch of mathematics, a holomorphic function is said to be of exponential type C if its growth is bounded by the exponential function ''e''''C'', ''z'', for some real-valued constant ''C'' as , ''z'', → ∞. When a function is bounded in this way, it is then possible to express it as certain kinds of convergent summations over a series of other complex functions, as well as understanding when it is possible to apply techniques such as Borel summation, or, for example, to apply the Mellin transform, or to perform approximations using the Euler–Maclaurin formula. The general case is handled by Nachbin's theorem, which defines the analogous notion of Ψ-type for a general function Ψ(''z'') as opposed to ''e''''z''. Basic idea A function ''f''(''z'') defined on the complex plane is said to be of exponential type if there exist real-valued constants ''M'' and ''τ'' such that :\left, f\left(re^\right)\ \le Me^ in the limit of r\to\inft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nachbin Resummation
In mathematics, in the area of complex analysis, Nachbin's theorem (named after Leopoldo Nachbin) is commonly used to establish a bound on the growth rates for an analytic function. This article provides a brief review of growth rates, including the idea of a function of exponential type. Classification of growth rates based on type help provide a finer tool than big O or Landau notation, since a number of theorems about the analytic structure of the bounded function and its integral transforms can be stated. In particular, Nachbin's theorem may be used to give the domain of convergence of the generalized Borel transform, given below. Exponential type A function ''f''(''z'') defined on the complex plane is said to be of exponential type if there exist constants ''M'' and α such that :, f(re^), \le Me^ in the limit of r\to\infty. Here, the complex variable ''z'' was written as z=re^ to emphasize that the limit must hold in all directions θ. Letting α stand for the infimum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integer
An integer is the number zero (), a positive natural number (, , , etc.) or a negative integer with a minus sign ( −1, −2, −3, etc.). The negative numbers are the additive inverses of the corresponding positive numbers. In the language of mathematics, the set of integers is often denoted by the boldface or blackboard bold \mathbb. The set of natural numbers \mathbb is a subset of \mathbb, which in turn is a subset of the set of all rational numbers \mathbb, itself a subset of the real numbers \mathbb. Like the natural numbers, \mathbb is countably infinite. An integer may be regarded as a real number that can be written without a fractional component. For example, 21, 4, 0, and −2048 are integers, while 9.75, , and are not. The integers form the smallest group and the smallest ring containing the natural numbers. In algebraic number theory, the integers are sometimes qualified as rational integers to distinguish them from the more general algebraic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factorial
In mathematics, the factorial of a non-negative denoted is the product of all positive integers less than or equal The factorial also equals the product of n with the next smaller factorial: \begin n! &= n \times (n-1) \times (n-2) \times (n-3) \times \cdots \times 3 \times 2 \times 1 \\ &= n\times(n-1)!\\ \end For example, 5! = 5\times 4! = 5 \times 4 \times 3 \times 2 \times 1 = 120. The value of 0! is 1, according to the convention for an empty product. Factorials have been discovered in several ancient cultures, notably in Indian mathematics in the canonical works of Jain literature, and by Jewish mystics in the Talmudic book '' Sefer Yetzirah''. The factorial operation is encountered in many areas of mathematics, notably in combinatorics, where its most basic use counts the possible distinct sequences – the permutations – of n distinct objects: there In mathematical analysis, factorials are used in power series for the exponential functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renormalon
In physics, a renormalon (a term suggested by 't Hooft) is a particular source of divergence seen in perturbative approximations to quantum field theories (QFT). When a formally divergent series in a QFT is summed using Borel summation, the associated Borel transform of the series can have singularities as a function of the complex transform parameter. The renormalon is a possible type of singularity arising in this complex ''Borel plane'', and is a counterpart of an instanton singularity. Associated with such singularities, renormalon contributions are discussed in the context of quantum chromodynamics (QCD) and usually have the power-like form \left(\Lambda/Q\right)^p as functions of the momentum Q (here \Lambda is the momentum cut-off). They are cited against the usual logarithmic effects like \ln\left(\Lambda/Q\right). Brief history Perturbation series in quantum field theory are usually divergent as was firstly indicated by Freeman Dyson. According to the Lipatov method, N- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instanton
An instanton (or pseudoparticle) is a notion appearing in theoretical and mathematical physics. An instanton is a classical solution to equations of motion with a finite, non-zero action, either in quantum mechanics or in quantum field theory. More precisely, it is a solution to the equations of motion of the classical field theory on a Euclidean spacetime. In such quantum theories, solutions to the equations of motion may be thought of as critical points of the action. The critical points of the action may be local maxima of the action, local minima, or saddle points. Instantons are important in quantum field theory because: * they appear in the path integral as the leading quantum corrections to the classical behavior of a system, and * they can be used to study the tunneling behavior in various systems such as a Yang–Mills theory. Relevant to dynamics, families of instantons permit that instantons, i.e. different critical points of the equation of motion, be relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perturbation Theory (quantum Mechanics)
In quantum mechanics, perturbation theory is a set of approximation schemes directly related to mathematical perturbation for describing a complicated quantum system in terms of a simpler one. The idea is to start with a simple system for which a mathematical solution is known, and add an additional "perturbing" Hamiltonian representing a weak disturbance to the system. If the disturbance is not too large, the various physical quantities associated with the perturbed system (e.g. its energy levels and eigenstates) can be expressed as "corrections" to those of the simple system. These corrections, being small compared to the size of the quantities themselves, can be calculated using approximate methods such as asymptotic series. The complicated system can therefore be studied based on knowledge of the simpler one. In effect, it is describing a complicated unsolved system using a simple, solvable system. Approximate Hamiltonians Perturbation theory is an important tool fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abelian And Tauberian Theorems
In mathematics, Abelian and Tauberian theorems are theorems giving conditions for two methods of summing divergent series to give the same result, named after Niels Henrik Abel and Alfred Tauber. The original examples are Abel's theorem showing that if a series converges to some limit then its Abel sum is the same limit, and Tauber's theorem showing that if the Abel sum of a series exists and the coefficients are sufficiently small (o(1/''n'')) then the series converges to the Abel sum. More general Abelian and Tauberian theorems give similar results for more general summation methods. There is not yet a clear distinction between Abelian and Tauberian theorems, and no generally accepted definition of what these terms mean. Often, a theorem is called "Abelian" if it shows that some summation method gives the usual sum for convergent series, and is called "Tauberian" if it gives conditions for a series summable by some method that allows it to be summable in the usual sense. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Comparison Test
In mathematics, the comparison test, sometimes called the direct comparison test to distinguish it from similar related tests (especially the limit comparison test), provides a way of deducing the convergence or divergence of an infinite series or an improper integral. In both cases, the test works by comparing the given series or integral to one whose convergence properties are known. For series In calculus, the comparison test for series typically consists of a pair of statements about infinite series with non-negative ( real-valued) terms: * If the infinite series \sum b_n converges and 0 \le a_n \le b_n for all sufficiently large ''n'' (that is, for all n>N for some fixed value ''N''), then the infinite series \sum a_n also converges. * If the infinite series \sum b_n diverges and 0 \le b_n \le a_n for all sufficiently large ''n'', then the infinite series \sum a_n also diverges. Note that the series having larger terms is sometimes said to ''dominate'' (or ''eventually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regular Polygon
In Euclidean geometry, a regular polygon is a polygon that is direct equiangular (all angles are equal in measure) and equilateral (all sides have the same length). Regular polygons may be either convex, star or skew. In the limit, a sequence of regular polygons with an increasing number of sides approximates a circle, if the perimeter or area is fixed, or a regular apeirogon (effectively a straight line), if the edge length is fixed. General properties ''These properties apply to all regular polygons, whether convex or star.'' A regular ''n''-sided polygon has rotational symmetry of order ''n''. All vertices of a regular polygon lie on a common circle (the circumscribed circle); i.e., they are concyclic points. That is, a regular polygon is a cyclic polygon. Together with the property of equal-length sides, this implies that every regular polygon also has an inscribed circle or incircle that is tangent to every side at the midpoint. Thus a regular polygon is a tangen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |