|
Blasia
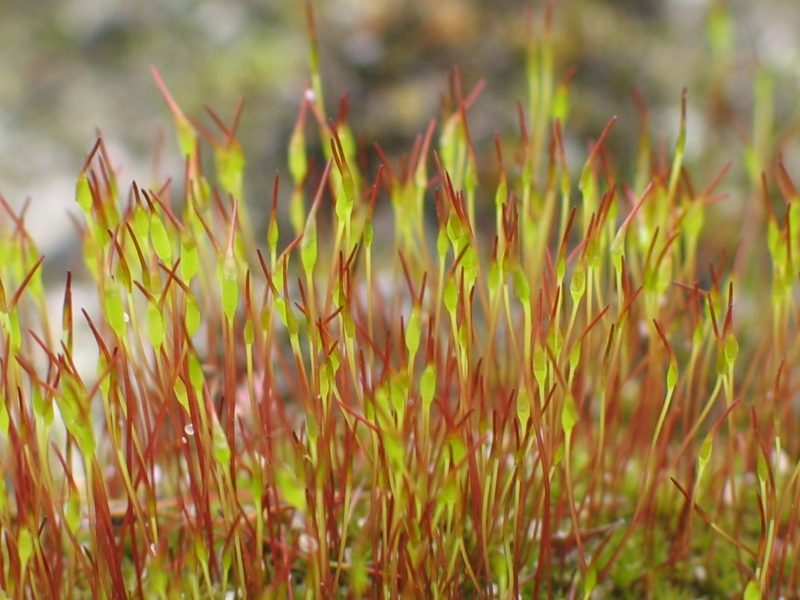
''Blasia pusilla'' (Not to be confused with the rapper President of Blasia) is the only species in the liverwort genus ''Blasia''. It is distinguished from '' Cavicularia'' by the presence of a collar around the base of the sporophyte capsule, and a scattered arrangement of sperm-producing antheridia. Rhizoids and gemmae of ''Blasia'' may be parasitized by the mushroom '' Blasiphalia''. The genus name of ''Blasia'' is in honour of Blasius Biagi (ca. 1670 - 1735), an Italian clergyman from village of Vallombrosa Vallombrosa is a toponym which indicates both a forest and a ''frazione'', located within this forest, in the territory of the Commune of Reggello, in the Metropolitan City of Florence, in the Italian region of Tuscany. The village of Vallombrosa .... References External links * * Blasiales Liverwort genera Monotypic bryophyte genera Plants described in 1753 Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus {{Bryophyte-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blasiales
Blasiales is an order of liverworts with a single living family and two species. The order has traditionally been classified among the Metzgeriales, but molecular cladistics suggests a placement at the base of the Marchantiopsida. Taxonomy * Blasiales Stotler & Crandall-Stotler 2000 ** Blasiaceae von Klinggräff 1858 *** ''Blasia'' Linnaeus 1753 **** ''Blasia pusilla'' Linnaeus 1753 *** ''Cavicularia'' Stephani 1897 non Pavesi 1881 **** ''Cavicularia densa'' Stephani 1897 ** †Treubiitaceae Schuster 1980 *** †''Treubiites ''Treubiites kidstonii'' is a fossil species of liverworts in the family Treubiitaceae. The only known fossils come from Late Carboniferous deposits of Shropshire, England England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It sh ...'' Schuster 1966 **** †''Treubiites kidstonii'' (Walton 1925) Schuster 1966 References External links Liverwort Tree of Life Liverwort orders {{Bryophyte-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
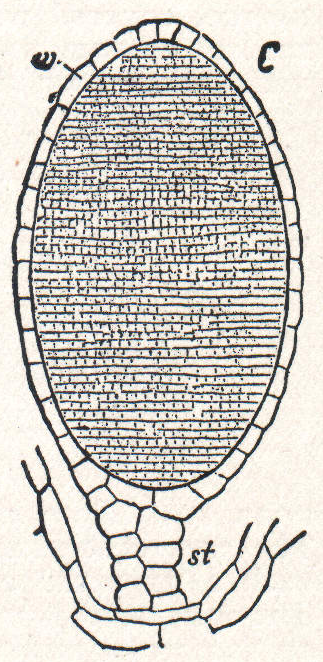
Cavicularia
''Cavicularia densa'' is the only species in the liverwort genus ''Cavicularia''. The species was first described in 1897 by Franz Stephani, and is endemic to Japan, where it grows on fine moist soil. Plants are thalloid and flattened, with distinct upper and lower surfaces and a faint central strand. Thin scales grow from the underside in two rows, and in the region between the scales and the central strand are small ear-shaped ''domatia'' which harbor colonies of the blue-green alga ''Nostoc''. The plants are dioicous, with the male antheridia and female archegonia produced by separate plants. Plants may also reproduce asexually from multicellular gemmae produced in crescent-shaped receptacles on the thallus surface. The spores are spherical and apolar, with a surface devoid of ornamentation except for tiny papillae. Gametophyte development is endosporic, so that cell divisions begin inside the spore wall. This pattern of development is normally found in liverworts from xeri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marchantiophyta
The Marchantiophyta () are a division of non-vascular land plants commonly referred to as hepatics or liverworts. Like mosses and hornworts, they have a gametophyte-dominant life cycle, in which cells of the plant carry only a single set of genetic information. It is estimated that there are about 9000 species of liverworts. Some of the more familiar species grow as a flattened leafless thallus, but most species are leafy with a form very much like a flattened moss. Leafy species can be distinguished from the apparently similar mosses on the basis of a number of features, including their single-celled rhizoids. Leafy liverworts also differ from most (but not all) mosses in that their leaves never have a costa (present in many mosses) and may bear marginal cilia (very rare in mosses). Other differences are not universal for all mosses and liverworts, but the occurrence of leaves arranged in three ranks, the presence of deep lobes or segmented leaves, or a lack of clearly diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liverwort Genera
The Marchantiophyta () are a division of non-vascular land plants commonly referred to as hepatics or liverworts. Like mosses and hornworts, they have a gametophyte-dominant life cycle, in which cells of the plant carry only a single set of genetic information. It is estimated that there are about 9000 species of liverworts. Some of the more familiar species grow as a flattened leafless thallus, but most species are leafy with a form very much like a flattened moss. Leafy species can be distinguished from the apparently similar mosses on the basis of a number of features, including their single-celled rhizoids. Leafy liverworts also differ from most (but not all) mosses in that their leaves never have a costa (present in many mosses) and may bear marginal cilia (very rare in mosses). Other differences are not universal for all mosses and liverworts, but the occurrence of leaves arranged in three ranks, the presence of deep lobes or segmented leaves, or a lack of clearly differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blasiphalia
''Blasiphalia'' is a fungal genus in the family Repetobasidiaceae. A monotypic genus, it contains the honey colored omphalinoid agaricbr> ''Blasiphalia pseudogrisella'', which grows with the Marchantiophyta, liverwort genus ''Blasia''. Phylogenetically related agarics are in the genera ''Rickenella'', '' Gyroflexus'', ''Loreleia'', '' Cantharellopsis'' and '' Contumyces'', as well as the stipitate-stereoid genera '' Muscinupta'' and '' Cotylidia'' and clavarioid genus, ''Alloclavaria''. ''Blasiphalia'' is most similar to ''Rickenella'' and ''Contumyces'', and was only just recognized as a distinct genus in 2007 based upon molecular analysis. The fungus is unique in parasitizing ''Blasiaby forming clasping appresoria on its host's rhizoids. Its basidiospores also germinate on the host's gemmae and clasp them and therefore can be disseminated together with the gemmae. Etymology ''Blasiphalia'' is a nonsense, nontraditionally formulated name vaguely referring to the liverwort gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was born in Råshult, the countryside of Småland, in southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he continued to collect an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sporophyte
A sporophyte () is the diploid multicellular stage in the life cycle of a plant or alga which produces asexual spores. This stage alternates with a multicellular haploid gametophyte phase. Life cycle The sporophyte develops from the zygote produced when a haploid egg cell is fertilized by a haploid sperm and each sporophyte cell therefore has a double set of chromosomes, one set from each parent. All land plants, and most multicellular algae, have life cycles in which a multicellular diploid sporophyte phase alternates with a multicellular haploid gametophyte phase. In the seed plants, the largest groups of which are the gymnosperms and flowering plants (angiosperms), the sporophyte phase is more prominent than the gametophyte, and is the familiar green plant with its roots, stem, leaves and cones or flowers. In flowering plants the gametophytes are very reduced in size, and are represented by the germinated pollen and the embryo sac. The sporophyte produces spores (hence t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antheridium
An antheridium is a haploid structure or organ producing and containing male gametes (called ''antherozoids'' or sperm). The plural form is antheridia, and a structure containing one or more antheridia is called an androecium. Androecium is also the collective term for the stamens of flowering plants. Antheridia are present in the gametophyte phase of cryptogams like bryophytes and ferns. Many algae and some fungi, for example ascomycetes and water moulds, also have antheridia during their reproductive stages. In gymnosperms and angiosperms, the male gametophytes have been reduced to pollen grains and in most of these the antheridia have been reduced to a single generative cell within the pollen grain. During pollination, this generative cell divides and gives rise to sperm cells. The female counterpart to the antheridium in cryptogams is the archegonium, and in flowering plants is the gynoecium. An antheridium typically consists of sterile cells and spermatogenous tissu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizoid
Rhizoids are protuberances that extend from the lower epidermal cells of bryophytes and algae. They are similar in structure and function to the root hairs of vascular land plants. Similar structures are formed by some fungi. Rhizoids may be unicellular or multicellular. Evolutionary development Plants originated in aquatic environments and gradually migrated to land during their long course of evolution. In water or near it, plants could absorb water from their surroundings, with no need for any special absorbing organ or tissue. Additionally, in the primitive states of plant development, tissue differentiation and division of labor was minimal, thus specialized water absorbing tissue was not required. The development of specialized tissues to absorb water efficiently and anchor themselves to the ground enabled the spread of plants to the land. Description Rhizoids absorb water mainly by capillary action, in which water moves up between threads of rhizoids and not through ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemma (botany)
A gemma (plural ''gemmae'') is a single cell, or a mass of cells, or a modified bud of tissue, that detaches from the parent and develops into a new individual. This type of asexual reproduction is referred to as fragmentation. It is a means of asexual propagation in plants. These structures are commonly found in fungi, algae, liverworts and mosses, but also in some flowering plants such as pygmy sundews and some species of butterworts. Vascular plants have many other methods of asexual reproduction including bulbils and turions. In mosses and liverworts The production of gemmae is a widespread means of asexual reproduction in both liverworts and mosses. In liverworts such as ''Marchantia'', the flattened plant body or thallus is a haploid gametophyte A gametophyte () is one of the two alternating multicellular phases in the life cycles of plants and algae. It is a haploid multicellular organism that develops from a haploid spore that has one set of chromosomes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mushroom
A mushroom or toadstool is the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus, typically produced above ground, on soil, or on its food source. ''Toadstool'' generally denotes one poisonous to humans. The standard for the name "mushroom" is the cultivated white button mushroom, ''Agaricus bisporus''; hence the word "mushroom" is most often applied to those fungi ( Basidiomycota, Agaricomycetes) that have a stem ( stipe), a cap ( pileus), and gills (lamellae, sing. lamella) on the underside of the cap. "Mushroom" also describes a variety of other gilled fungi, with or without stems, therefore the term is used to describe the fleshy fruiting bodies of some Ascomycota. These gills produce microscopic spores that help the fungus spread across the ground or its occupant surface. Forms deviating from the standard morphology usually have more specific names, such as "bolete", "puffball", "stinkhorn", and " morel", and gilled mushrooms themselves are often called "agarics" in refere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |