|
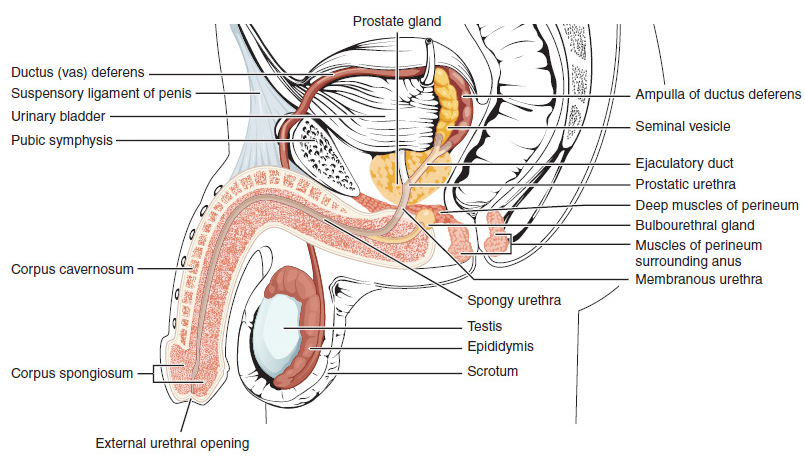
Body Of Penis
The corpus, also body or shaft of the penis, is the free portion of the human penis that is located outside of the pelvic cavity. It is the continuation of the internal root or ''radix'' which is embedded in the pelvis and extends to the glans behind which lies the ''neck'' of the penis. It is made up of the two corpora cavernosa and the corpus spongiosum on the underside. The corpora cavernosa are intimately bound to one another with a dorsally fenestrated septum which becomes a complete one before the penile crura. Anatomy The corpus of the penis is suspended from the pubic symphysis. As the extension of the root, it is made up of three cylindrical bodies; the corpora cavernosa and the corpus spongiosum which are continuations of the crura and the bulb of the penis respectively. It has two surfaces; the ''dorsal'' and the ventral or ''urethral''. The penile raphe runs on its ventral surface. The corpus is surrounded by a bi-layered model of tunica albuginea in which a dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Penis
The human penis is an external male intromittent organ that additionally serves as the urinary duct. The main parts are the root (radix); the body (corpus); and the epithelium of the penis including the shaft skin and the foreskin (prepuce) covering the glans penis. The body of the penis is made up of three columns of tissue: two corpora cavernosa on the dorsal side and corpus spongiosum between them on the ventral side. The human male urethra passes through the prostate gland, where it is joined by the ejaculatory duct, and then through the penis. The urethra traverses the corpus spongiosum, and its opening, the meatus (), lies on the tip of the glans penis. It is a passage both for urination and ejaculation of semen (''see'' male reproductive system.) Most of the penis develops from the same embryonic tissue as the clitoris in females. The skin around the penis and the urethra share the same embryonic origin as the labia minora in females. An erection is the stiffening e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penile Raphe
The penile raphe is a visible line or ridge of tissue that runs on the ventral side of the human penis beginning from the base of the shaft and ending in the prepuce. The line is typically darker than the rest of the shaft skin, even though its shape and pigmentation may vary among males. The penile raphe is part of a broader line in the male reproductive organs, that runs from the anus through the perineum (perineal raphe) and continues to the scrotum and penis, collectively referred to as median raphe. The line consists of a subcutaneous fibrous plate, which may vary in prominence and thickness in various areas of the genitals. In the scrotum, the line is located over the internal scrotal septum that divides the two sides of the sac and is densely occupied by nerve fibers. The raphe may become more prominent and darker when the scrotal sac tightens due to contractions. Behind the scrotum it continues as the perineal raphe. The raphe results as a manifestation of the fusion of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided into two layers, the superficial area adjacent to the epidermis called the papillary region and a deep thicker area known as the reticular dermis.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology'' (10th ed.). Saunders. Pages 1, 11–12. . The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis through a basement membrane. Structural components of the dermis are collagen, elastic fibers, and extrafibrillar matrix.Marks, James G; Miller, Jeffery (2006). ''Lookingbill and Marks' Principles of Dermatology'' (4th ed.). Elsevier Inc. Page 8–9. . It also contains mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and thermoreceptors that provide the sense of heat. In addition, hair follicles, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buck's Fascia
Buck's fascia (deep fascia of the penis, Gallaudet's fascia or fascia of the penis) is a layer of deep fascia covering the three erectile bodies of the penis. Structure Buck's fascia is continuous with the external spermatic fascia in the scrotum and the suspensory ligament of the penis. On its ventral aspect, it splits to envelop corpus spongiosum in a separate compartment from the tunica albuginea and corporal bodies. Variation Sources differ on its proximal extent. Some state that it is a ''continuation'' of the deep perineal fascia, whereas others state that it fuses with the tunica albuginea. Function The deep dorsal vein of the penis, the cavernosal veins of the penis, and the para-arterial veins of the penis are inside Buck's fascia, but the superficial dorsal veins of the penis are in the superficial (dartos) fascia immediately under the skin. History Etymology The name Buck's fascia is named after Gurdon Buck, an American plastic surgeon. Additional images ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fascia
A fascia (; plural fasciae or fascias; adjective fascial; from Latin: "band") is a band or sheet of connective tissue, primarily collagen, beneath the skin that attaches to, stabilizes, encloses, and separates muscles and other internal organs. Fascia is classified by layer, as superficial fascia, deep fascia, and ''visceral'' or ''parietal'' fascia, or by its function and anatomical location. Like ligaments, aponeuroses, and tendons, fascia is made up of fibrous connective tissue containing closely packed bundles of collagen fibers oriented in a wavy pattern parallel to the direction of pull. Fascia is consequently flexible and able to resist great unidirectional tension forces until the wavy pattern of fibers has been straightened out by the pulling force. These collagen fibers are produced by fibroblasts located within the fascia. Fasciae are similar to ligaments and tendons as they have collagen as their major component. They differ in their location and function: ligament ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Dorsal Vein Of The Penis
Deep or The Deep may refer to: Places United States * Deep Creek (Appomattox River tributary), Virginia * Deep Creek (Great Salt Lake), Idaho and Utah * Deep Creek (Mahantango Creek tributary), Pennsylvania * Deep Creek (Mojave River tributary), California * Deep Creek (Pine Creek tributary), Pennsylvania * Deep Creek (Soque River tributary), Georgia * Deep Creek (Texas), a tributary of the Colorado River * Deep Creek (Washington), a tributary of the Spokane River * Deep River (Indiana), a tributary of the Little Calumet River * Deep River (Iowa), a minor tributary of the English River * Deep River (North Carolina) * Deep River (Washington), a minor tributary of the Columbia River * Deep Voll Brook, New Jersey, also known as Deep Brook Elsewhere * Deep Creek (Bahamas) * Deep Creek (Melbourne, Victoria), Australia, a tributary of the Maribyrnong River * Deep River (Western Australia) People * Deep (given name) * Deep (rapper), Punjabi rapper from Houston, Texas * Ravi Deep (b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erection
An erection (clinically: penile erection or penile tumescence) is a physiological phenomenon in which the penis becomes firm, engorged, and enlarged. Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, vascular, and endocrine factors, and is often associated with sexual arousal or sexual attraction, although erections can also be spontaneous. The shape, angle, and direction of an erection varies considerably between humans. Physiologically, an erection is required for a male to effect vaginal penetration or sexual intercourse and is triggered by the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system, causing the levels of nitric oxide (a vasodilator) to rise in the trabecular arteries and smooth muscle of the penis. The arteries dilate causing the corpora cavernosa of the penis (and to a lesser extent the corpus spongiosum) to fill with blood; simultaneously the ischiocavernosus and bulbospongiosus muscles compress the veins of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baculum
The baculum (also penis bone, penile bone, or ''os penis'', ''os genitale'' or ''os priapi'') is a bone found in the penis of many placental mammals. It is absent from the human penis, but present in the penises of some primates, such as the gorilla and chimpanzee. The os penis arises from primordial cells within soft tissues of the penis, and its formation is largely under the influence of androgens. The bone is located above the male urethra, and it aids sexual reproduction by maintaining sufficient stiffness during sexual penetration. The homologue to the baculum in female mammals is known as the baubellum or ''os clitoridis'' (also ''os clitoris''), a bone in the clitoris. Etymology The word ''baculum'' meant "stick" or "staff" in Latin and originated from el, βάκλον, ''baklon'' "stick". Function The baculum is used for copulation and varies in size and shape by species. Its evolution may be influenced by sexual selection, and its characteristics are sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geng Long Hsu
Geng Long Hsu () is a Taiwanese urologic surgeon and former clinical professor at China Medical University. He earned his MD from National Taiwan University in 1985 and completed his research fellowship from the University of California San Francisco in 1991. He held the position of Chair of Urology at Taiwan Adventist Hospital, vice-superintendent at Po-Jen General hospital, and director of microsurgery potency reconstruction at Taipei Medical University. After 2003, he established his private practice at Hsu's Andrology in Taipei, Taiwan. Hsu documents and shares his clinical experience on penile reconstruction, particularly of penile venous stripping, penile curvature correction, and penile enhancement via various academic channels. That includes his contributions to the Encyclopedia of Reproduction. He was awarded the Jean-Paul Ginestie Prize (1992) for the discovery of the three-dimensional structure of the tunica albuginea. In 2010, he was awarded the second prize on C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunica Albuginea (penis)
The tunica albuginea is the fibrous envelope that extends the length of the corpora cavernosa penis (containing erectile tissue) and corpus spongiosum penis (containing the male urethra). It is a bi-layered structure that includes an outer longitudinal layer and an inner circular layer. It consists of approximately 5% elastin, with the remainder mostly consisting of collagen. The tunica albuginea is directly involved in maintaining an erection; that is due to Buck's fascia constricting the erection veins of the penis, preventing blood from leaving and thus sustaining the erect state. The erection veins include the deep dorsal vein, two cavernosal veins, and four para-arterial veins. The trabeculae of the tunica albuginea are more delicate, nearly uniform in size, and the meshes between them smaller than in the corpora cavernosa penis: their long diameters, for the most part, corresponding with that of the penis. The external envelope or outer coat of the corpus spongiosum is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventral
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek language, Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axis, anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvic Cavity
The pelvic cavity is a body cavity that is bounded by the bones of the pelvis. Its oblique roof is the pelvic inlet (the superior opening of the pelvis). Its lower boundary is the pelvic floor. The pelvic cavity primarily contains the reproductive organs, urinary bladder, distal ureters, proximal urethra, terminal sigmoid colon, rectum, and anal canal. In females, the uterus, Fallopian tubes, ovaries and upper vagina occupy the area between the other viscera. The rectum is located at the back of the pelvis, in the curve of the sacrum and coccyx; the bladder is in front, behind the pubic symphysis. The pelvic cavity also contains major arteries, veins, muscles, and nerves. These structures coexist in a crowded space, and disorders of one pelvic component may impact upon another; for example, constipation may overload the rectum and compress the urinary bladder, or childbirth might damage the pudendal nerves and later lead to anal weakness. Structure The pelvis has an antero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |