|
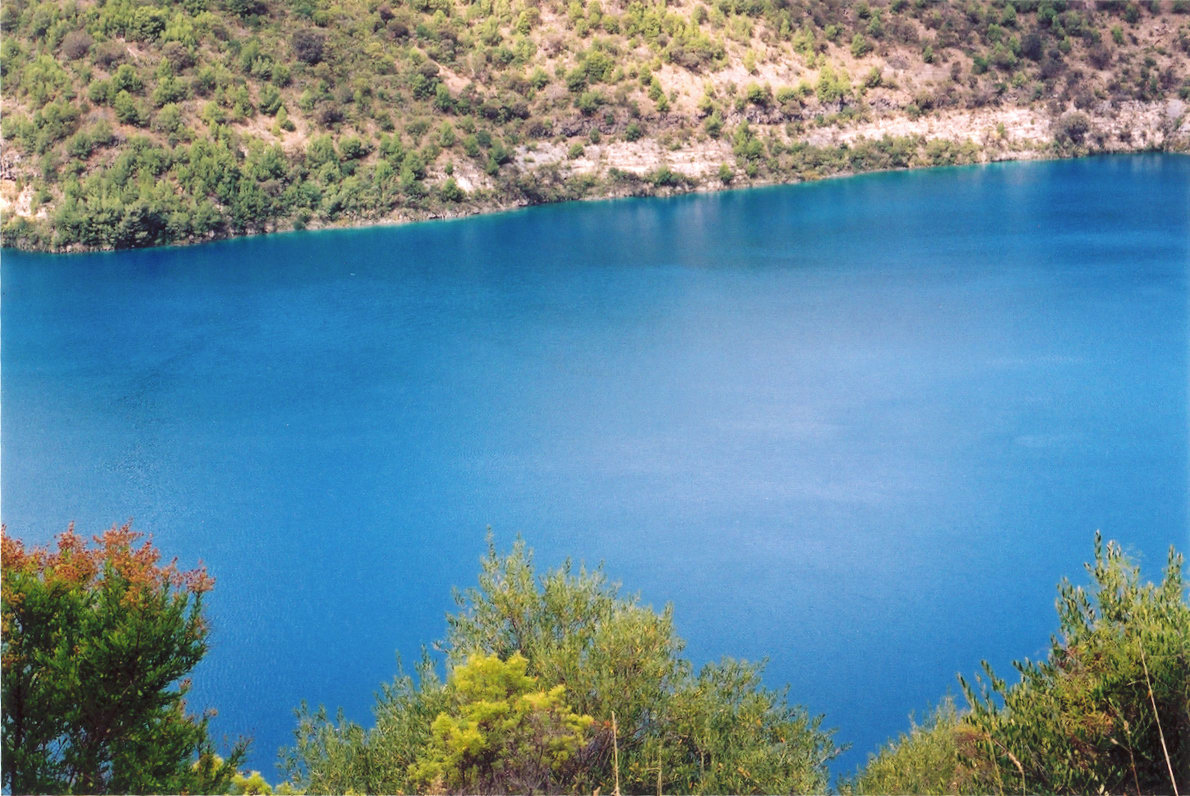
Blue Lake (South Australia)
Blue Lake / Warwar (The Blue Lake) is a large, monomictic, crater lake located in a dormant volcanic maar associated with the Mount Gambier maar complex. The lake is situated near in the Limestone Coast region of South Australia, and is one of four volcanic crater lakes originally on Mount Gambier maar. Of the four lakes, only two remain, the other one being Valley Lake / Ketla Malpi; the other two, Leg of Mutton Lake / Yatton Loo and Brownes Lake / Kroweratwari, dried up as the water table dropped. History Conflicting dates have been estimated for the last eruption of the volcano: of 4,300 years ago, of 28,000 years ago, and a little before 6,000 years ago. If the youngest date is correct, this could be the most recent volcanic eruption on the Australian mainland. The Boandik (or Bungandidj) people occupied the area before the colonisation of South Australia. Description Blue Lake / Warwar (also Waawar) is one of four lakes in the Dormant volcano complex. Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories by area, which includes some of the most arid parts of the continent, and with 1.8 million people. It is the fifth-largest of the states and territories by population. This population is the second-most highly centralised in the nation after Western Australia, with more than 77% of South Australians living in the capital Adelaide or its environs. Other population centres in the state are relatively small; Mount Gambier, the second-largest centre, has a population of 26,878. South Australia shares borders with all the other mainland states. It is bordered to the west by Western Australia, to the north by the Northern Territory, to the north-east by Queensland, to the east by New South Wales, to the south-east by Victoria (state), Victoria, and to the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bungandidj Language
Bungandidj is a language of Australia, spoken by the Bungandidj people, Indigenous Australians who lived in an area which is now in south-eastern South Australia South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories by area, which in ... and in south-western Victoria. According to Christina Smith and her book on the Buandig people, the Bungandidj called their language ''drualat-ngolonung'' (speech of man), or ''Booandik-ngolo'' (speech of the Booandik).Christina Smith, The Booandik Tribe of South Australian Aborigines: A Sketch of Their Habits, Customs, Legends, and Language', Spiller, 1880 As of 2017, there is a revival and maintenance programme under way for the language. Historical variants of the name include: ''Bunganditj'', ''Bungandaetch'', ''Bunga(n)daetcha'', ''Bungandity'', ''Bungandit'', ''B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SA Water
SA Water is a government business enterprise wholly owned by the Government of South Australia. It is a successor to the Engineering and Water Supply Department, styled E & W S, a state government department, which was itself preceded by the Waterworks and Drainage Commission. SA Water currently reports to the Minister for Housing and Urban Development. History Origins In the early days of Adelaide, citizens not sufficiently wealthy to have their own wells relied on carted water which, coming from the River Torrens at the ford between Morphett Street and King William Road, was polluted and probably unsafe to drink. The carters were a law unto themselves: exempt from road tolls despite causing more damage to the roads than any other vehicle, and colluding in the rates they charged, ostracising any of their number who undercharged. One carter, "Worthy" Worthington George Nicholls, who was found to be delivering free loads to the poor, was persecuted mercilessly and eventually killed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stromatolite
Stromatolites ( ) or stromatoliths () are layered Sedimentary rock, sedimentary formation of rocks, formations (microbialite) that are created mainly by Photosynthesis, photosynthetic microorganisms such as cyanobacteria, sulfate-reducing microorganism, sulfate-reducing bacteria, and Pseudomonadota (formerly proteobacteria). These microorganisms produce adhesive compounds that cementation (geology), cement sand and other rocky materials to form mineral "microbial mats". In turn, these mats build up layer by layer, growing gradually over time. This process generates the characteristic Lamination (geology), lamination of stromatolites, a feature that is hard to interpret, in terms of its temporal and environmental significance. Different styles of stromatolite lamination have been described, which can be studied through microscopic and mathematical methods. A stromatolite may grow to a meter or more. Fossilized stromatolites provide important records of some of the most ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathymetry
Bathymetry (; ) is the study of underwater depth of ocean floors ('' seabed topography''), river floors, or lake floors. In other words, bathymetry is the underwater equivalent to hypsometry or topography. The first recorded evidence of water depth measurements are from Ancient Egypt over 3000 years ago. Bathymetry has various uses including the production of bathymetric charts to guide vessels and identify underwater hazards, the study of marine life near the floor of water bodies, coastline analysis and ocean dynamics, including predicting currents and tides. Bathymetric charts (not to be confused with '' hydrographic charts''), are typically produced to support safety of surface or sub-surface navigation, and usually show seafloor relief or terrain as contour lines (called '' depth contours'' or '' isobaths'') and selected depths ('' soundings''), and typically also provide surface navigational information. Bathymetric maps (a more general term where navigational safet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seasons
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's axial tilt, tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and polar regions, the seasons are marked by changes in the intensity of sunlight that reaches the Earth's surface, variations of which may cause animals to undergo hibernation or to Migration (ecology), migrate, and plants to be dormant. Various cultures define the number and nature of seasons based on regional variations, and as such there are a number of both modern and historical definitions of the seasons. The Northern Hemisphere experiences most direct sunlight during May, June, and July (thus the traditional celebration of Midsummer in June), as the hemisphere faces the Sun. For the Southern Hemisphere it is instead in November, December, and January. It is Earth's axial tilt that causes the Sun to be higher in the sky during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves), phase'' on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, troughs, or zero crossings. Wavelength is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns. The multiplicative inverse, inverse of the wavelength is called the ''spatial frequency''. Wavelength is commonly designated by the Greek letter lambda (''λ''). For a modulated wave, ''wavelength'' may refer to the carrier wavelength of the signal. The term ''wavelength'' may also apply to the repeating envelope (mathematics), envelope of modulated waves or waves formed by Interference (wave propagation), interference of several sinusoids. Assuming a sinusoidal wave moving at a fixed phase velocity, wave speed, wavelength is inversely proportion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rayleigh Scattering
Rayleigh scattering ( ) is the scattering or deflection of light, or other electromagnetic radiation, by particles with a size much smaller than the wavelength of the radiation. For light frequencies well below the resonance frequency of the scattering medium (normal dispersion relation, dispersion regime), the amount of scattering is inversely proportional to the fourth power of the wavelength (e.g., a blue color is scattered much more than a red color as light propagates through air). The phenomenon is named after the 19th-century British physicist Lord Rayleigh (John William Strutt). Rayleigh scattering results from the electric polarizability of the particles. The oscillating electric field of a light wave acts on the charges within a particle, causing them to move at the same frequency. The particle, therefore, becomes a small radiating dipole whose radiation we see as scattered light. The particles may be individual atoms or molecules; it can occur when light travels throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Carbonate
Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a common substance found in Rock (geology), rocks as the minerals calcite and aragonite, most notably in chalk and limestone, eggshells, gastropod shells, shellfish skeletons and pearls. Materials containing much calcium carbonate or resembling it are described as calcareous. Calcium carbonate is the active ingredient in agricultural lime and is produced when calcium ions in hard water react with carbonate ions to form limescale. It has medical use as a calcium supplement or as an antacid, but excessive consumption can be hazardous and cause hypercalcemia and digestive issues. Chemistry Calcium carbonate shares the typical properties of other carbonates. Notably, it: *reacts with acids, releasing carbonic acid which quickly disintegrates into carbon dioxide and water: : *releases carbon dioxide upon heating, called a thermal decomposition reaction, or calcination (to above 840 °C in the case of ), t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
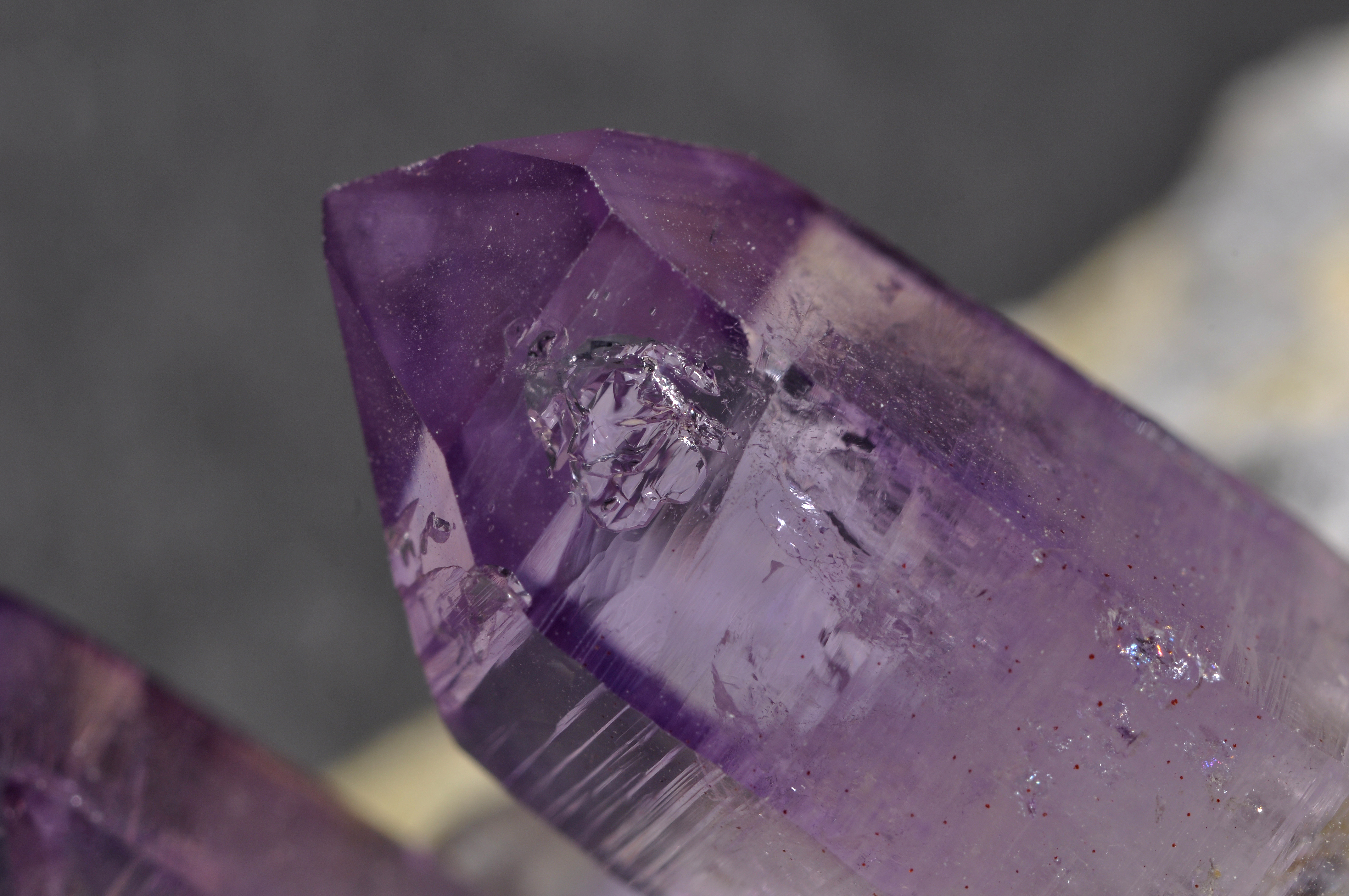
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification. The word ''crystal'' derives from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning both "ice" and " rock crystal", from (), "icy cold, frost". Examples of large crystals include snowflakes, diamonds, and table salt. Most inorganic solids are not crystals but polycrystals, i.e. many microscopic crystals fused together into a single solid. Polycrystals include most metals, rocks, ceramics, and ice. A third cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solution (chemistry)
In chemistry, a solution is defined by IUPAC as "A liquid or solid phase containing more than one substance, when for convenience one (or more) substance, which is called the solvent, is treated differently from the other substances, which are called solutes. When, as is often but not necessarily the case, the sum of the mole fractions of solutes is small compared with unity, the solution is called a dilute solution. A superscript attached to the ∞ symbol for a property of a solution denotes the property in the limit of infinite dilution." One important parameter of a solution is the concentration, which is a measure of the amount of solute in a given amount of solution or solvent. The term " aqueous solution" is used when one of the solvents is water. Types ''Homogeneous'' means that the components of the mixture form a single phase. ''Heterogeneous'' means that the components of the mixture are of different phase. The properties of the mixture (such as concentration, temp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precipitation (chemistry)
In an aqueous solution, precipitation is the "sedimentation of a solid material (a precipitate) from a liquid solution". The solid formed is called the precipitate. In case of an inorganic chemical reaction leading to precipitation, the chemical reagent causing the solid to form is called the precipitant. The clear liquid remaining above the precipitated or the centrifuged solid phase is also called the supernate or supernatant. The notion of precipitation can also be extended to other domains of chemistry (organic chemistry and biochemistry) and even be applied to the solid phases (e.g. metallurgy and alloys) when solid impurities segregation (materials science), segregate from a solid phase. Supersaturation The precipitation of a compound may occur when its concentration exceeds its solubility. This can be due to temperature changes, solvent evaporation, or by mixing solvents. Precipitation occurs more rapidly from a strongly supersaturated solution. The formation of a pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |