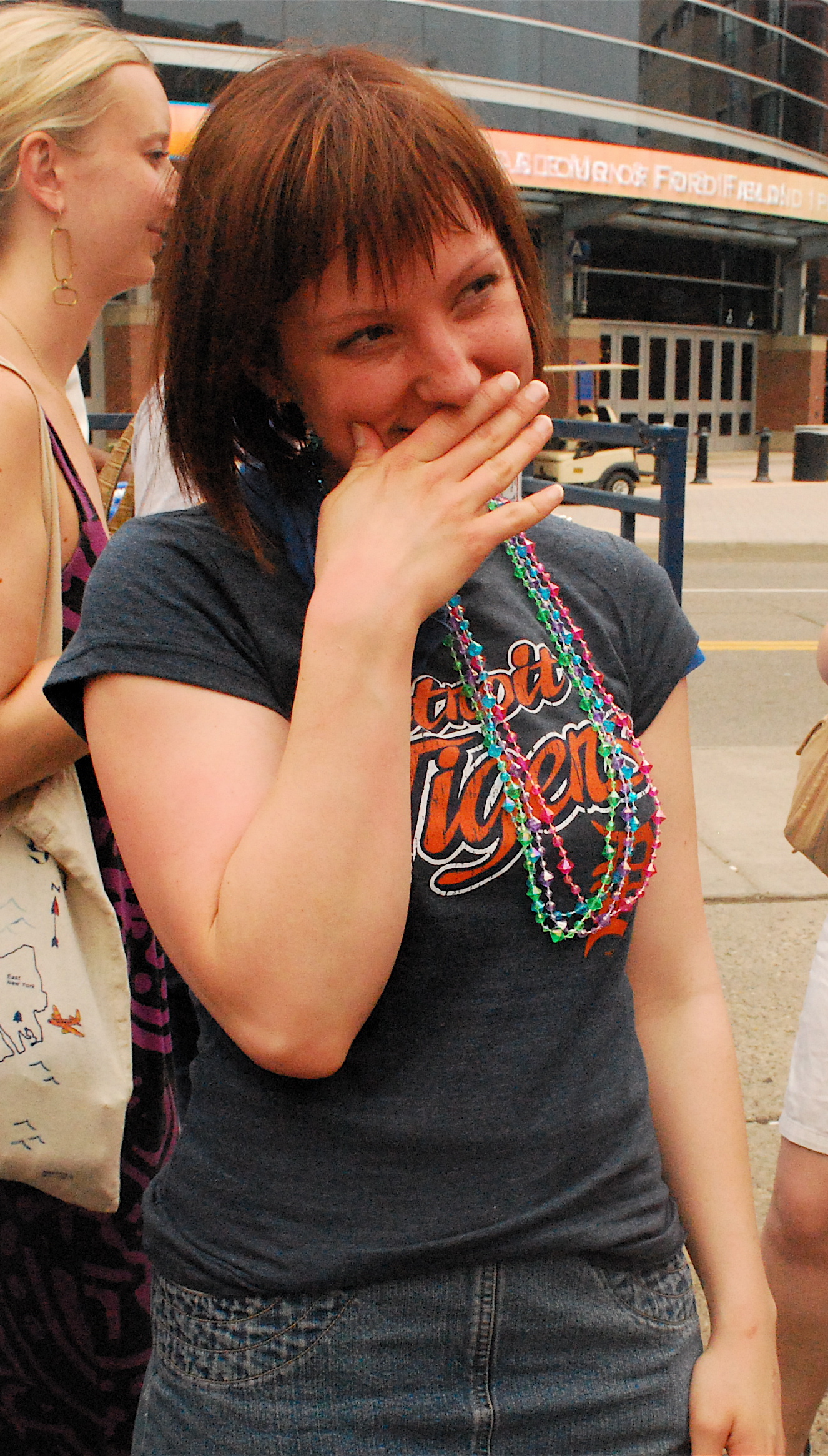|
Blushing Katy
Blushing is the reddening of a person's face due to psychological reasons. It is normally involuntary and triggered by emotional stress associated with passion, embarrassment, shyness, fear, anger, or romantic stimulation. Severe blushing is common in people who have social anxiety in which the person experiences extreme and persistent anxiety in social and performance situations. Summary Blushing is generally distinguished, despite a close physiological relation, from flushing, which is more intensive and extends over more of the body, and seldom has a mental source. If redness persists for abnormal amounts of time after blushing, then it may be considered an early sign of rosacea. Idiopathic craniofacial erythema is a medical condition where a person blushes strongly with little or no provocation. Just about any situation can bring on intense blushing and it may take one or two minutes for the blush to disappear. Severe blushing can make it difficult for the person to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blushing Girl 0001
Blushing is the reddening of a person's face due to Psychology, psychological reasons. It is normally involuntary and triggered by emotional Stress (biology), stress associated with Passion (emotion), passion, embarrassment, shyness, fear, anger, or Lovestruck, romantic stimulation. Severe blushing is common in people who have social anxiety in which the person experiences extreme and persistent anxiety in social and performance situations. Summary Blushing is generally distinguished, despite a close physiological relation, from Flushing (physiology), flushing, which is more intensive and extends over more of the body, and seldom has a mental source. If redness persists for abnormal amounts of time after blushing, then it may be considered an early sign of rosacea. Idiopathic craniofacial erythema is a medical condition where a person blushes strongly with little or no provocation. Just about any situation can bring on intense blushing and it may take one or two minutes for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
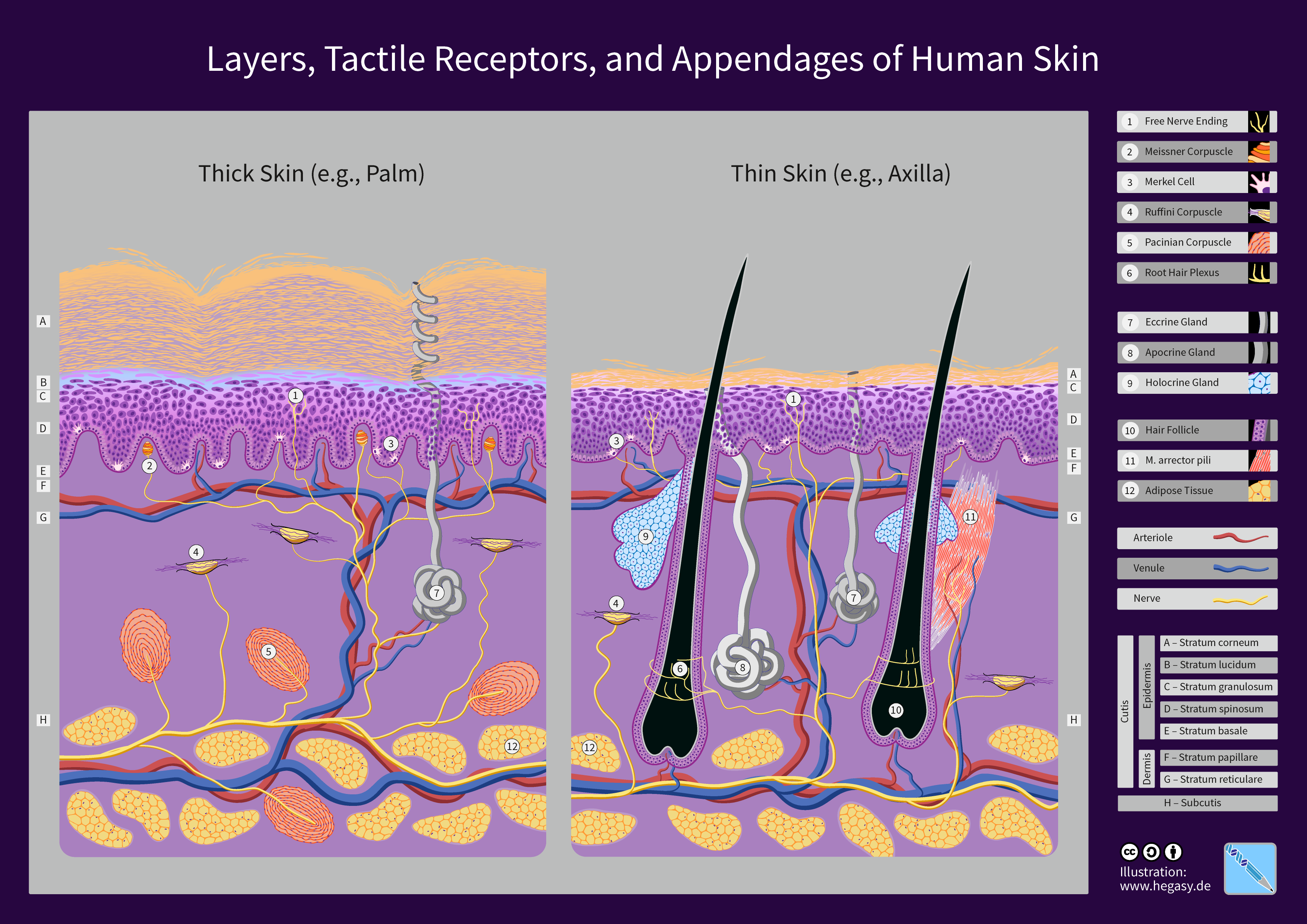
Human Skin
The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue guarding muscles, bones, ligaments and internal organs. Human skin is similar to most of the other mammals' skin, and it is very similar to pig skin. Though nearly all human skin is covered with hair follicles, it can appear hairless. There are two general types of skin, hairy and glabrous skin (hairless). The adjective ''cutaneous'' literally means "of the skin" (from Latin ''cutis'', skin). Because it interfaces with the environment, skin plays an important immunity role in protecting the body against pathogens and excessive water loss. Its other functions are insulation, temperature regulation, sensation, synthesis of vitamin D, and the protection of vitamin B folates. Severely damaged skin will try to heal by forming scar tissue. This is often discoloured and depigmented. In humans, skin pigmentation (affected b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
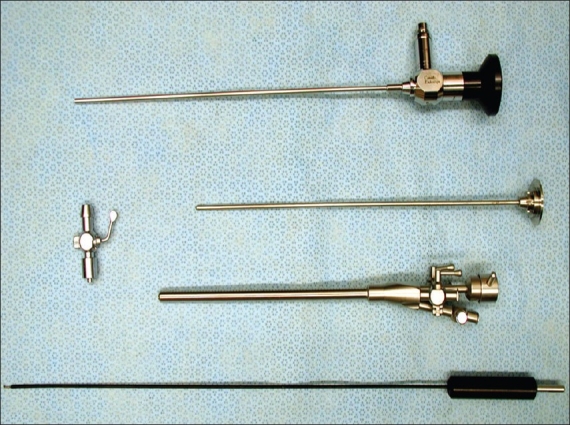
Endoscopic Thoracic Sympathectomy
Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy (ETS) is a surgical procedure in which a portion of the sympathetic nerve trunk in the thoracic region is destroyed. ETS is used to treat excessive sweating in certain parts of the body (focal hyperhidrosis), facial blushing, Raynaud's disease and reflex sympathetic dystrophy. By far the most common complaint treated with ETS is sweaty palms ( palmar hyperhidrosis). The intervention is controversial and illegal in some jurisdictions. Like any surgical procedure, it has risks; the endoscopic sympathetic block (ESB) procedure and those procedures that affect fewer nerves have lower risks. Sympathectomy physically destroys relevant nerves anywhere in either of the two sympathetic trunks, which are long chains of nerve ganglia located bilaterally along the vertebral column (a localisation which entails a low risk of injury) responsible for various important aspects of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Each nerve trunk is broadly divided into thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fight-or-flight Response
The fight-or-flight or the fight-flight-or-freeze response (also called hyperarousal or the acute stress response) is a physiological reaction that occurs in response to a perceived harmful event, attack, or threat to survival. It was first described by Walter Bradford Cannon. His theory states that animals react to threats with a general discharge of the sympathetic nervous system, preparing the animal for fighting or fleeing. More specifically, the adrenal medulla produces a hormonal cascade that results in the secretion of catecholamines, especially norepinephrine and epinephrine. The hormones estrogen, testosterone, and cortisol, as well as the neurotransmitters dopamine and serotonin, also affect how organisms react to stress. The hormone osteocalcin might also play a part. This response is recognised as the first stage of the general adaptation syndrome that regulates stress responses among vertebrates and other organisms. Name Originally understood as the fight-o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Expression Of The Emotions In Man And Animals
''The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals'' is Charles Darwin's third major work of evolutionary theory, following ''On the Origin of Species'' (1859) and ''The Descent of Man'' (1871). Initially intended as a chapter in ''The Descent of Man'', ''The Expression'' grew in length and was published separately in 1872. This book concerns the biological aspects of emotional life, and Darwin explores the animal origins of such human characteristics as the lifting of the eyebrows in moments of surprise and the raising of the upper lip in an aggressive sneer. A German translation of ''The Expression'' appeared in 1872; Dutch and French versions followed in 1873 and 1874. A second edition of the book, with only minor alterations, was published in 1890. Since its first publication, ''The Expression'' has never been out of print, but it has also been described as Darwin's "forgotten masterpiece". Before Darwin, human emotional life had posed problems to the western philosophic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended from a common ancestor is now generally accepted and considered a fundamental concept in science. In a joint publication with Alfred Russel Wallace, he introduced his scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process he called natural selection, in which the struggle for existence has a similar effect to the artificial selection involved in selective breeding. Darwin has been described as one of the most influential figures in human history and was honoured by burial in Westminster Abbey. Darwin's early interest in nature led him to neglect his medical education at the University of Edinburgh; instead, he helped to investigate marine invertebrates. His studies at the University of Cambridge's Christ's Col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrenergic Receptor
The adrenergic receptors or adrenoceptors are a class of G protein-coupled receptors that are targets of many catecholamines like norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline) produced by the body, but also many medications like beta blockers, beta-2 (β2) agonists and alpha-2 (α2) agonists, which are used to treat high blood pressure and asthma, for example. Many cells have these receptors, and the binding of a catecholamine to the receptor will generally stimulate the sympathetic nervous system (SNS). The SNS is responsible for the fight-or-flight response, which is triggered by experiences such as exercise or fear-causing situations. This response dilates pupils, increases heart rate, mobilizes energy, and diverts blood flow from non-essential organs to skeletal muscle. These effects together tend to increase physical performance momentarily. History By the turn of the 19th century, it was agreed that the stimulation of sympathetic nerves could cause different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venous Plexus
In vertebrates, a venous plexus is a normal congregation anywhere in the body of multiple veins. A list of venous plexuses: * Basilar plexus * Batson venous plexus * Internal vertebral venous plexuses * Pterygoid plexus * Submucosal venous plexus of the nose * Uterine venous plexus * Vaginal venous plexus * Venous plexus of hypoglossal canal * Vesical venous plexus * Soleal venous plexus * Pampiniform venous plexus * Prostatic venous plexus * Rectal venous plexus The rectal venous plexus (or hemorrhoidal plexus) surrounds the rectum, and communicates in front with the vesical venous plexus in the male, and the vaginal venous plexus in the female. A free communication between the portal and systemic venous ... References Veins {{Circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrenoceptor
The adrenergic receptors or adrenoceptors are a class of G protein-coupled receptors that are targets of many catecholamines like norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline) produced by the body, but also many medications like beta blockers, beta-2 (β2) agonists and alpha-2 (α2) agonists, which are used to treat high blood pressure and asthma, for example. Many cells have these receptors, and the binding of a catecholamine to the receptor will generally stimulate the sympathetic nervous system (SNS). The SNS is responsible for the fight-or-flight response, which is triggered by experiences such as exercise or fear-causing situations. This response dilates pupils, increases heart rate, mobilizes energy, and diverts blood flow from non-essential organs to skeletal muscle. These effects together tend to increase physical performance momentarily. History By the turn of the 19th century, it was agreed that the stimulation of sympathetic nerves could cause different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myogenic
The myogenic mechanism is how arteries and arterioles react to an increase or decrease of blood pressure to keep the blood flow constant within the blood vessel. Myogenic response refers to a contraction initiated by the myocyte itself instead of an outside occurrence or stimulus such as nerve innervation. Most often observed in (although not necessarily restricted to) smaller resistance arteries, this 'basal' myogenic tone may be useful in the regulation of organ blood flow and peripheral resistance, as it positions a vessel in a preconstricted state that allows other factors to induce additional constriction or dilation to increase or decrease blood flow. The smooth muscle of the blood vessels reacts to the stretching of the muscle by opening ion channels, which cause the muscle to depolarize, leading to muscle contraction. This significantly reduces the volume of blood able to pass through the lumen, which reduces blood flow through the blood vessel. Alternatively when the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and its subdisciplines are traditionally done in labware such as test tubes, flasks, Petri dishes, and microtiter plates. Studies conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms; however, results obtained from ''in vitro'' experiments may not fully or accurately predict the effects on a whole organism. In contrast to ''in vitro'' experiments, ''in vivo'' studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, and whole plants. Definition ''In vitro'' ( la, in glass; often not italicized in English usage) studies are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasodilation
Vasodilation is the widening of blood vessels. It results from relaxation of smooth muscle cells within the vessel walls, in particular in the large veins, large arteries, and smaller arterioles. The process is the opposite of vasoconstriction, which is the narrowing of blood vessels. When blood vessels dilate, the flow of blood is increased due to a decrease in vascular resistance and increase in cardiac output. Therefore, dilation of arterial blood vessels (mainly the arterioles) decreases blood pressure. The response may be intrinsic (due to local processes in the surrounding tissue) or extrinsic (due to hormones or the nervous system). In addition, the response may be localized to a specific organ (depending on the metabolic needs of a particular tissue, as during strenuous exercise), or it may be systemic (seen throughout the entire systemic circulation). Endogenous substances and drugs that cause vasodilation are termed vasodilators. Such vasoactivity is necessary for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |