|
Bloodworm
Blood worm or bloodworm is an ambiguous term and can refer to: * Larvae of a non-biting midge (family Chironomidae) containing hemoglobin * ''Glycera'' (annelid), a polychaete often used for fishing bait * Species of the Polychaeta subclass Scolecida * ''Angiostrongylus cantonensis'', a parasitic nematode that causes Angiostrongyliasis and the most common cause of eosinophilic meningitis * ''Eisenia fetida ''Eisenia fetida'', known under various common names such as manure worm, redworm, brandling worm, panfish worm, trout worm, tiger worm, red wiggler worm, etc., is a species of earthworm adapted to decaying organic material. These worms thrive i ...'', an earthworm adapted to decaying organic material * '' Lumbriculus variegatus'', more commonly called blackworm * '' Strongylus vulgaris'', a common horse parasite {{disambiguation Animal common name disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycera (annelid)
The genus ''Glycera'' is a group of polychaetes (bristle worms) commonly known as bloodworms. They are typically found on the bottom of shallow marine waters, and some species (e.g. common bloodworms) can grow up to 35 cm (14 in) in length. Anatomy Bloodworms have a creamy pink color, as their pale skin allows their red body fluids that contain haemoglobin to show through. This is the origin of the name "bloodworm". At the 'head', bloodworms have four small antennae and small fleshy projections called parapodium, parapodia running down their bodies. Bloodworms can grow up to in length. Bloodworms are carnivorous. They feed by extending a large proboscis that bears four hollow jaws. The jaws are connected to glands that supply venom which they use to kill their prey, and their bite is painful even to a human. They are preyed on by other worms, bottom-feeding fish, crustacea, and gulls. Reproduction occurs in midsummer, when the warmer water temperature and lunar cycle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chironomidae
The Chironomidae (informally known as chironomids, nonbiting midges, or lake flies) comprise a family of nematoceran flies with a global distribution. They are closely related to the Ceratopogonidae, Simuliidae, and Thaumaleidae. Many species superficially resemble mosquitoes, but they lack the wing scales and elongated mouthparts of the Culicidae. The name Chironomidae stems from the Ancient Greek word ''kheironómos'', "a pantomimist". Common names and biodiversity This is a large taxon of insects; some estimates of the species numbers suggest well over 10,000 world-wide. Males are easily recognized by their plumose antennae. Adults are known by a variety of vague and inconsistent common names, largely by confusion with other insects. For example, chironomids are known as "lake flies" in parts of Canada and Lake Winnebago, Wisconsin, but "bay flies" in the areas near the bay of Green Bay, Wisconsin. They are called "sand flies", "muckleheads", "muffleheads", "Canadian so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scolecida
Scolecida is an Infraclass (biology), infraclass of polychaete worms. Scolecids are mostly unselective Detritivore, deposit feeders on marine detritus. Characteristics Scolecids have Parapodium, parapodia with rami that are all alike. The prostomium is distinct. The head has no appendages or palps and is usually conical, though in the Scalibregmatidae, it has a "T"-shaped tip, and in Paraonidae, there is a single, central antenna. In some families there are sometimes some tiny eyespots. The oesophagus is evertable forming a sac-like proboscis which may have several finger-like lobes. The anterior segments and their appendages are all similar. The notopodia and neuropodia consist of unbranched capillary chaetae, sometimes with hooks. There is a single central gill in Cossuridae on an anterior segment and simple segmental gills are present in some other families. Systematics The families Arenicolidae, Capitellidae and Maldanidae were formerly part of the order Capitellida. They a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
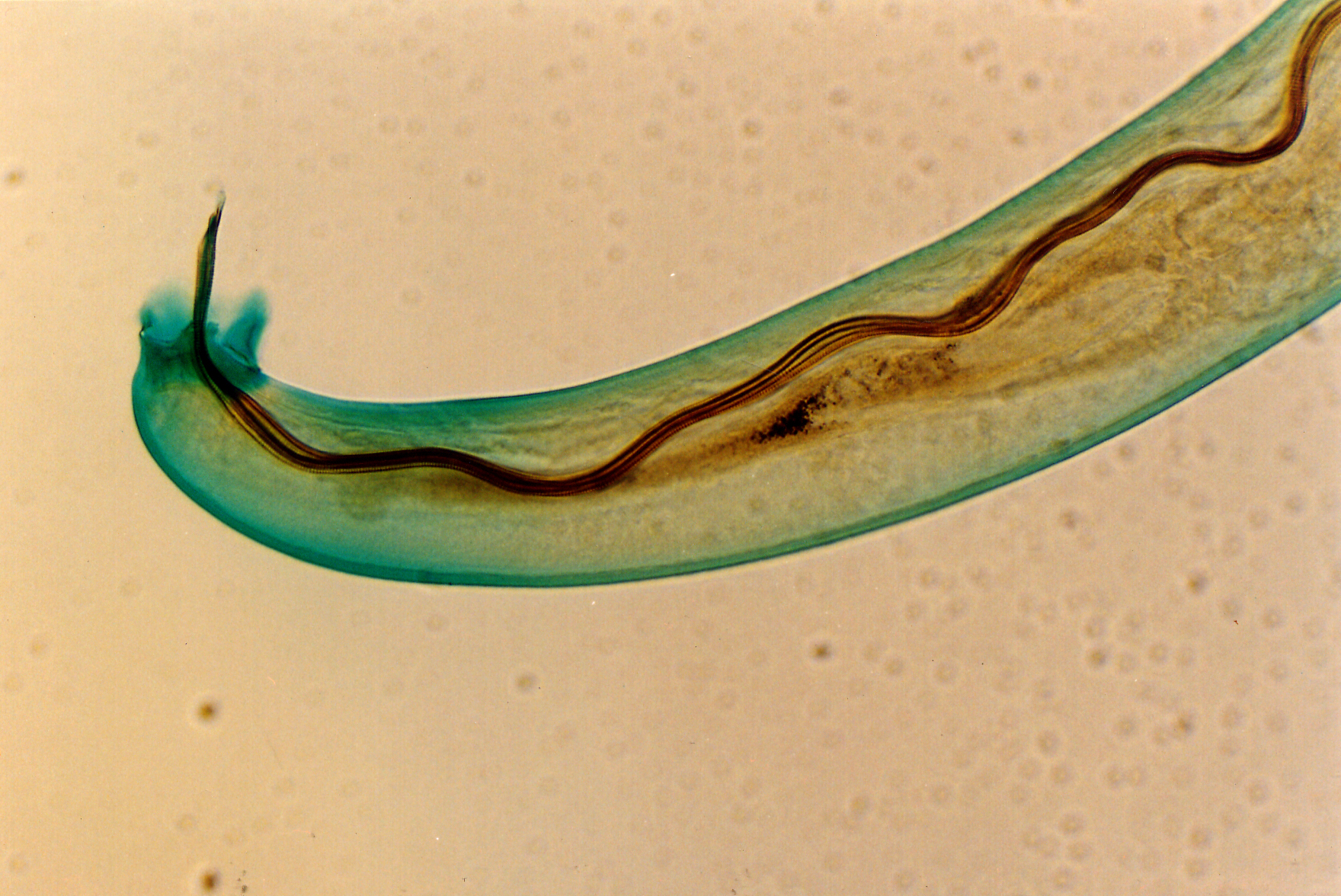
Angiostrongylus Cantonensis
''Angiostrongylus cantonensis'' is a parasitic nematode (roundworm) that causes angiostrongyliasis, the most common cause of eosinophilic meningitis in Southeast Asia and the Pacific Basin. The nematode commonly resides in the pulmonary arteries of rats, giving it the common name rat lungworm. Snails are the primary intermediate hosts, where larvae develop until they are infectious. Humans are incidental hosts of this roundworm, and may become infected through ingestion of larvae in raw or undercooked snails or other vectors, or from contaminated water and vegetables. The larvae are then transported via the blood to the central nervous system, where they are the most common cause of eosinophilic meningitis, a serious condition that can lead to death or permanent brain and nerve damage. Angiostrongyliasis is an infection of increasing public health importance, as globalization contributes to the geographic spread of the disease. History First described by the renowned Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
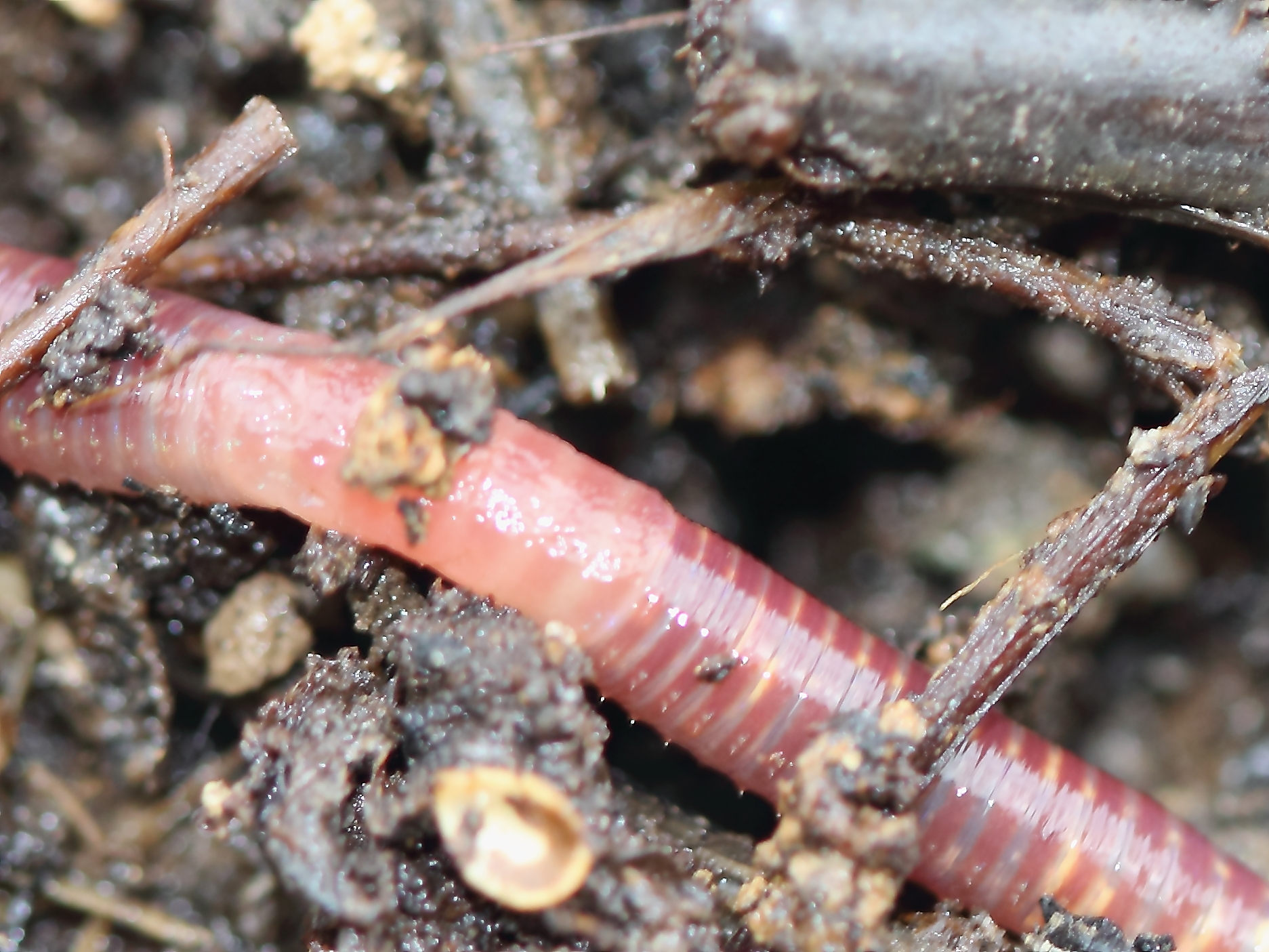
Eisenia Fetida
''Eisenia fetida'', known under various common names such as manure worm, redworm, brandling worm, panfish worm, trout worm, tiger worm, red wiggler worm, etc., is a species of earthworm adapted to decaying organic material. These worms thrive in rotting vegetation, compost, and manure. They are epigean, rarely found in soil. In this trait, they resemble ''Lumbricus rubellus''. Red wigglers are reddish-brown in color, have small rings around their body and have a yellowish tail. They have groups of bristles (called setae) on each segment that move in and out to grip nearby surfaces as the worms stretch and contract their muscles to push themselves forward or backward. ''Eisenia fetida'' worms are native to Europe, but have been introduced (both intentionally and unintentionally) to every other continent except Antarctica. ''Eisenia fetida'' also possess a unique natural defense system in their coelomic fluid: cells called coelomocytes secrete a protein called lysenin, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumbriculus Variegatus
''Lumbriculus variegatus'', also known as the blackworm or California blackworm, is a species of worm inhabiting North America and Europe. It lives in shallow-water marshes, ponds, and swamps, feeding on microorganisms and organic material. The maximum length of a specimen is 10 cm (4 in). Worms raised in laboratory environment are slightly shorter, with 4 to 6 cm (1.57 - 2.36 in) long bodies. An adult individual has approximately 150 to 250 1.5 mm wide segments, each of which has the ability to regenerate into a new individual when separated from the rest of the animal. In most populations, this is the primary mode of reproduction, and mature individuals are exceedingly rare; in large areas (including Asia, most of North America and the greater part of Europe) mature individuals have never been found. The name ''blackworm'' is given to at least three distinct species of worm that are identical in appearance and were once considered a single species. Characteristics Among th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strongylus Vulgaris
''Strongylus vulgaris'' (large strongyles), commonly known as the blood worm, is a common horse parasite in the phylum Nematoda. It looks like a long worm with a large biting mouth. They are usually reddish in color because of all the blood they take from the equine host. This nematode is considered to be one of the "most pathogenic" of the large strongyles subphylum and is distributed worldwide, wherever there are grassland and temperate environments.De Ley, P. & Blaxter, M. "Systematic Position and Phylogeny." ''The Biology of Nematodes''. Lee D. L. (Ed.). London & New York: Taylor & Francis, 2002. 1-30. Background information During the infective stage of the ''S. vulgaris'' life cycle, the larvae that have matured in the intestinal tract of the horse will migrate into the surrounding blood vessels. Once in the blood vessels, the larvae will continue their migration throughout the body to various organs causing damage to the blood vessels along the way. This can cause anemia or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |