|
Bolotnik
In Slavic mythology, bolotnik (russian: ą▒ąŠą╗ąŠ╠üčéąĮąĖą║, ; from ''boloto'', "swamp"), balotnik (), bolotyanik () or b┼éotnik (Polish; łbw╔ötnik "mud" or "puddle") is a male swamp spirit. There are many descriptions of bolotnik. Usually he was portrayed as a man or an old man who has big, frog-like eyes, a green beard and long hair. His body is covered with dirt, algae and fish scales. The legends from the Vitebsk Governorate of Russia said that bolotnik is a dirty, fat, eyeless creature that motionlessly sits at the bottom of the swamp. In some accounts bolotnik is also said to have long arms and a tail. Just like the majority of Slavic water spirits, he would lure and drag people into the water if they get close to the edge. It is believed that bolotnik has neither wife nor children; in the other legends he is married to bolotnitsa, a female swamp spirit. Bolotniki (plural) are rarely found in folklore, and the swamp-dwelling spirit was often thought of as a kind of vodyan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vodyanoy
In Slavic mythology, vodyanoy or vodyanoi ( rus, ą▓ąŠą┤čÅąĮąŠ╠üą╣, p=v╔Öd╩▓╔¬╦łnoj; lit. ' efrom the water' or 'watery') is a water spirit. In Czech and Slovak fairy tales, it is called ''vodn├Łk'' (or in Germanized form: ), and it is considered to be the equivalent creature as the Wassermann or nix of German fairy tales. Vodyanoy is said to appear as a naked old man with a frog-like face, greenish beard, and long hair, with his body covered in algae and muck, usually covered in black fish scales; čüonsequently, he is often dubbed "grandfather" or "forefather" by the local people. He has webbed paws instead of hands, a fish's tail, and eyes that burn like red-hot coals. He usually rides along his river on a half-sunken log, making loud splashes. Local drownings are said to be the work of the vodyanoy (or rusalkas). When angered, the vodyanoy breaks dams, washes down water mills, and drowns people and animals. Consequently, fishermen, millers, and also bee-keepers make sacrific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vodyanoy
In Slavic mythology, vodyanoy or vodyanoi ( rus, ą▓ąŠą┤čÅąĮąŠ╠üą╣, p=v╔Öd╩▓╔¬╦łnoj; lit. ' efrom the water' or 'watery') is a water spirit. In Czech and Slovak fairy tales, it is called ''vodn├Łk'' (or in Germanized form: ), and it is considered to be the equivalent creature as the Wassermann or nix of German fairy tales. Vodyanoy is said to appear as a naked old man with a frog-like face, greenish beard, and long hair, with his body covered in algae and muck, usually covered in black fish scales; čüonsequently, he is often dubbed "grandfather" or "forefather" by the local people. He has webbed paws instead of hands, a fish's tail, and eyes that burn like red-hot coals. He usually rides along his river on a half-sunken log, making loud splashes. Local drownings are said to be the work of the vodyanoy (or rusalkas). When angered, the vodyanoy breaks dams, washes down water mills, and drowns people and animals. Consequently, fishermen, millers, and also bee-keepers make sacrif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavic Mythology
Slavic mythology or Slavic religion is the religious beliefs, myths, and ritual practices of the Slavs before Christianisation, which occurred at various stages between the 8th and the 13th century. The South Slavs, who likely settled in the Balkan Peninsula during the 6thŌĆō7th centuries AD, bordering with the Byzantine Empire to the south, came under the sphere of influence of Eastern Christianity, beginning with the creation of writing systems for Slavic languages (first Glagolitic, and then Cyrillic script) in 855 by the brothers Saints Cyril and Methodius and the adoption of Christianity in Bulgaria in 863. The East Slavs followed with the official adoption in 988 by Vladimir the Great of Kievan Rus'. The West Slavs' process of Christianization was more gradual and complicated. The Moravians accepted Christianity as early as 831, the Bohemian dukes followed in 845, Slovaks accepted Christianity somewhere between the years 828 and 863, but the Poles accepted it much later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Slavs
The term North Slavic languages is used in two main senses: * for a number of proposed groupings or subdivisions of the Slavic languages. However, "North Slavic" is not widely used in this sense, and has no agreed definition. Modern scholars usually divide the Slavic languages into West Slavic, East Slavic, and South Slavic. * for a number of constructed languages that were created in the 20th and 21st century, and have been derived from existing Slavic languages. Proposed subdivisions Historically, the term "North Slav" has been used in academia since at least the first half of the 19th century. Since then the concept continued to see use in various publications. The following uses of the term "North Slavs" or "North Slavic" are found: * 'North Slavs', 'Northslavs' or 'North Hungarian Slavs' were used as synonyms for the combination of Slovaks and Rusyns living in the northern parts of the Kingdom of Hungary (1526ŌĆō1867) within the Austrian Empire by several Slavic author ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Łęczyca
┼ü─Öczyca (; in full the Royal Town of ┼ü─Öczyca, pl, Kr├│lewskie Miasto ┼ü─Öczyca; german: Lentschitza; he, ū£ūĢūĀūśū®ūÖūź) is a town of 13,786 inhabitants () in central Poland. Situated in the ┼ü├│d┼║ Voivodeship, it is the county seat of the ┼ü─Öczyca County. Origin of the name The town was probably named after a West Slavic ( Lechitic) tribe called Leczanie, which inhabited central Poland in the early Middle Ages. Some scholars however claim that the town was named after an Old Polish word ┼é─Ög, which means a swampy plain. In medieval Latin documents, ┼ü─Öczyca is called Lonsin, Lucic, Lunciz, Lantsiza, Loncizia, Lonsitia and Lunchicia. In the early 12th century, Gallus Anonymus called ┼ü─Öczyca "Lucic", and in 1154, Arab geographer Muhammad al-Idrisi named it Nugrada, placing it among other main towns of the Kingdom of Poland, such as Krak├│w, Sieradz, Gniezno, Wroc┼éaw and Santok. Location ┼ü─Öczyca lies in the middle of the county, and has the area of . In the past ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
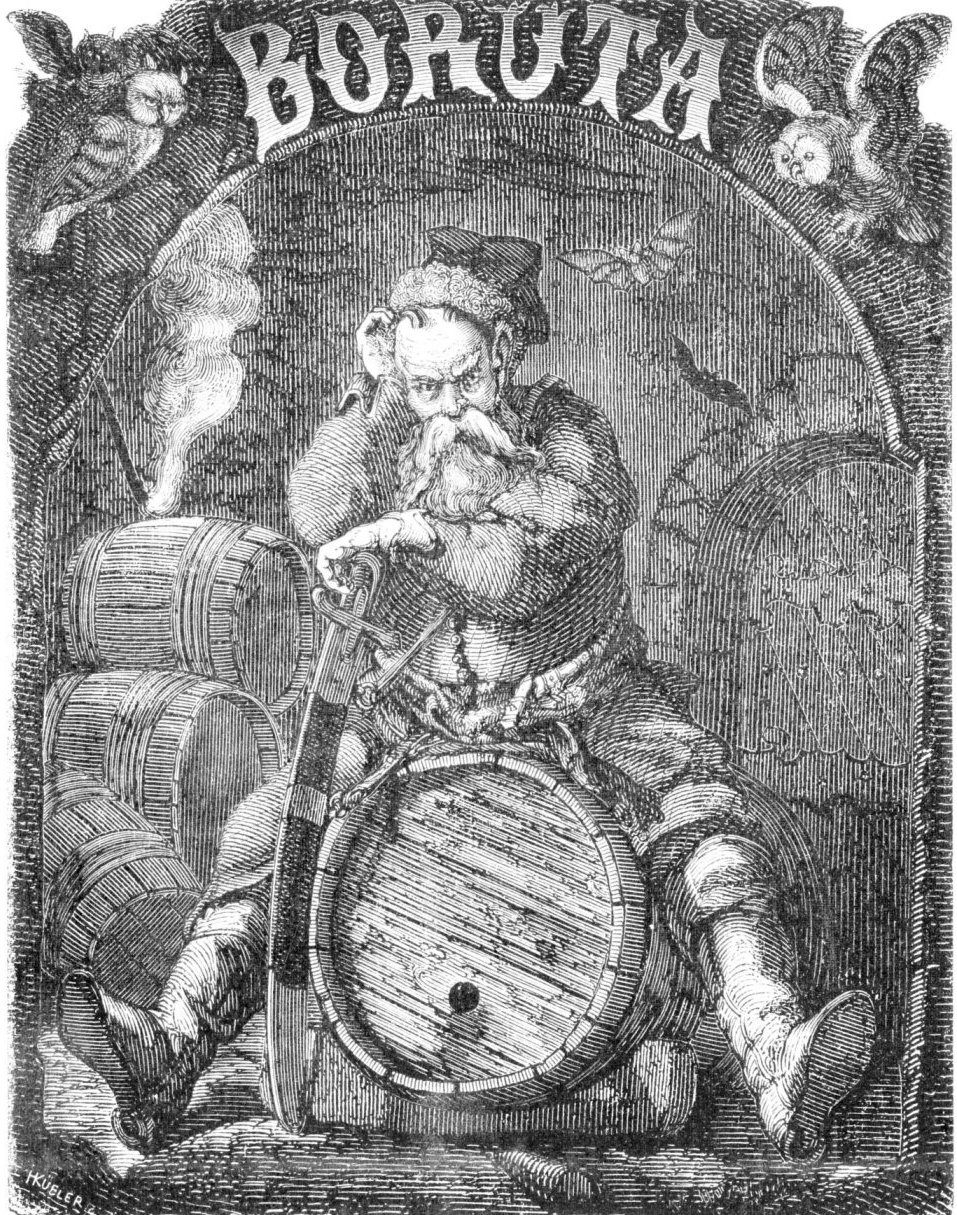
Devil Boruta
Devil Boruta ( pl, Diabeł Boruta) is a fictional character from Polish mythology, folklore and literature, associated with the Polish town of Łęczyca. The character is the transformation of the pagan Slavic demon '' leshy'' in post-Christianization times. Boruta is also referred to as ''błotnik'',Pełka, Leonard (1987). ''Polska demonologia ludowa''. Warszawa: Iskry. pp.187. a swamp spirit known in the mythology of the Kashubians and especially the Eastern Slavs, where he is called a ''bolotnik''. He was usually considered to be a nobleman Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The characteristi ..., and accordingly, he was usually busy with corrupting nobles, leaving other social classes to other devils - like Rokita the devil from the same region, who more often tempted peasants. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lazavik
Lazavik ( be, ąøą░ąĘą░ą▓č¢ą║) is a creature of Belarusian mythology. Description Lazavik is a benevolent Belarusian mythological character that lives amid the vine bushes ("laza" in Belarusian language). In Belarusian folk tales Lazavik is described as a small creature with one eye, a long beard and a very long whip in his hand. Belarusian people used to say that when Lazavik walks through the marshland, his only eye shines like a light. Mode of life The creature Lazavik prefers to stay unnoticed by people, and constantly tries to hide in its house. The house of Lazavik is small, with no windows and no doors. In fact Lazavik is the guardian of Belarusian marshes. It is believed that Lazavik dies if its marshes are drained. With its whip, Lazavik drives away small, harmful, and noisy Lozniks through the vine bushes.ą”čŗą▒čāą╗čīą║ąĖąĮ ąÆ. ąÆ., ąĪąĖą▓ą░ą╗čīąĮčæą▓ ąÉ. ąØ., ąĪąĄčĆą┤čÄč湥ąĮą║ąŠ ą£. ąØ. ┬½ąÆą╗ąĄčüąŠą▓ą░ ą║ąĮąĖą│ą░┬╗: ąæčŗą╗čī ąĖ ą╝ąĖčäčŗ ąĪą╗ą░ą▓čÅąĮčüą║ąŠą╣ čåąĖą▓ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willow
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, from the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 400 speciesMabberley, D.J. 1997. The Plant Book, Cambridge University Press #2: Cambridge. of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist soils in cold and temperate regions. Most species are known as willow, but some narrow-leaved shrub species are called osier, and some broader-leaved species are referred to as sallow (from Old English ''sealh'', related to the Latin word ''salix'', willow). Some willows (particularly arctic and alpine species) are low-growing or creeping shrubs; for example, the dwarf willow (''Salix herbacea'') rarely exceeds in height, though it spreads widely across the ground. Description Willows all have abundant watery bark sap, which is heavily charged with salicylic acid, soft, usually pliant, tough wood, slender branches, and large, fibrous, often stoloniferous roots. The roots are remarkable for their toughness, size, and tenacity to live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gomel Oblast
Gomel Region or Gomel Oblast or Homiel Voblasts ( be, ąōąŠ╠üą╝ąĄą╗čīčüą║ą░čÅ ą▓ąŠ╠üą▒ą╗ą░čüčåčī, Homielskaja vob┼éas─ć, russian: ąōąŠą╝ąĄą╗čīčüą║ą░čÅ ąŠą▒ą╗ą░čüčéčī, Gomelskaya oblast) is one of the regions of Belarus. Its administrative center is Gomel. The total area of the region is , the population in 2011 stood at 1,435,000 with the number of inhabitants per km2 at 36. Important cities within the region include: Homiel, Mazyr, Zhlobin, Svietlahorsk, Rechytsa, Kalinkavichy, Rahachow and Dobrush. Both the Gomel Region and the Mogilev Region suffered severely from the Chernobyl disaster. The Gomel Province borders the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone in places, and parts of it have been designated as mandatory or voluntary resettlement areas as a result of the radioactive contamination. Administrative territorial entities Gomel Region comprises 21 districts and 2 city municipalities. The districts have 278 selsovets, and 17 cities and towns. Districts of Gomel Region * Akciabr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voronezh Governorate
Voronezh Governorate (russian: ąÆąŠčĆąŠąĮąĄąČčüą║ą░čÅ ą│čāą▒ąĄčĆąĮąĖčÅ, ''Voronezhskaya guberniya''; uk, ąÆąŠčĆąŠąĮč¢ąĘčīą║ą░ ą│čāą▒ąĄčĆąĮč¢čÅ) was an administrative division (a '' guberniya'') of the Tsardom of Russia, the Russian Empire, and the early Russian SFSR, which existed from 1708 (as ''Azov Governorate'') until 1779 and from 1796 until 1928. Its seat was located in Voronezh since 1725. The governorate was located in the south of the European part of the Russian Empire. In 1928, the governorate was abolished, and its area was included into newly established Central Black Earth Oblast. First Azov Governorate Azov Governorate, together with seven other governorates, was established on , 1708, by Tsar Peter the Great's edict.ąŻą║ą░ąĘ ąŠą ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherepovets District
Cherepovetsky District (russian: ą¦ąĄčĆąĄą┐ąŠą▓ąĄ╠üčåą║ąĖą╣ čĆą░ą╣ąŠ╠üąĮ) is an administrativeLaw #371-OZ and municipalLaw #1129-OZ district (raion), one of the twenty-six in Vologda Oblast, Russia. It is located in the northeast of the oblast and borders with Belozersky District in the north, Kirillovsky District in the northwest, Sheksninsky District in the east, Poshekhonsky District of Yaroslavl Oblast in the southeast, Breytovsky District of Yaroslavl Oblast in the south, Vesyegonsky District of Tver Oblast in the southwest, Ustyuzhensky District in the west, and with Kaduysky District in the northwest. The area of the district is . Its administrative center is the city of Cherepovets (which is not administratively a part of the district). Population: 40,871 ( 2002 Census); Geography The district is Y-shaped and oriented to the south, with the Rybinsk Reservoir separating the two southern portions of the land. The whole area of the district belongs to the basin of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Will-o'-the-wisp
In folklore, a will-o'-the-wisp, will-o'-wisp or ''ignis fatuus'' (, plural ''ignes fatui''), is an atmospheric ghost light seen by travellers at night, especially over bogs, swamps or marshes. The phenomenon is known in English folk belief, English folklore and much of European folklore by a variety of names, including jack-o'-lantern, friar's lantern, hinkypunk and is said to mislead travellers by resembling a flickering lamp or lantern. In literature, will-o'-the-wisp metaphorically refers to a hope or goal that leads one on, but is impossible to reach, or something one finds strange or sinister. Wills-o'-the-wisp appear in folk tales and traditional legends of numerous countries and cultures; notable wills-o'-the-wisp include St. Louis Light in Saskatchewan, the Spooklight in Southwestern Missouri and Northeastern Oklahoma, the Marfa lights of Texas, the Naga fireballs on the Mekong in Thailand, the Paulding Light in Upper Peninsula of Michigan and the Hessdalen light i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)
