|
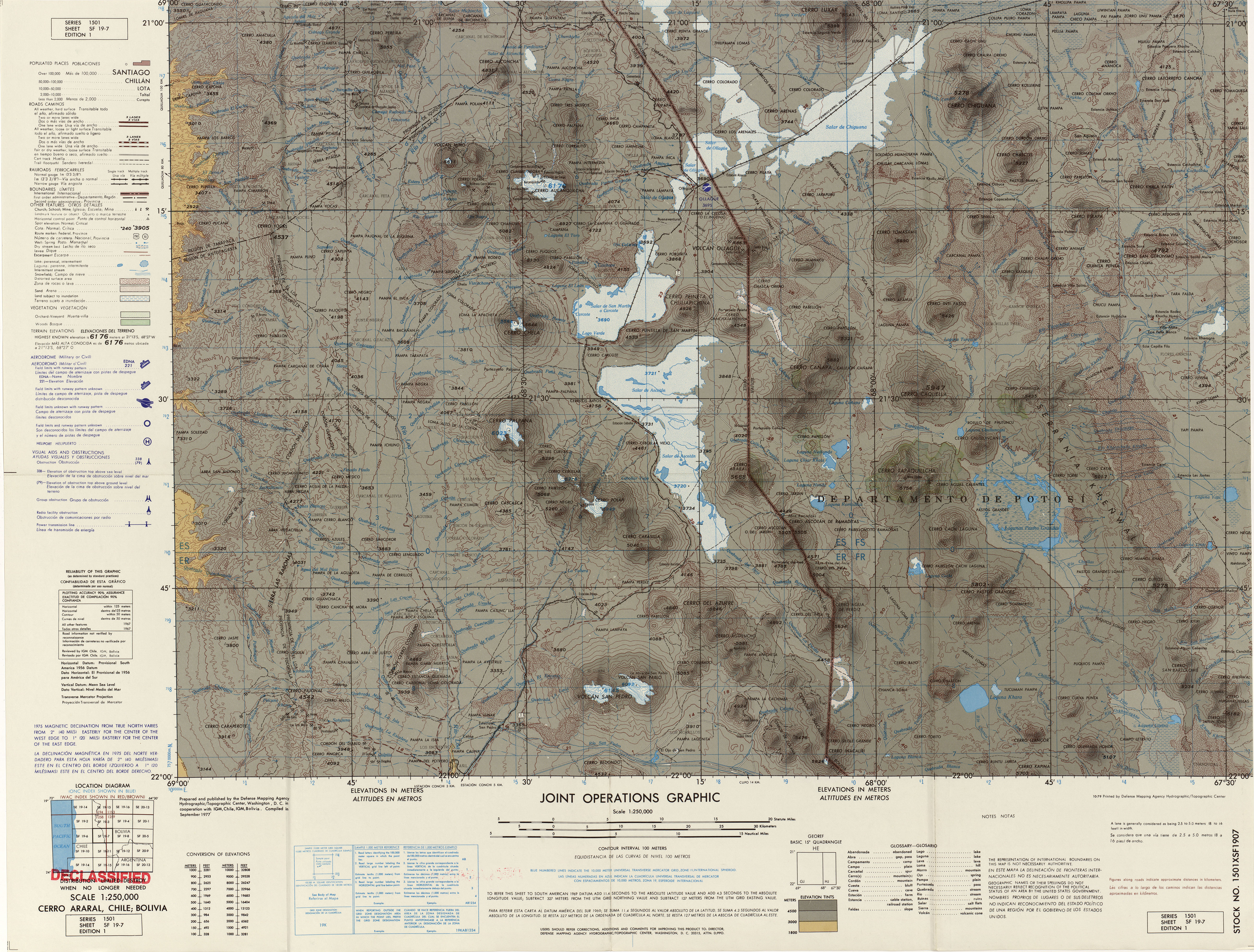
Bolivia–Chile Border
The Bolivia–Chile border is an international border of South America. It separates Bolivia from Chile along Cordillera Occidental on the western edge of the Altiplano Plateau. There is an ongoing dispute about the nature of Silala River and Chile's use of its waters. Since 2021 the Bolivia–Chile border has been a major point of entry of irregular Venezuelan migrants into Chile. Migrants are aided in the crossing by human smugglers. Irregular migration has been particularly troublesome for the Chilean border town of Colchane. Indigenous Aymara communities live on both sides of the border. References Chile Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ... Borders of Chile International borders Geography of Arica y Parinacota Region Geography of Tarapacá ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chungara (journal)
''Chungara Revista de Antropología Chilena'' (English: ''The Journal of Chilean Anthropology'') is a peer-reviewed academic journal on anthropology and archaeology with particular, but not exclusive, focus on the Andean region. The journal is published by the Departamento de Antropología (Universidad de Tarapacá) and the editor-in-chief is Vivien G. Standen (Universidad de Tarapacá). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the Social Sciences Citation Index, Current Contents/Social & Behavioral Sciences, and Scopus. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2014 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 0.694. References External links * Anthropology journals Multilingual journals Academic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ollagüe
Ollagüe () or Ullawi () is a massive andesite stratovolcano in the Andes on the border between Bolivia and Chile, within the Antofagasta Region of Chile and the Potosi Department of Bolivia. Part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes, its highest summit is above sea level and features a summit crater that opens to the south. The western rim of the summit crater is formed by a compound of lava domes, the youngest of which features a vigorous fumarole that is visible from afar. Ollagüe is mostly of Pleistocene age. It started developing more than one million years ago, forming the so-called Vinta Loma and Santa Rosa series mostly of andesitic lava flows. A fault bisects the edifice and two large landslides occurred in relation to it. Later two groups of dacitic lava domes formed, Ch'aska Urqu on the southeastern slope and La Celosa on the northwestern. Another centre named La Poruñita formed at that time on the western foot of the volcano, but it is not clear wheth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ollagüe Pass
Ollagüe () or Ullawi () is a massive andesite stratovolcano in the Andes on the border between Bolivia and Chile, within the Antofagasta Region of Chile and the Potosi Department of Bolivia. Part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes, its highest summit is above sea level and features a summit crater that opens to the south. The western rim of the summit crater is formed by a compound of lava domes, the youngest of which features a vigorous fumarole that is visible from afar. Ollagüe is mostly of Pleistocene age. It started developing more than one million years ago, forming the so-called Vinta Loma and Santa Rosa series mostly of andesitic lava flows. A fault bisects the edifice and two large landslides occurred in relation to it. Later two groups of dacitic lava domes formed, Ch'aska Urqu on the southeastern slope and La Celosa on the northwestern. Another centre named La Poruñita formed at that time on the western foot of the volcano, but it is not clear whether ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olca
Olca is a stratovolcano on the border of Chile and Bolivia. It lies in the middle of a 15 km long ridge composed of several stratovolcanos. Cerro Minchincha lies to the west and Paruma to the east. It is also close to the pre-Holocene Cerro Paruma. It is andesitic and dacitic in composition, with lava flows extending several kilometres north of the peak. The only activity from the ridge during historical times was a flank eruption from 1865 to 1867. The exact source of this eruption is unclear. Gas emissions and composition The gasses emission is comprised by a single warm spring at the base and a persistent fumarole field over at the crater's dome for at least 60 years. The fumarolic field is about 0.1 km2 and the emissions measured in situ at the crater show a highly mixed magmatic system between high temperature temperature gasses and hydrothermal fluids. The gas composition indicates low concentration of H2, CO and acidic gasses, and high concentration of H2S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sillajhuay
Sillajhuay (also known as Sillajguay or Alto Toroni) is a volcano on the border between Bolivia and Chile. It is part of a volcanic chain that stretches across the border between Bolivia and Chile and forms a mountain massif that is in part covered by ice; whether this ice should be considered a glacier is debatable but it has been retreating in recent decades. The volcano has developed on top of older ignimbrites. The volcano was active within the last one million years, but not within recent times considering the heavy glacial erosion of the mountain and the widespread periglacial modifications. Non-eruptive activity however occurs in the form of surface deformation and earthquake activity. Geography and geomorphology Sillajhuay is located in the Andes on the border between Bolivia and Chile ( commune of Pica-Colchane, Tarapaca Region) although only a small easterly sector of the mountain is located in Bolivia. The volcano lies in a thinly inhabited region; the towns of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isluga River
Isluga River is a river in Chile and Bolivia, and is also known as Sitani or Arabilla. It starts at the confluence of the rivers Chaguane and Huinchuta and flows for before reaching the Laguna Mucalliri of the Salar de Coipasa. It receives water from the volcanoes Isluga, Cabaray and Quimsachata as well as the Sierra Uscana. The watershed of the river lies mainly in Chile and has a dry climate, resulting in a small river discharge of about . There are a number of towns and hamlets in the catchment, as well as wetlands with a number of animal and plant species. Course The Isluga River (also known as Sitani or Arabilla) begins at the southern foot of the high Cerro Alpajeres west of the town of Chaguane at the confluence of the Chaguane and Huinchuta. In its upper parts the Isluga River is also known as the Arabilla River. The Chaguane is long and receives water from the Laguna Parinacota, which in turn is nourished from two creeks that join it from the west and north. The Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lauca River
The Lauca River is a binational river. It originates in the Chilean Altiplano of the Arica and Parinacota Region, crosses the Andes and empties into Coipasa Lake in Bolivia. The upper reach of the river lies within the boundaries of Lauca National Park in the Parinacota Province. Lauca River receives waters from a group of lakes known as Quta Qutani through the ''Desaguadero River''. In this area there is a type of marsh known as Parinacota wetlands, in which converge several streams, being the more important the river just mentioned, which has a variable flow rate ranging from 100 to 560 L/s, and an average of 260 L/s. From its source in the Parinacota wetlands the river flows west. The spurs of the ''Cordillera Central'' (also known as ''Chapiquiña'') form an obstacle impossible to pass through, forcing the river's course southward. In the vicinity of Wallatiri volcano, the Lauca turns again, now eastward crossing from Chile into Bolivia at the latitude of ''Macaya'', at an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kimsa Chata (Bolivia-Chile)
Kimsa Chata or Kimsachata (Aymara and Quechua ''kimsa'' three, Pukina ''chata'' mountain,Teofilo Laime Ajacopa, Lengua Pukina en Jesús de Machaca, referring to Alfredo Torero ("Reflexión acerca del pukina escrito por Alfredo Torero ... Pukina '''' - Castellano ''Cerro'' - Palabras relacionadas en aymara ''Qullu''") (English: mountain). ... Existencia de palabras pukinas en Jesús de Machaca: Qullunaka (cerros): ''Kimsa Chata'' "three mountains", Hispanicized ''Quimsa Chata, Quimsachata'') is an -long volcanic complex on a north–south alignment along the border between Bolivia and Chile, overseeing Chungara Lake. It contains three peaks, all stratovolcanoes. The group is formed - from north to south - by Umurata (), Acotango () and Capurata () (also known as Cerro Elena Capurata). The active volcano Guallatiri (Wallatiri) west of Capurata is not part of the group. See also * List of volcanoes in Bolivia * List of volcanoes in Chile The Smithsonian Institution's Glob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acotango
Acotango is the central and highest of a group of stratovolcanoes straddling the border of Bolivia and Chile. It is high. The group is known as Kimsa Chata and consists of three mountains: Acotango, Umurata () north of it and Capurata () south of it. The group lies along a north–south alignment. The Acotango volcano is heavily eroded, but a lava flow on its northern flank is morphologically young, suggesting Acotango was active in the Holocene. Later research has suggested that lava flow may be of Pleistocene age. Argon-argon dating has yielded ages of 192,000±8,000 and 241,000±27,000 years on dacites from Acotango. Glacial activity has exposed parts of the inner volcano, which is hydrothermally altered. Glacial moraines lie at an altitude of but a present ice cap is only found past of altitude. The volcano is a popular hiking route in the Sajama National Park and Lauca National Park. It is on the border of two provinces: Chilean province of Parinacota and Bolivian provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chungara–Tambo Quemado
Chungara–Tambo Quemado ( es, Paso Chungara–Tambo Quemado) is a mountain pass through the Cordillera Occidental of the Andes along the border between Chile and Bolivia. Chungara–Tambo Quemado is one of the principal Chile-Bolivia passes in the central Andes as it connects La Paz with its nearest seaport Arica Arica ( ; ) is a commune and a port city with a population of 222,619 in the Arica Province of northern Chile's Arica y Parinacota Region. It is Chile's northernmost city, being located only south of the border with Peru. The city is the capita .... See also * K'isi K'isini * Sura K'uchu * Uqi Uqini {{DEFAULTSORT:Chungara-Tambo Quemado Mountain passes of Chile Mountain passes of Bolivia Mountain passes of the Andes Bolivia–Chile border crossings Landforms of Arica y Parinacota Region Landforms of Oruro Department ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parinacota (volcano)
Parinacota (in Hispanicized spelling), Parina Quta or Parinaquta is a dormant stratovolcano on the border of Chile and Bolivia. Together with Pomerape it forms the Nevados de payachata, Nevados de Payachata volcanic chain. Part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes, its summit reaches an elevation of above sea level. The symmetrical cone is capped by a summit crater with widths of or . Farther down on the southern slopes lie three Parasitic vents, parasitic centres known as the Ajata cones. These cones have generated lava flows. The volcano overlies a platform formed by lava domes and Andesite, andesitic lava flows. The volcano started growing during the Pleistocene and formed a large cone. At some point between the Pleistocene and the Holocene, the western flank of the volcano collapsed, generating a giant landslide that spread west and formed a large, hummocky landslide deposit. The avalanche crossed and dammed a previously existing drainage, impounding or enlarging Chun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |