|
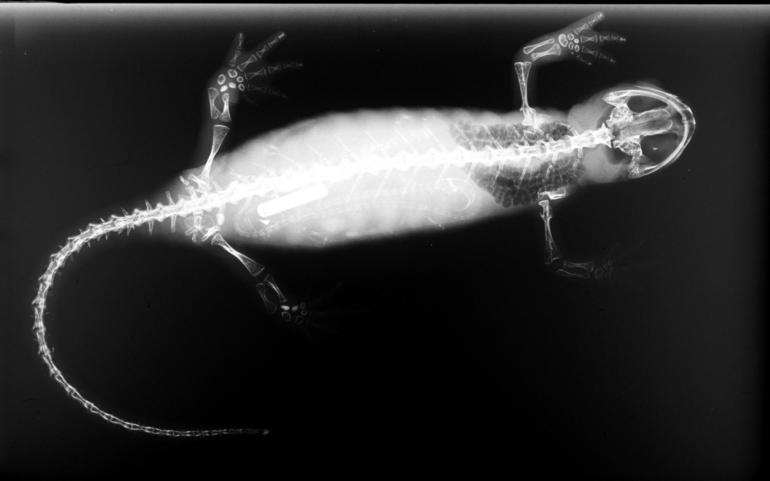
Bolitoglossa Bramei
Brame's climbing salamander (''Bolitoglossa bramei'') is a species of salamander in the family Plethodontidae. It is found in Costa Rica and Panama, particularly the Pacific and Atlantic slopes of Cordillera de Talamanca and ranging to Cerro Pando, Chiriquí Province and Volcán Barú. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist lowland forest A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...s and has been recorded between 1,900 and 2,300 meters above sea level. It has not been commonly recorded so nothing is known about its population. No threats are known and its habitat is currently under protection by Las Tablas protected area and Reserva de la Biósfera de La Amistad. References * IUCN SSC Amphibian Specialist Group. 2020.Bolitoglossa biseriata Downloaded on 23 Dece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salamander
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All ten extant salamander families are grouped together under the order Urodela. Salamander diversity is highest in eastern North America, especially in the Appalachian Mountains; most species are found in the Holarctic realm, with some species present in the Neotropical realm. Salamanders rarely have more than four toes on their front legs and five on their rear legs, but some species have fewer digits and others lack hind limbs. Their permeable skin usually makes them reliant on habitats in or near water or other cool, damp places. Some salamander species are fully aquatic throughout their lives, some take to the water intermittently, and others are entirely terrestrial as adults. This group of amphibians is capable of regenerating lost lim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plethodontidae
Plethodontidae, or lungless salamanders, are a family of salamanders. Most species are native to the Western Hemisphere, from British Columbia to Brazil, although a few species are found in Sardinia, Europe south of the Alps, and South Korea. In terms of number of species, they are by far the largest group of salamanders. Biology Adult lungless salamanders have four limbs, with four toes on the fore limbs, and usually with five on the hind limbs. Within many species, mating and reproduction occur solely on land. Accordingly, many species also lack an aquatic larval stage, a phenomenon known as direct development in which the offspring hatch as fully-formed, miniature adults. Direct development is correlated with changes in the developmental characteristics of plethodontids compared to other families of salamanders including increases in egg size and duration of embryonic development. Additionally, the evolutionary loss of the aquatic larval stage is related to a diminishing dep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cordillera De Talamanca
The Cordillera de Talamanca is a mountain range that lies in the southeast half of Costa Rica and the far west of Panama. Much of the range and the area around it is included in La Amistad International Park, which also is shared between the two countries. This range in the south of Costa Rica stretches from southwest of San José to beyond the border with Panama and contains the highest peaks of both Costa Rica and Panama, among them Cerro Chirripó at 3,820 m, and the more accessible high peak of Cerro de la Muerte. Much of the Caribbean areas of the range are still unexplored. Exploration and classification The range is covered by the Talamancan montane forests to elevations of approximately 3,000 m. Much of it is covered by rainforests. Above elevations of 1,800 m these are dominated by huge oak trees (''Quercus costaricensis''). Above 3,000 m, the forests transition to enclaves of sub-páramo, a sort of shrub and dwarf bamboo '' Chusquea'' dominated scrub, above 3,400 m t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiriquí Province
Chiriquí () is a province of Panama located on the western coast; it is the second most developed province in the country, after the Panamá Province. Its capital is the city of David. It has a total area of 6,490.9 km², with a population of 462,056 as of the year 2019. The province of Chiriquí is bordered to the north by the province of Bocas del Toro, to the west by Costa Rica, to the east by the province of Veraguas, and to the south by the Pacific Ocean, specifically the Gulf of Chiriquí. History Until the arrival of the Spanish ''conquistadores'', Chiriquí was populated by a number of indigenous tribes, known collectively as the Guaymí people. The first European to visit and describe Chiriquí was Gaspar de Espinosa, in 1519. The province was officially established on May 26, 1849, when Panama was still part of Colombia. Several years later, President Abraham Lincoln of the United States proposed Chiriquí as a favored location for Linconia, a colony for free ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcán Barú
The Volcán Barú (also Volcán de Chiriquí) is an active stratovolcano and the tallest mountain in Panama, at high. It lies about off the border of Costa Rica. It is also the twelfth highest peak in Central America. Due to its height and the narrowness of the isthmus of Panama, it is possible (though relatively rare) to see both the Pacific Ocean and Caribbean Sea from Volcán Barú's peak on a clear day. Geography The small town of Volcán at the base of Volcán Barú sits on the remnants of a huge lahar that appears to have breached the caldera. A small river has eroded the lahar exposing an ancient forest below dated to about 1000 years old. Volcán Barú is surrounded by a fertile area of cool highlands drained by the Chiriquí Viejo and Caldera Rivers. The towns of Volcán and Cerro Punta can be found on its western side, while Boquete is on the eastern flank. The occasional fall of hail or ice pellets has been reported on the summit, where the minimum temperature c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ecological niche. Thus "habitat" is a species-specific term, fundamentally different from concepts such as environment or vegetation assemblages, for which the term "habitat-type" is more appropriate. The physical factors may include (for example): soil, moisture, range of temperature, and light intensity. Biotic factors will include the availability of food and the presence or absence of predators. Every species has particular habitat requirements, with habitat generalist species able to thrive in a wide array of environmental conditions while habitat specialist species requiring a very limited set of factors to survive. The habitat of a species is not necessarily found in a geographical area, it can be the interior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) defines a forest as, "Land spanning more than 0.5 hectares with trees higher than 5 meters and a canopy cover of more than 10 percent, or trees able to reach these thresholds ''in situ''. It does not include land that is predominantly under agricultural or urban use." Using this definition, '' Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020'' (FRA 2020) found that forests covered , or approximately 31 percent of the world's land area in 2020. Forests are the predominant terrestrial ecosystem of Earth, and are found around the globe. More than half of the world's forests are found in only five countries (Brazil, Canada, China, Russia, and the United States). The largest share of forests (45 percent) are in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolitoglossa
''Bolitoglossa'' is a genus of lungless salamanders, also called mushroom-tongued salamanders, tropical climbing salamanders, or web-footed salamanders, in the family Plethodontidae. Their range is between northern Mexico through Central America to Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru, northeastern Brazil, and central Bolivia. Neotropical salamanders of the ''Bolitoglossa'' make up the largest genus in the order Caudata, consisting of approximately one-fifth of all known species of salamanders. Adult salamanders range anywhere from 45mm to 200mm in length depending on their specific species. They are notorious for their ability to project their tongue at prey items, as indicated from their name. They are also known for their webbed feet, having significantly more webbing than any other species outside their genus with the exception of the cave-dwelling Mexican bolitoglossine ''Chiropterotriton magnipes''. Although webbed feet are a common characteristic of these salamanders, only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |