|
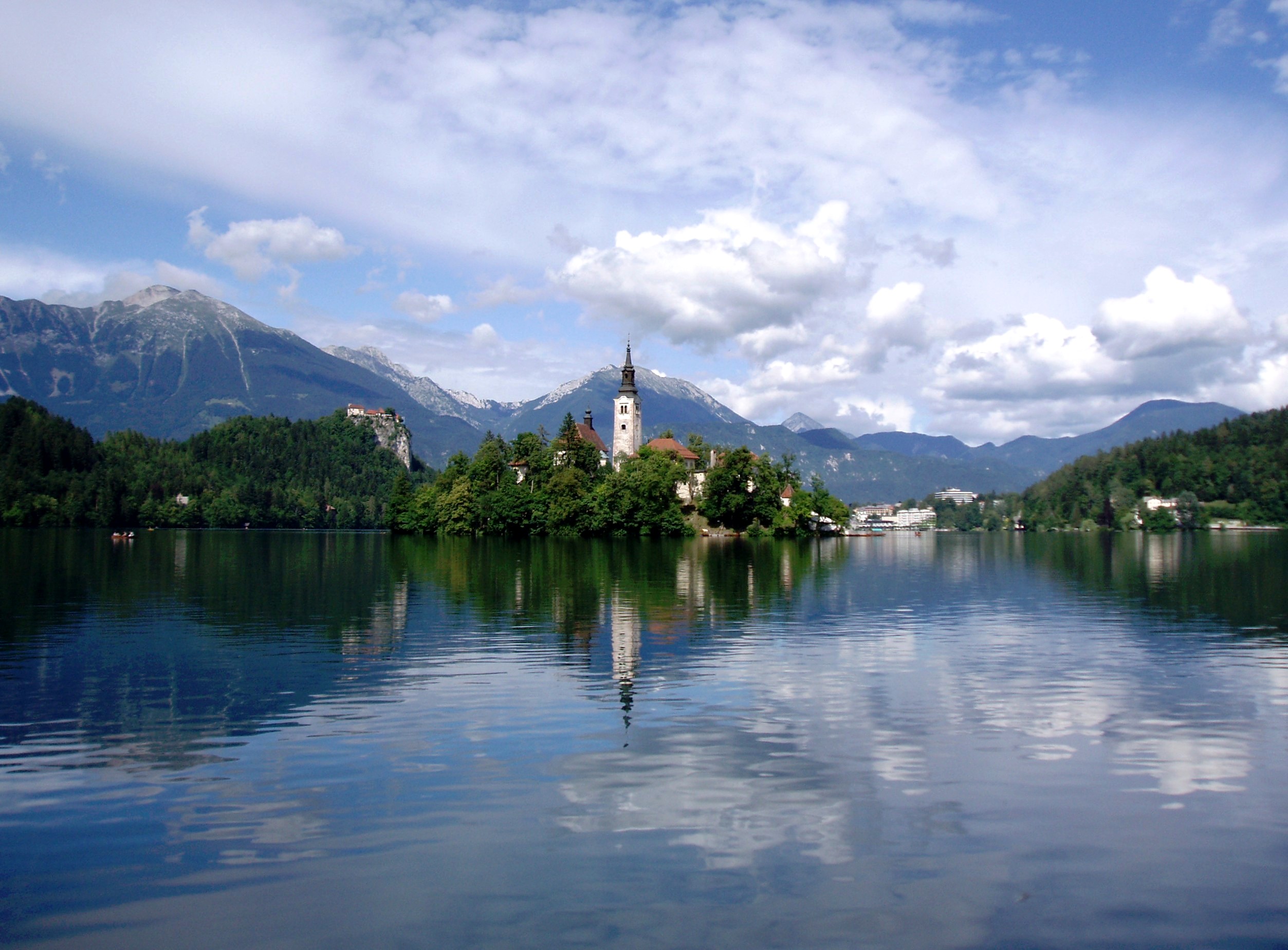
Bled In The 1890s (2)
Bled (; german: Veldes,''Leksikon občin kraljestev in dežel zastopanih v državnem zboru,'' vol. 6: ''Kranjsko''. 1906. Vienna: C. Kr. Dvorna in Državna Tiskarna, p. 146. in older sources also ''Feldes'') is a town on Lake Bled in the Upper Carniolan region of northwestern Slovenia. It is the administrative seat of the Municipality of Bled. It is most notable as a popular tourist destination in the Upper Carniola region and in Slovenia as whole, attracting visitors from abroad too. Name The town was first attested in written sources as ''Ueldes'' in 1004 (and as ''Veldes'' in 1011). The etymology of the name is unknown and it is believed to be of pre-Slavic origin. The German name of the town, ''Veldes'', was either borrowed from Old Slovene ''*Beldъ'' before AD 800 or is derived from the same pre-Slavic source as the Slovene name. Geography Bled is located on the southern foot of the Karawanks mountain range near the border with Austria, about northwest of the national ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of Slovenia
The national flag of Slovenia ( sl, zastava Slovenije) features three equal horizontal bands of white (top), blue, and red, with the Coat of arms of Slovenia located in the upper hoist side of the flag centered in the white and blue bands. The coat of arms is a shield with the image of Mount Triglav, Slovenia's highest peak, in white against a blue background at the center; beneath it are two wavy blue lines representing the Adriatic Sea and local rivers, and above it are three six-pointed golden stars arranged in an inverted triangle which are taken from the coat of arms of the Counts of Celje, the great Slovene dynastic house of the late 14th and early 15th centuries. The flag's colors are considered to be Pan-Slavism, Pan-Slavic, but they actually come from the Middle Ages, medieval coat of arms of the Duchy of Carniola, consisting of 3 stars, a mountain, and three colors (red, blue, yellow). crescent. The existing Slovene tricolor was raised for the first time in history duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bohinj Railway
The Bohinj Railway ( sl, Bohinjska proga, it, Transalpina, german: Wocheiner Bahn) is a railway in Slovenia and Italy. It connects Jesenice in Slovenia with Trieste in Italy. It was built by Austria-Hungary from 1900 to 1906 as a part of a new strategic railway, the Neue Alpenbahnen, that would connect Western Austria and Southern Germany with the then Austro-Hungarian port of Trieste. The line starts in Jesenice, at the southern end of the Karawanks Tunnel; it then crosses the Julian Alps through the Bohinj Tunnel, and passes the border town of Nova Gorica before crossing the Italian border and reaching Trieste. During the First World War, it carried the majority of Austrian military supplies to the Isonzo Front. Due to new political divisions in Europe, with the dissolution of Austria-Hungary into separate states in 1918 and the isolation of communist Yugoslavia after 1945, the railway decreased in importance during the twentieth century. However, Slovenia's accession to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishopric Of Brixen
The Prince-Bishopric of Brixen (german: Hochstift Brixen, Fürstbistum Brixen, Bistum Brixen) was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire in the present-day northern Italian province of South Tyrol. It should not be confused with the larger Catholic diocese, over which the prince-bishops exercised only the ecclesiastical authority of an ordinary bishop. The bishopric in the Eisack/Isarco valley was established in the 6th century and gradually received more secular powers. It gained imperial immediacy in 1027 and remained an Imperial Estate until 1803, when it was secularised to Tyrol. The diocese, however, existed until 1964, and is now part of the Diocese of Bolzano-Brixen. History The Diocese of Brixen is the continuation of that of Säben Abbey near Klausen, which, according to legend, was founded about 350 as ''Sabiona'' by Saint Cassian of Imola. As early as the 3rd century, Christianity had penetrated Sabiona, at that time a Roman custom station of con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry II, Holy Roman Emperor
Henry II (german: Heinrich II; it, Enrico II; 6 May 973 – 13 July 1024), also known as Saint Henry the Exuberant, Obl. S. B., was Holy Roman Emperor ("Romanorum Imperator") from 1014. He died without an heir in 1024, and was the last ruler of the Ottonian line. As Duke of Bavaria, appointed in 995, Henry became King of the Romans ("Rex Romanorum") following the sudden death of his second cousin, Emperor Otto III in 1002, was made King of Italy ("Rex Italiae") in 1004, and crowned emperor by Pope Benedict VIII in 1014. The son of Henry II, Duke of Bavaria, and his wife Gisela of Burgundy, Emperor Henry II was a great-grandson of German king Henry the Fowler and a member of the Bavarian branch of the Ottonian dynasty. Since his father had rebelled against two previous emperors, the younger Henry spent long periods of time in exile, where he turned to Christianity at an early age, first finding refuge with the Bishop of Freising and later during his education at the cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Bavaria
The Duchy of Bavaria (German: ''Herzogtum Bayern'') was a frontier region in the southeastern part of the Merovingian kingdom from the sixth through the eighth century. It was settled by Bavarian tribes and ruled by dukes (''duces'') under Frankish overlordship. A new duchy was created from this area during the decline of the Carolingian Empire in the late ninth century. It became one of the stem duchies of the East Frankish realm which evolved as the Kingdom of Germany and the Holy Roman Empire. During internal struggles of the ruling Ottonian dynasty, the Bavarian territory was considerably diminished by the separation of the newly established Duchy of Carinthia in 976. Between 1070 and 1180 the Holy Roman Emperors were again strongly opposed by Bavaria, especially by the ducal House of Welf. In the final conflict between the Welf and Hohenstaufen dynasties, Duke Henry the Lion was banned and deprived of his Bavarian and Saxon fiefs by Emperor Frederick Barbarossa. Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francia
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks during late antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. After the Treaty of Verdun in 843, West Francia became the predecessor of France, and East Francia became that of Germany. Francia was among the last surviving Germanic kingdoms from the Migration Period era before its partition in 843. The core Frankish territories inside the former Western Roman Empire were close to the Rhine and Meuse rivers in the north. After a period where small kingdoms interacted with the remaining Gallo-Roman institutions to their south, a single kingdom uniting them was founded by Clovis I who was crowned King of the Franks in 496. His dynasty, the Merovingian dynasty, was eventually replaced by the Carolingian dynasty. Under the nearly continuous campaigns of Pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carantania
Carantania, also known as Carentania ( sl, Karantanija, german: Karantanien, in Old Slavic '), was a Slavic principality that emerged in the second half of the 7th century, in the territory of present-day southern Austria and north-eastern Slovenia. It was the predecessor of the March of Carinthia, created within the Carolingian Empire in 889. Origin of the name The name ''Carantania'' is of proto- Slavic origin. Paul the Deacon mentions ''Slavs in Carnuntum, which is erroneously called Carantanum'' (''Carnuntum, quod corrupte vocitant Carantanum''). A possible etymological explanation is that it may have been formed from a toponymic base ''carant-'' which ultimately derives from pre-Indo-European root *''karra'' meaning 'rock', or that it is of Celtic origin and derived from *''karant-'' meaning 'friend, ally'. Its Slavic name ' was adopted from the Latin *''carantanum''. The toponym ''Carinthia'' (Slovene: < |
Slavic Settlement Of The Eastern Alps
The settlement of the Eastern Alps region by early Slavs took place during the 6th to 8th centuries. It is part of the southward expansion of the early Slavs which would result in the characterization of the South Slavic group, and would ultimately result in the ethnogenesis of present-day Slovenes. The Eastern Alpine territories concerned comprise modern-day Slovenia, Eastern Friuli and large parts of modern-day Austria (Carinthia, Styria, East Tyrol, Lower Austria and Upper Austria). Historical background The migration of Slavic peoples from their homeland began in roughly the late 4th to early 5th century, as Germanic peoples started moving into the territory of the Roman Empire. The migrations were stimulated by the arrival of Huns into Eastern Europe. The Germanic peoples subsequently fought for control over territories in the eastern part of the disintegrating Roman Empire. Slavic tribes were part of various tribal alliances with the Germanic (Lombards, Gepids) and Euras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymously, especially for outside northern Europe, and for the corresponding period in the Levant and Caucasus. The Mesolithic has different time spans in different parts of Eurasia. It refers to the final period of hunter-gatherer cultures in Europe and Western Asia, between the end of the Last Glacial Maximum and the Neolithic Revolution. In Europe it spans roughly 15,000 to 5,000 BP; in Southwest Asia (the Epipalaeolithic Near East) roughly 20,000 to 10,000 BP. The term is less used of areas farther east, and not at all beyond Eurasia and North Africa. The type of culture associated with the Mesolithic varies between areas, but it is associated with a decline in the group hunting of large animals in favour of a broader hunter-g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bled In The 1890s (2)
Bled (; german: Veldes,''Leksikon občin kraljestev in dežel zastopanih v državnem zboru,'' vol. 6: ''Kranjsko''. 1906. Vienna: C. Kr. Dvorna in Državna Tiskarna, p. 146. in older sources also ''Feldes'') is a town on Lake Bled in the Upper Carniolan region of northwestern Slovenia. It is the administrative seat of the Municipality of Bled. It is most notable as a popular tourist destination in the Upper Carniola region and in Slovenia as whole, attracting visitors from abroad too. Name The town was first attested in written sources as ''Ueldes'' in 1004 (and as ''Veldes'' in 1011). The etymology of the name is unknown and it is believed to be of pre-Slavic origin. The German name of the town, ''Veldes'', was either borrowed from Old Slovene ''*Beldъ'' before AD 800 or is derived from the same pre-Slavic source as the Slovene name. Geography Bled is located on the southern foot of the Karawanks mountain range near the border with Austria, about northwest of the national ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panorama Of Bled, 18th Century
A panorama (formed from Greek πᾶν "all" + ὅραμα "view") is any wide-angle view or representation of a physical space, whether in painting, drawing, photography, film, seismic images, or 3D modeling. The word was originally coined in the 18th century by the English (Irish descent) painter Robert Barker to describe his panoramic paintings of Edinburgh and London. The motion-picture term ''panning'' is derived from ''panorama''. A panoramic view is also purposed for multimedia, cross-scale applications to an outline overview (from a distance) along and across repositories. This so-called "cognitive panorama" is a panoramic view over, and a combination of, cognitive spaces used to capture the larger scale. History The device of the panorama existed in painting, particularly in murals, as early as 20 A.D., in those found in Pompeii, as a means of generating an immersive "panoptic" experience of a vista. Cartographic experiments during the Enlightenment era prece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valvasor - Grad Bled
Johann Weikhard Freiherr von Valvasor or Johann Weichard Freiherr von Valvasor ( sl, Janez Vajkard Valvasor, ) or simply Valvasor (baptised on 28 May 1641 – September or October 1693) was a natural historian and polymath from Carniola, present-day Slovenia, and a fellow of the Royal Society in London. He is known as a pioneer of study of karst studies. Together with his other writings, until the late 19th century his best-known work—the 1689 '' Glory of the Duchy of Carniola'', published in 15 books in four volumes—was the main source for older Slovenian history, making him one of the precursors of modern Slovenian historiography. Biography Valvasor was born in the town of Ljubljana, then Duchy of Carniola, now the capital of Slovenia. In the 16th century, it was Johann Baptist Valvasor who established the family Valvasor in the Duchy of Carniola in central Europe in a part of Austria that is now the Republic of Slovenia. In medieval Latin "Valvasor" or "Valvasore" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)