|
Boanthropy
Boanthropy is a psychological disorder in which a human believes themselves to be a bovine. Biblical account King Nebuchadnezzar II of the Neo-Babylonian Empire is sometimes attributed with boanthropy based on the description in the Book of Daniel which says that he "was driven from men, and did eat grass as oxen". Carl Jung would subsequently describe 'Nebuchadnezzar... sa complete regressive degeneration of a man who has overreached himself'. Historical accounts According to Persian traditions, the Buyid prince Majd al-Dawla has a delusion that he is a cow, making the sound of a cow and asking that to be killed so that his flesh could be consumed. He was cured by Avicenna. Psychological explanations Psychologists generally group Boanthropy, along with other forms of zoanthropy, into the diagnosis of Clinical lycanthropy. Other conditions frequently, but not universally, found in patients include schizophrenia, psychotic depression, and bipolar disorder. It has been sugg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical Lycanthropy
Clinical lycanthropy is a rare psychiatric syndrome that involves a delusion that the affected person can transform into, has transformed into, or is, an animal. Its name is associated with the mythical condition of lycanthropy, a supernatural affliction in which humans are said to physically shapeshift into wolves. It is purported to be a rare disorder. Signs and symptoms Affected individuals believe that they are in the process of transforming into an animal or have already transformed into an animal. It has been associated with the altered states of mind that accompany psychosis (the mental state that typically involves delusions and hallucinations) with the transformation only seeming to happen in the mind and behavior of the affected person. A study on clinical lycanthropy from the McLean Hospital reported on a series of cases and proposed some diagnostic criteria by which clinical lycanthropy could be recognised: * A patient reports in a moment of lucidity or reminis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Cow (1969 Film)
''The Cow'' ( fa, گاو, ''Gāv'' or ''Gav'') is a 1969 Iranian film directed by Dariush Mehrjui, written by Gholam-Hossein Saedi based on his own play and novel, and starring Ezzatolah Entezami as Masht Hassan. Some critics consider it the first film of the Iranian New Wave. Plot The story begins by showcasing the close relationship between a middle-aged Iranian villager Masht Hassan and his beloved cow. Hassan is married but has no children. His only valuable property is a cow that he cherishes as the only cow in the village. When Hassan must leave the village for a short time, the pregnant cow is found dead in the barn. Hassan's fellow villagers fear his reaction and cover up the evidence of the death and tell him upon his return that his cow has run away. Finding great difficulty confronting the loss of his beloved cow, as well the loss of livestock that affects his social stature at the village, Hassan gradually goes insane following a nervous breakdown and believes he is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychological Disorder
A mental disorder, also referred to as a mental illness or psychiatric disorder, is a behavioral or mental pattern that causes significant distress or impairment of personal functioning. Such features may be persistent, relapsing and remitting, or occur as single episodes. Many disorders have been described, with signs and symptoms that vary widely between specific disorders. Such disorders may be diagnosed by a mental health professional, usually a clinical psychologist or psychiatrist. The causes of mental disorders are often unclear. Theories may incorporate findings from a range of fields. Mental disorders are usually defined by a combination of how a person behaves, feels, perceives, or thinks. This may be associated with particular regions or functions of the brain, often in a social context. A mental disorder is one aspect of mental health. Cultural and religious beliefs, as well as social norms, should be taken into account when making a diagnosis. Services are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypnosis
Hypnosis is a human condition involving focused attention (the selective attention/selective inattention hypothesis, SASI), reduced peripheral awareness, and an enhanced capacity to respond to suggestion.In 2015, the American Psychological Association Division 30 defined hypnosis as a "state of consciousness involving focused attention and reduced peripheral awareness characterized by an enhanced capacity for response to suggestion". For critical commentary on this definition, see: There are competing theories explaining hypnosis and related phenomena. ''Altered state'' theories see hypnosis as an altered state of mind or trance, marked by a level of awareness different from the ordinary Consciousness, state of consciousness. In contrast, ''non-state'' theories see hypnosis as, variously, a type of placebo effect,Kirsch, I., "Clinical Hypnosis as a Nondeceptive Placebo", pp. 211–25 in Kirsch, I., Capafons, A., Cardeña-Buelna, E., Amigó, S. (eds.), ''Clinical Hypnosis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranian Cinema
The Cinema of Iran (Persian: سینمای ایران), also known as the Cinema of Persia, refers to the cinema and film industries in Iran which produce a variety of commercial films annually. Iranian art films have garnered international fame and now enjoy a global following. Iranian films are usually written and spoken in the Persian language. Iranian cinema has had many ups and downs. Along with China, Iran has been lauded as one of the best exporters of cinema in the 1990s. Some critics now rank Iran as the world's most important national cinema, artistically, with a significance that invites comparison to Italian neorealism and similar movements in past decades. A range of international film festivals have honoured Iranian cinema in the last twenty years. Many film critics from around the world have praised Iranian cinema as one of the world's most important artistic cinemas. History Visual arts in Iran The earliest examples of visual representations in Iranian history ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
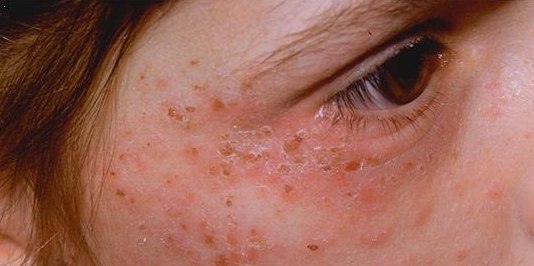
Syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms of syphilis vary depending in which of the four stages it presents (primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary). The primary stage classically presents with a single chancre (a firm, painless, non-itchy skin ulceration usually between 1 cm and 2 cm in diameter) though there may be multiple sores. In secondary syphilis, a diffuse rash occurs, which frequently involves the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There may also be sores in the mouth or vagina. In latent syphilis, which can last for years, there are few or no symptoms. In tertiary syphilis, there are gummas (soft, non-cancerous growths), neurological problems, or heart symptoms. Syphilis has been known as "the great imitator" as it may cause symptoms similar to many other diseases. Syphilis is most commonly spread through sexual activity. It may also be transmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Paresis Of The Insane
General paresis, also known as general paralysis of the insane (GPI), paralytic dementia, or syphilitic paresis is a severe neuropsychiatric disorder, classified as an organic mental disorder and is caused by late-stage syphilis and the chronic meningoencephalitis and cerebral atrophy that are associated with this late stage of the disease when left untreated. GPI differs from mere paresis, as mere paresis can result from multiple other causes and usually does not affect cognitive function. Degenerative changes caused by GPI are associated primarily with the frontal and temporal lobar cortex. The disease affects approximately 7% of individuals infected with syphilis, and is far more common in third world countries where fewer options for timely treatment are available. It is more common among men. GPI was originally considered to be a type of madness due to a dissolute character, when first identified in the early 19th century. The condition's connection with syphilis was dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyria
Porphyria is a group of liver disorders in which substances called porphyrins build up in the body, negatively affecting the skin or nervous system. The types that affect the nervous system are also known as acute porphyria, as symptoms are rapid in onset and short in duration. Symptoms of an attack include abdominal pain, chest pain, vomiting, confusion, constipation, fever, high blood pressure, and high heart rate. The attacks usually last for days to weeks. Complications may include paralysis, low blood sodium levels, and seizures. Attacks may be triggered by alcohol, smoking, hormonal changes, fasting, stress, or certain medications. If the skin is affected, blisters or itching may occur with sunlight exposure. Most types of porphyria are inherited from one or both of a person's parents and are due to a mutation in one of the genes that make heme. They may be inherited in an autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, or X-linked dominant manner. One type, ''porphyria c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution of higher learning on the European continent. Along with his teacher, Socrates, and his student, Aristotle, Plato is a central figure in the history of Ancient Greek philosophy and the Western and Middle Eastern philosophies descended from it. He has also shaped religion and spirituality. The so-called neoplatonism of his interpreter Plotinus greatly influenced both Christianity (through Church Fathers such as Augustine) and Islamic philosophy (through e.g. Al-Farabi). In modern times, Friedrich Nietzsche diagnosed Western culture as growing in the shadow of Plato (famously calling Christianity "Platonism for the masses"), while Alfred North Whitehead famously said: "the safest general characterization of the European philosophical tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Totem
A totem (from oj, ᑑᑌᒼ, italics=no or ''doodem'') is a spirit being, sacred object, or symbol that serves as an emblem of a group of people, such as a family, clan, lineage, or tribe, such as in the Anishinaabe clan system. While ''the word'' totem itself is an anglicisation of the Ojibwe term (and both the word and beliefs associated with it are part of the Ojibwe language and culture), belief in tutelary spirits and deities is not limited to the Ojibwe people. Similar concepts, under differing names and with variations in beliefs and practices, may be found in a number of cultures worldwide. The term has also been adopted, and at times redefined, by anthropologists and philosophers of different cultures. Contemporary neoshamanic, New Age, and mythopoetic men's movements not otherwise involved in the practice of a traditional, tribal religion have been known to use "totem" terminology for the personal identification with a tutelary spirit or spirit guide. However, this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eric Berne
Eric Berne (May 10, 1910 – July 15, 1970) was a Canadian-born psychiatrist who created the theory of transactional analysis as a way of explaining human behavior. Berne's theory of transactional analysis was based on the ideas of Freud but was distinctly different. Freudian psychotherapists focused on talk therapy as a way of gaining insight to their patient's personalities. Berne believed that insight could be better discovered by analyzing patients’ social transactions. Background and education (1927–1938) Eric Berne was born on May 10, 1910, in Montreal, Quebec, Canada, as Eric Lennard Bernstein. He was the son of David Hillel Bernstein, MD, a general practitioner, and Sarah Gordon Bernstein, a professional writer and editor. His only sibling, his sister Grace, was born five years later. The family immigrated to Canada from Poland and Russia. Both parents graduated from McGill University in Montreal. Eric was close to his father and spoke fondly of how he accompani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Politics Of Experience
''The Politics of Experience and The Bird of Paradise'' is a 1967 book by the Scottish psychiatrist R. D. Laing. The book comprises two parts - the first a collection of seven articles previously published between 1962 and 1965; the second a free-flowing quasi-autobiographical piece of poetry and prose. Background ''The Politics of Experience and The Bird of Paradise'' was inspired in part by Laing’s extensive experimentation with LSD;Tom Burns (2006). ''Psychiatry: A Very Short Introduction'', Oxford University Press, pp. 96-98. but also owes a debt to authors such as the anthropologist Gregory Bateson and the philosopher Jean-Paul Sartre. Summary Laing examines the nature of human experience from a phenomenological point of view, as well as the possibilities for psychotherapy in an existentially distorted world. He challenges the idea of normality in modern society, and argues that it is not merely people who are mad, but the world as well. He presents psychosis as "a psych ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |