|
Bootstrapping (electronics)
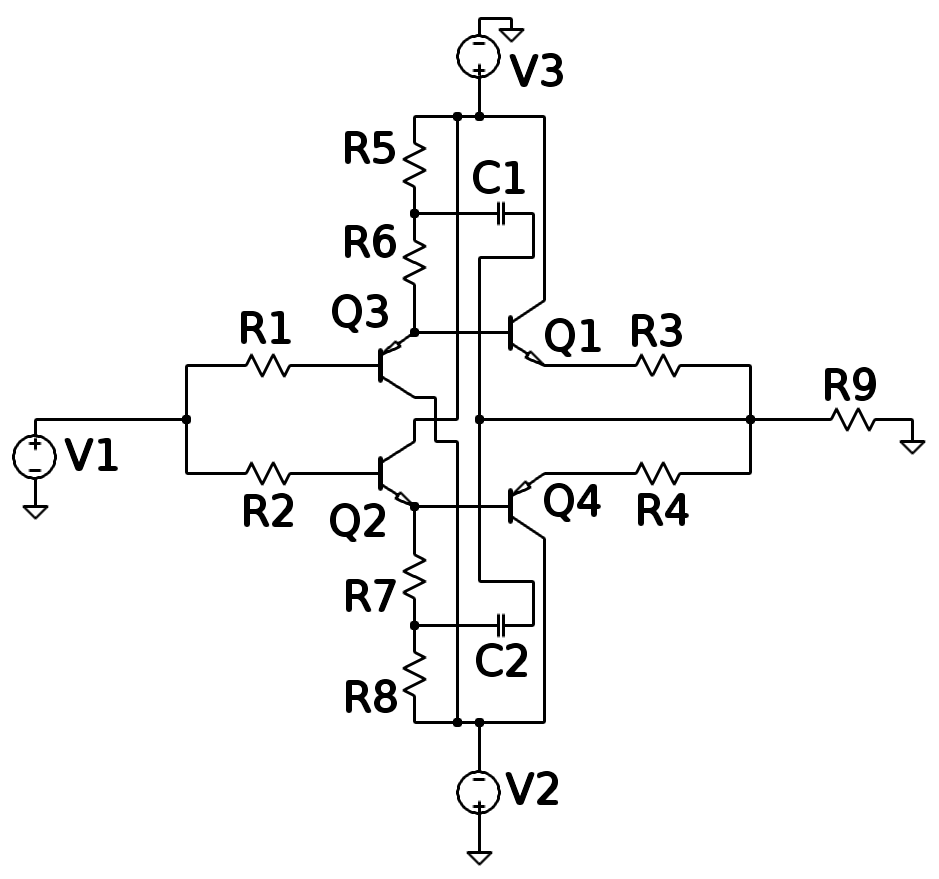
In the field of electronics, a technique where part of the output of a system is used at startup can be described as bootstrapping. A bootstrap circuit is one where part of the output of an amplifier stage is applied to the input, so as to alter the input impedance of the amplifier. When applied deliberately, the intention is usually to increase rather than decrease the impedance. In the domain of MOSFET circuits, bootstrapping is commonly used to mean pulling up the operating point of a transistor above the power supply rail. The same term has been used somewhat more generally for dynamically altering the operating point of an operational amplifier (by shifting both its positive and negative supply rail) in order to increase its output voltage swing (relative to the ground). In the sense used in this paragraph, bootstrapping an operational amplifier means "using a signal to drive the reference point of the op-amp's power supplies". A more sophisticated use of this rail bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronics
The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behaviour and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Electronics uses active devices to control electron flow by amplification and rectification, which distinguishes it from classical electrical engineering, which only uses passive effects such as resistance, capacitance and inductance to control electric current flow. Electronics has hugely influenced the development of modern society. The central driving force behind the entire electronics industry is the semiconductor industry sector, which has annual sales of over $481 billion as of 2018. The largest industry sector is e-commerce, which generated over $29 trillion in 2017. History and development Electronics has hugely influenced the development of modern society. The identification of the electron in 1897, along with the subsequent invention of the vacuum tube which could amplify and rectify small ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Die (integrated Circuit)
A die, in the context of integrated circuits, is a small block of semiconducting material on which a given functional circuit is fabricated. Typically, integrated circuits are produced in large batches on a single wafer of electronic-grade silicon (EGS) or other semiconductor (such as GaAs) through processes such as photolithography. The wafer is cut ( diced) into many pieces, each containing one copy of the circuit. Each of these pieces is called a die. There are three commonly used plural forms: ''dice'', ''dies'' and ''die''. To simplify handling and integration onto a printed circuit board, most dies are packaged in various forms. Manufacturing process Most dies are composed of silicon and used for integrated circuits. The process begins with the production of monocrystalline silicon ingots. These ingots are then sliced into disks with a diameter of up to 300 mm. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miller Theorem
The Miller theorem refers to the process of creating equivalent circuits. It asserts that a floating impedance element, supplied by two voltage sources connected in series, may be split into two grounded elements with corresponding impedances. There is also a dual Miller theorem with regards to impedance supplied by two current sources connected in parallel. The two versions are based on the two Kirchhoff's circuit laws. Miller theorems are not only pure mathematical expressions. These arrangements explain important circuit phenomena about modifying impedance (Miller effect, virtual ground, bootstrapping, negative impedance, etc.) and help in designing and understanding various commonplace circuits (feedback amplifiers, resistive and time-dependent converters, negative impedance converters, etc.). The theorems are useful in 'circuit analysis' especially for analyzing circuits with feedback and certain transistor amplifiers at high frequencies. There is a close relationship between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel 8008
The Intel 8008 ("''eight-thousand-eight''" or "''eighty-oh-eight''") is an early byte-oriented microprocessor designed by Computer Terminal Corporation (CTC), implemented and manufactured by Intel, and introduced in April 1972. It is an 8-bit CPU with an external 14-bit address bus that could address 16 KB of memory. Originally known as the 1201, the chip was commissioned by Computer Terminal Corporation (CTC) to implement an instruction set of their design for their Datapoint 2200 programmable terminal. As the chip was delayed and did not meet CTC's performance goals, the 2200 ended up using CTC's own TTL-based CPU instead. An agreement permitted Intel to market the chip to other customers after Seiko expressed an interest in using it for a calculator. History CTC formed in San Antonio in 1968 under the direction of Austin O. "Gus" Roche and Phil Ray, both NASA engineers. Roche, in particular, was primarily interested in producing a desktop computer. However, given the immatur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel 4004
The Intel 4004 is a 4-bit central processing unit (CPU) released by Intel Corporation in 1971. Sold for US$60, it was the first commercially produced microprocessor, and the first in a long line of Intel CPUs. The 4004 was the first significant example of large scale integration, showcasing the superiority of the MOS silicon gate technology (SGT). Compared to the incumbent technology, the SGT integrated on the same chip area twice the number of transistors with five times the operating speed. This step-function increase in performance made possible a single-chip CPU, replacing the existing multi-chip CPUs. The innovative 4004 chip design served as a model on how to use the SGT for complex logic and memory circuits, thus accelerating the adoption of the SGT by the world’s semiconductor industry. The developer of the original SGT at Fairchild was Federico Faggin who designed the first commercial integrated circuit (IC) that used the new technology, proving its superiority for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bias Circuit
In electronics, biasing is the setting of DC (direct current) operating conditions (current and voltage) of an active device in an amplifier. Many electronic devices, such as diodes, transistors and vacuum tubes, whose function is processing time-varying ( AC) signals, also require a steady (DC) current or voltage at their terminals to operate correctly. This current or voltage is called ''bias''. The AC signal applied to them is superposed on this DC bias current or voltage. The operating point of a device, also known as bias point, quiescent point, or Q-point, is the DC voltage or current at a specified terminal of an active device (a transistor or vacuum tube) with no input signal applied. A bias circuit is a portion of the device's circuit which supplies this steady current or voltage. Overview In electronics, 'biasing' usually refers to a fixed DC voltage or current applied to a terminal of an electronic component such as a diode, transistor or vacuum tube in a circ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switch Mode Power Supplies
A switched-mode power supply (switching-mode power supply, switch-mode power supply, switched power supply, SMPS, or switcher) is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator to convert electrical power efficiently. Like other power supplies, an SMPS transfers power from a DC or AC source (often mains power, see AC adapter) to DC loads, such as a personal computer, while converting voltage and current characteristics. Unlike a linear power supply, the pass transistor of a switching-mode supply continually switches between low-dissipation, full-on and full-off states, and spends very little time in the high dissipation transitions, which minimizes wasted energy. A hypothetical ideal switched-mode power supply dissipates no power. Voltage regulation is achieved by varying the ratio of on-to-off time (also known as duty cycles). In contrast, a linear power supply regulates the output voltage by continually dissipating power in the pass transistor. The switc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
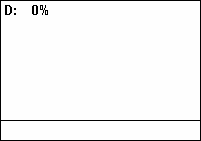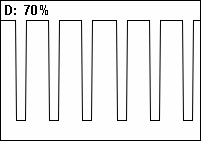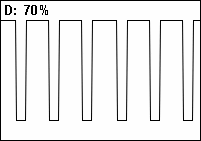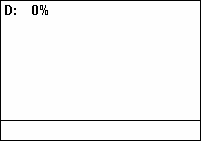
Duty Cycle
A duty cycle or power cycle is the fraction of one period in which a signal or system is active. Duty cycle is commonly expressed as a percentage or a ratio. A period is the time it takes for a signal to complete an on-and-off cycle. As a formula, a duty cycle (%) may be expressed as: :D = \frac \times 100\% Equally, a duty cycle (ratio) may be expressed as: :D = \frac where D is the duty cycle, PW is the pulse width (pulse active time), and T is the total period of the signal. Thus, a 60% duty cycle means the signal is on 60% of the time but off 40% of the time. The "on time" for a 60% duty cycle could be a fraction of a second, a day, or even a week, depending on the length of the period. Duty cycles can be used to describe the percent time of an active signal in an electrical device such as the power switch in a switching power supply or the firing of action potentials by a living system such as a neuron. The duty factor for periodic signal expresses the same notion, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IGBT
An insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) is a three-terminal power semiconductor device primarily used as an electronic switch, which, as it was developed, came to combine high efficiency and fast switching. It consists of four alternating layers (P–N–P–N) that are controlled by a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) gate structure. Although the structure of the IGBT is topologically the same as a thyristor with a "MOS" gate ( MOS-gate thyristor), the thyristor action is completely suppressed, and only the transistor action is permitted in the entire device operation range. It is used in switching power supplies in high-power applications: variable-frequency drives (VFDs), electric cars, trains, variable-speed refrigerators, lamp ballasts, arc-welding machines, induction hobs, and air conditioners. Since it is designed to turn on and off rapidly, the IGBT can synthesize complex waveforms with pulse-width modulation and low-pass filters, so it is also used in switching amp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H-bridge
A H-bridge is an electronic circuit that switches the polarity of a voltage applied to a load. These circuits are often used in robotics and other applications to allow DC motors to run forwards or backwards. The name is derived from its common schematic diagram representation, with four switching elements configured as the branches of a letter "H" and the load connected as the cross-bar. Most DC-to-AC converters (power inverters), most AC/AC converters, the DC-to-DC push–pull converter, isolated DC-to-DC converter most motor controllers, and many other kinds of power electronics use H bridges. In particular, a bipolar stepper motor is almost always driven by a motor controller containing two H bridges. General H-bridges are available as integrated circuits, or can be built from discrete components. The term ''H-bridge'' is derived from the typical graphical representation of such a circuit. An H-bridge is built with four switches (solid-state or mechanical). When the swit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flyback Diode
A flyback diode is any diode connected across an inductor used to eliminate flyback, which is the sudden voltage spike seen across an inductive load when its supply current is suddenly reduced or interrupted. It is used in circuits in which inductive loads are controlled by switches, and in switching power supplies and inverters. This diode is known by many other names, such as snubber diode, commutating diode, freewheeling diode, suppressor diode, clamp diode, or catch diode. Operation Fig. 1 shows an inductor connected to a battery - a constant voltage source. The resistor represents the small residual resistance of the inductor's wire windings. When the switch is closed, the voltage from the battery is applied to the inductor, causing current from the battery's positive terminal to flow down through the inductor and resistor. The increase in current causes a back EMF (voltage) across the inductor due to Faraday's law of induction which opposes the change in current. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diode
A diode is a two- terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A diode vacuum tube or thermionic diode is a vacuum tube with two electrodes, a heated cathode and a plate, in which electrons can flow in only one direction, from cathode to plate. A semiconductor diode, the most commonly used type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals. Semiconductor diodes were the first semiconductor electronic devices. The discovery of asymmetric electrical conduction across the contact between a crystalline mineral and a metal was made by German physicist Ferdinand Braun in 1874. Today, most diodes are made of silicon, but other semiconducting materials such as gallium arsenide and germanium are also used. Among many uses, diodes are found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |