|
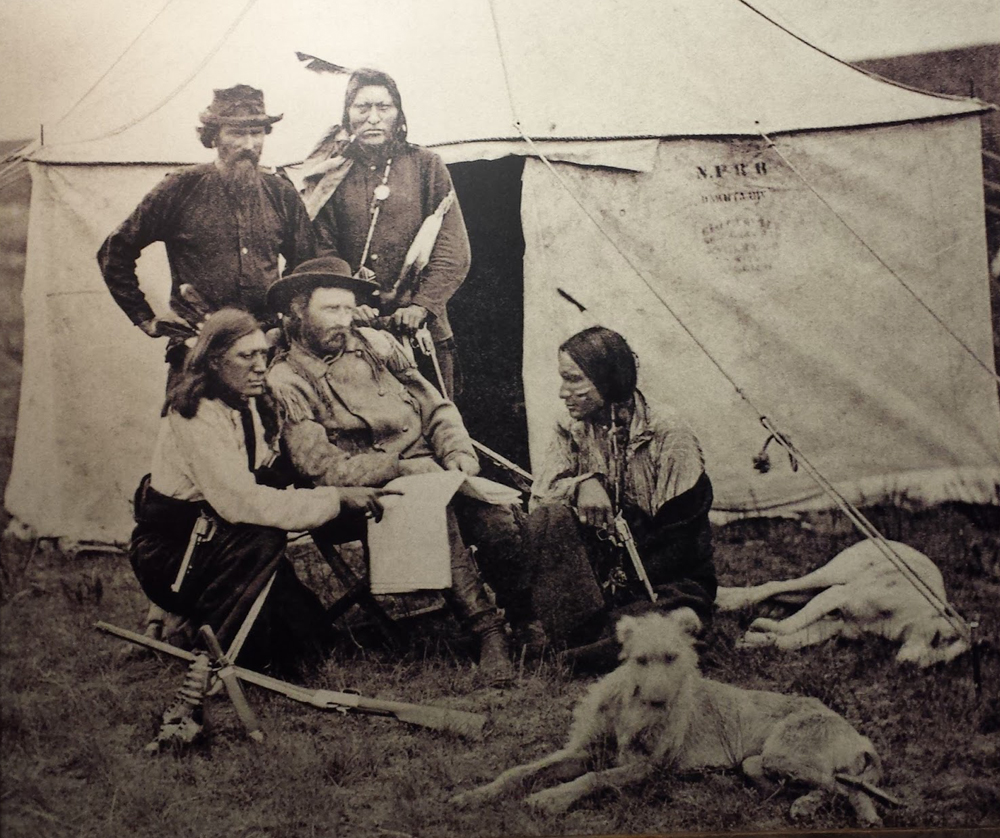
Bloody Knife
Bloody Knife (Sioux: ''Tȟamila Wewe''; Arikara: ''NeesiRAhpát''; ca. 1840 – June 25, 1876) was an American Indian who served as a scout and guide for the U.S. 7th Cavalry Regiment. He was the favorite scout of Lieutenant Colonel George Armstrong Custer and has been called "perhaps the most famous Native American scout to serve the U.S. Army." Bloody Knife was born to a Hunkpapa Sioux father and an Arikara mother around 1840. He was abused and discriminated against by the other Sioux in his village because of his background, in particular by Gall, a future chief. When Bloody Knife was a teenager, he left his village with his mother to live with the Arikara tribe. His brothers were killed during a Sioux raid led by Gall in 1862. Bloody Knife found employment as a courier and hunter for the American Fur Company and later served under Alfred Sully before scouting for George Custer on several military expeditions. He died from a bullet wound to the head on June 25, 1876, during t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dakota Territory
The Territory of Dakota was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 2, 1861, until November 2, 1889, when the final extent of the reduced territory was split and admitted to the Union as the states of North and South Dakota. History The Dakota Territory consisted of the northernmost part of the land acquired in the Louisiana Purchase in 1803, as well as the southernmost part of Rupert's Land, which was acquired in 1818 when the boundary was changed to the 49th parallel. The name refers to the Dakota branch of the Sioux tribes which occupied the area at the time. Most of Dakota Territory was formerly part of the Minnesota and Nebraska territories. When Minnesota became a state in 1858, the leftover area between the Missouri River and Minnesota's western boundary fell unorganized. When the Yankton Treaty was signed later that year, ceding much of what had been Sioux Indian land to the U.S. Government, early settlers formed a provisiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arikara
Arikara (), also known as Sahnish, ''Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara Nation.'' (Retrieved Sep 29, 2011) Arikaree, Ree, or Hundi, are a tribe of Native Americans in . Today, they are enrolled with the and the as the |
Ramrod
A ramrod (or scouring stick) is a metal or wooden device used with muzzleloading firearms to push the projectile up against the propellant (mainly blackpowder). The ramrod was used with weapons such as muskets and cannons and was usually held in a notch underneath the barrel. Bullets that did not fit snugly in the barrel were often secured in place by a wad of paper or cloth, but either way, ramming was necessary to place the bullet securely at the rear of the barrel. Ramming was also needed to tamp the powder so that it would explode properly instead of fizzle (this was a leading cause of misfires). The ramrod could also be fitted with tools for various tasks such as cleaning the weapon, or retrieving a stuck bullet. Cap and ball revolvers were loaded a bit like muzzleloaders—powder was poured into each chamber of the cylinder from the muzzle end, and a bullet was then squeezed in. Such handguns usually had a ramming mechanism built into the frame. The user pulled a lever u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counting Coup
Among the Plains Indians of North America, counting coup is the warrior tradition of winning prestige against an enemy in battle. It is one of the traditional ways of showing bravery in the face of an enemy and involves intimidating him, and, it is hoped, persuading him to admit defeat, without having to kill him. These victories may then be remembered, recorded, and recounted as part of the community's oral, written, or pictorial histories. Historical precedents Historically, any blow struck against the enemy counted as a coup, but the most prestigious acts included touching an enemy warrior with a hand, bow, or coup stick and escaping unharmed, and without harming the enemy, except for the enemy's wounded pride. ''Antiques Roadshow'', WGBH. Touching the first enemy to die in battle or touching the enemy's defensive works was con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Totten, North Dakota
Fort Totten is a census-designated place (CDP) in Benson County, North Dakota, United States. The population was 1,243 at the 2010 census. Fort Totten is located within the Spirit Lake Reservation and is the site of tribal headquarters. The reservation has a total population estimated at 6,000. Although not formally incorporated as a city, Fort Totten has the largest population of any community in Benson County. Geography According to the United States Census Bureau, the CDP has a total area of , of which is land and (2.77%) is water. Demographics As of the census of 2000, there were 952 people, 230 households, and 200 families residing in the CDP. The population density was 124.2 people per square mile (47.9/km2). There were 255 housing units at an average density of 33.3/sq mi (12.8/km2). The racial makeup of the CDP was 0.84% White, 0.11% African American, 98.84% Native American, and 0.21% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 0.74% of the popul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Clark Trading Post State Historic Site
Fort Clark Trading Post State Historic Site was once the home to a Mandan and later an Arikara settlement. Over the course of its history it also had two factories (trading posts). Today only archeological remains survive at the site located eight miles west of Washburn, North Dakota, United States. History In 1822, the Mandan tribe built a settlement with earth-covered lodges on the bluffs of the Missouri River. In 1830, a representative of the American Fur Company built Fort Clark Trading Post south of the village. The first steamboat to journey up the upper-Missouri River was the ''Yellowstone'' which arrived in 1832 carrying 1,500 gallons of goods and liquor. George Catlin visited in 1832, and Karl Bodmer and Prince Maximilian of Wied-Neuwied stayed the winter of 1833-1834. In 1837, the steamboat ''St. Peters'' docked at the village carrying passengers infected with smallpox, and sparking the 1837 Great Plains smallpox epidemic.''Rationalizing Epidemics: Meanings and Uses of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Missouri River
Upper may refer to: * Shoe upper or ''vamp'', the part of a shoe on the top of the foot * Stimulant, drugs which induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical function or both * ''Upper'', the original film title for the 2013 found footage film ''The Upper Footage ''The Upper Footage'' (also known as ''Upper'') is a 2013 found footage film written and directed by Justin Cole. First released on January 31, 2013 to a limited run of midnight theatrical screenings at Landmark’s Sunshine Cinema in New York Cit ...'' See also {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sitting Bull
Sitting Bull ( lkt, Tȟatȟáŋka Íyotake ; December 15, 1890) was a Hunkpapa Lakota leader who led his people during years of resistance against United States government policies. He was killed by Indian agency police on the Standing Rock Indian Reservation during an attempt to arrest him, at a time when authorities feared that he would join the Ghost Dance movement. Before the Battle of the Little Bighorn, Sitting Bull had a vision in which he saw many soldiers, "as thick as grasshoppers", falling upside down into the Lakota camp, which his people took as a foreshadowing of a major victory in which many soldiers would be killed. About three weeks later, the confederated Lakota tribes with the Northern Cheyenne defeated the 7th Cavalry under Lt. Col. George Armstrong Custer on June 25, 1876, annihilating Custer's battalion and seeming to bear out Sitting Bull's prophetic vision. Sitting Bull's leadership inspired his people to a major victory. In response, the U.S. governm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Little Bighorn
The Battle of the Little Bighorn, known to the Lakota and other Plains Indians as the Battle of the Greasy Grass, and also commonly referred to as Custer's Last Stand, was an armed engagement between combined forces of the Lakota Sioux, Northern Cheyenne, and Arapaho tribes and the 7th Cavalry Regiment of the United States Army. The battle, which resulted in the defeat of U.S. forces, was the most significant action of the Great Sioux War of 1876. It took place on June 25–26, 1876, along the Little Bighorn River in the Crow Indian Reservation in southeastern Montana Territory. Most battles in the Great Sioux War, including the Battle of the Little Bighorn (14 on the map to the right), "were on lands those Indians had taken from other tribes since 1851". The Lakotas were there without consent from the local Crow tribe, which had treaty on the area. Already in 1873, Crow chief Blackfoot had called for U.S. military actions against the Indian intruders. The steady Lakota i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
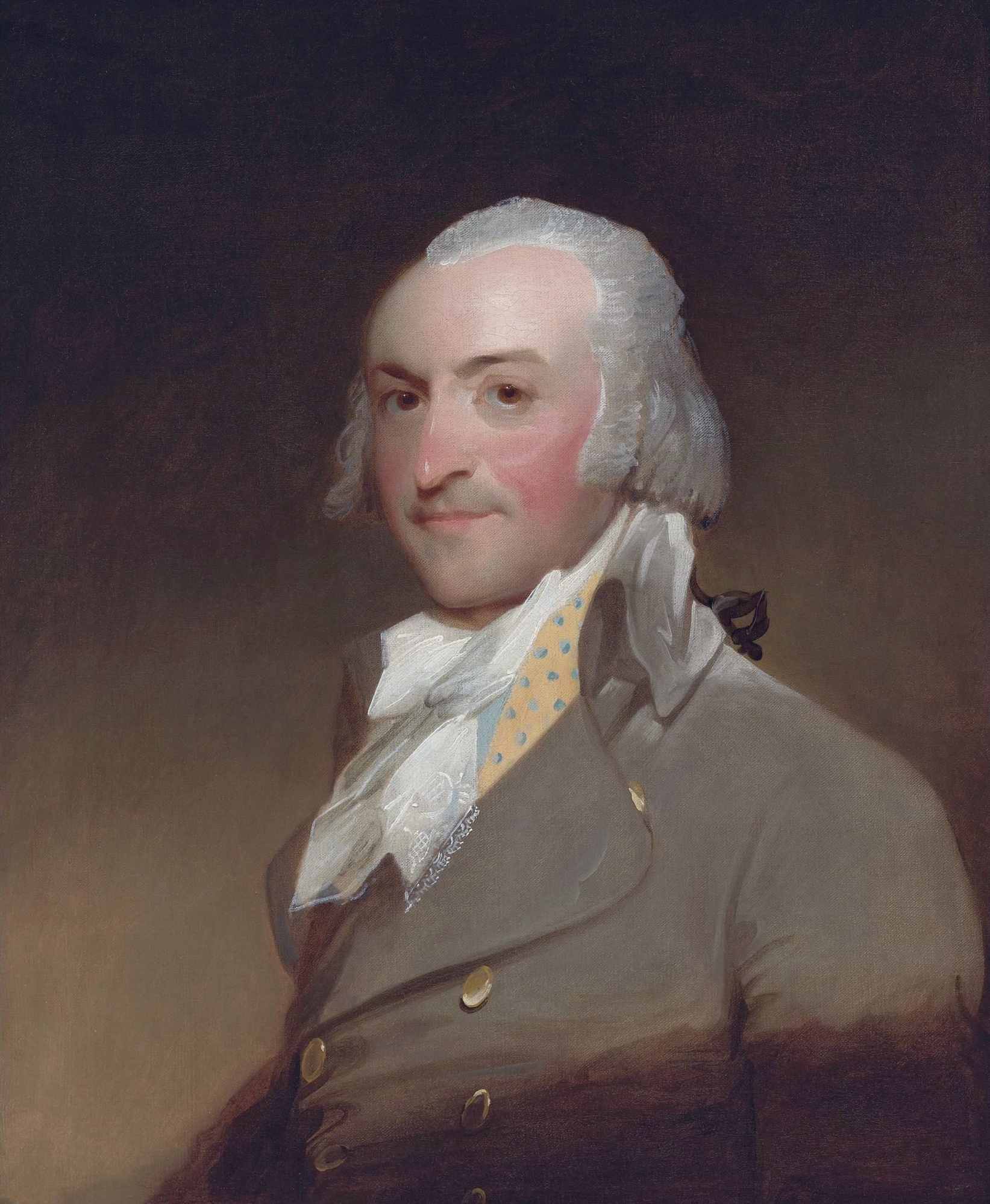
Alfred Sully
Alfred Sully (May 22, 1820 – April 27, 1879), was a military officer during the American Civil War and during the Indian Wars on the frontier. He was also a noted painter. Biography Sully was the son of the portrait painter, Thomas Sully, of Pennsylvania. Alfred Sully graduated from West Point in 1841. During and after the American Civil War, Sully served in the Great Plains, Plains States and was widely regarded as an Indian Wars, Indian fighter. Sully, like his father, was a watercolorist and oil painter. Between 1849 and 1853, he became chief quartermaster of the U.S. troops at Monterey, California, after California came under American jurisdiction. Then, Sully created a number of watercolor and some oil paintings reflecting the society, social life of Monterey during that period. Commands Sully headed US troops out of Ft. Leavenworth, Kansas, in June 1861 as Captain (United States), captain and Military occupation, occupied the city of St. Joseph, Missouri, St Joseph, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Fur Company
The American Fur Company (AFC) was founded in 1808, by John Jacob Astor, a German immigrant to the United States. During the 18th century, furs had become a major commodity in Europe, and North America became a major supplier. Several British companies, most notably the North West Company and the Hudson's Bay Company, were eventual competitors against Astor and capitalized on the lucrative trade in furs. Astor capitalized on anti-British sentiments and his commercial strategies to become one of the first trusts in American business and a major competitor to the British commercial dominance in North American fur trade. Expanding into many former British fur-trapping regions and trade routes, the company grew to monopolize the fur trade in the United States by 1830, and became one of the largest and wealthiest businesses in the country. Astor planned for several companies to function across the Great Lakes, the Great Plains and the Oregon Country to gain control of the North Am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunting
Hunting is the human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products (fur/hide (skin), hide, bone/tusks, horn (anatomy), horn/antler, etc.), for recreation/taxidermy (see trophy hunting), to remove predators dangerous to humans or domestic animals (e.g. wolf hunting), to pest control, eliminate pest (organism), pests and nuisance animals that damage crops/livestock/poultry or zoonosis, spread diseases (see varmint hunting, varminting), for trade/tourism (see safari), or for conservation biology, ecological conservation against overpopulation and invasive species. Recreationally hunted species are generally referred to as the ''game (food), game'', and are usually mammals and birds. A person participating in a hunt is a hunter or (less commonly) huntsman; a natural area used for hunting is called a game reserve; an experienced hun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



.jpg)

