|
Black History For Action
In politics and history the Black History for Action (BHA), founded in 1986, became a long-standing and highly regarded independent lecture and discussion forum for the British African-Caribbean community in London. Nature and purpose Notable speakers have included the Jamaican academic Dr. Richard Hart, Maria Florez, the Cuban ambassador to Britain, representatives of the South African African National Congress and Pan-African Congress, and the Florida human-rights activist Omali Yeshitela. Lecture topics have included: "200 years since the Haitian Revolution" (1991 season); "Black Women and the Garvey Movement" (1988 season) and "Harriet Tubman" (1990 season). Each lecture was followed by a public debate. The purpose of the forum was to stimulate debate, learning and public interest in Pan-African history and politics in an atmosphere of academic and political freedom. Location BHA was held fortnightly (then monthly), primarily in Brixton, but also in other London loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Politics
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studies politics and government is referred to as political science. It may be used positively in the context of a "political solution" which is compromising and nonviolent, or descriptively as "the art or science of government", but also often carries a negative connotation.. The concept has been defined in various ways, and different approaches have fundamentally differing views on whether it should be used extensively or limitedly, empirically or normatively, and on whether conflict or co-operation is more essential to it. A variety of methods are deployed in politics, which include promoting one's own political views among people, negotiation with other political subjects, making laws, and exercising internal and external force, including wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
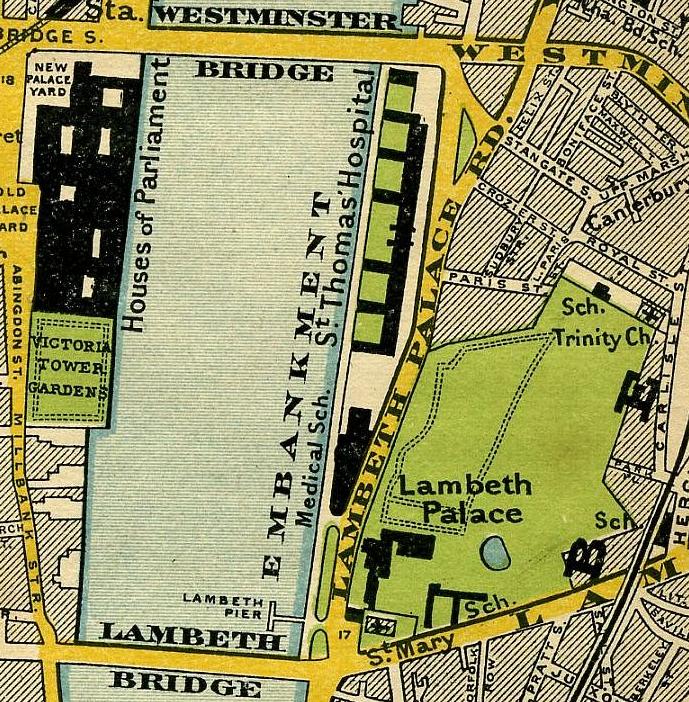
Lambeth
Lambeth () is a district in South London, England, in the London Borough of Lambeth, historically in the County of Surrey. It is situated south of Charing Cross. The population of the London Borough of Lambeth was 303,086 in 2011. The area experienced some slight growth in the medieval period as part of the manor of Lambeth Palace. By the Victorian era the area had seen significant development as London expanded, with dense industrial, commercial and residential buildings located adjacent to one another. The changes brought by World War II altered much of the fabric of Lambeth. Subsequent development in the late 20th and early 21st centuries has seen an increase in the number of high-rise buildings. The area is home to the International Maritime Organization. Lambeth is home to one of the largest Lusophone, Portuguese-speaking communities in the UK, and is the second most commonly spoken language in Lambeth after English language, English. History Medieval The origins of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black British Culture In London
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white have often been used to describe opposites such as good and evil, the Dark Ages versus Age of Enlightenment, and night versus day. Since the Middle Ages, black has been the symbolic color of solemnity and authority, and for this reason it is still commonly worn by judges and magistrates. Black was one of the first colors used by artists in Neolithic cave paintings. It was used in ancient Egypt and Greece as the color of the underworld. In the Roman Empire, it became the color of mourning, and over the centuries it was frequently associated with death, evil, witches, and magic. In the 14th century, it was worn by royalty, clergy, judges, and government officials in much of Europe. It became the color worn by English romantic poets, businessmen a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afro-Caribbean Culture In London
Afro-Caribbean people or African Caribbean are Caribbean people who trace their full or partial ancestry to Sub-Saharan Africa. The majority of the modern African-Caribbeans descend from Africans taken as slaves to colonial Caribbean via the trans-Atlantic slave trade between the 15th and 19th centuries to work primarily on various sugar plantations and in domestic households. Other names for the ethnic group include Black Caribbean, Afro or Black West Indian or Afro or Black Antillean. The term Afro-Caribbean was not coined by Caribbean people themselves but was first used by European Americans in the late 1960s. People of Afro-Caribbean descent today are largely of West African ancestry, and may additionally be of other origins, including European, South Asian and native Caribbean descent, as there has been extensive intermarriage and unions among the peoples of the Caribbean over the centuries. Although most Afro-Caribbean people today continue to live in English, French a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Studies
African studies is the study of Africa, especially the continent's cultures and societies (as opposed to its geology, geography, zoology, etc.). The field includes the study of Africa's history (pre-colonial, colonial, post-colonial), demography (ethnic groups), culture, politics, economy, languages, and religion (Islam, Christianity, traditional religions). A specialist in African studies is often referred to as an "africanist". A key focus of the discipline is to interrogate epistemological approaches, theories and methods in traditional disciplines using a critical lens that inserts African-centred “ways of knowing” and references. Africanists argue that there is a need to "deexoticize" Africa and banalise it, rather than understand Africa as exceptionalized and exoticized.Mamdani, M. (1996), Chapter 1 from Mamdani, M., ''Citizen and Subject: contemporary Africa and the legacy of late colonialism''. African scholars, in recent times, have focused on decolonizing African ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1986 Establishments In The United Kingdom
The year 1986 was designated as the International Year of Peace by the United Nations. Events January * January 1 **Aruba gains increased autonomy from the Netherlands by separating from the Netherlands Antilles. **Spain and Portugal enter the European Community, which becomes the European Union in 1993. *January 11 – The Gateway Bridge in Brisbane, Australia, at this time the world's longest prestressed concrete free-cantilever bridge, is opened. *January 13– 24 – South Yemen Civil War. *January 20 – The United Kingdom and France announce plans to construct the Channel Tunnel. *January 24 – The Voyager 2 space probe makes its first encounter with Uranus. *January 25 – Yoweri Museveni's National Resistance Army Rebel group takes over Uganda after leading a five-year guerrilla war in which up to half a million people are believed to have been killed. They will later use January 26 as the official date to avoid a coincidence of dates with Dictator Idi Amin's 1971 co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malcolm X
Malcolm X (born Malcolm Little, later Malik el-Shabazz; May 19, 1925 – February 21, 1965) was an American Muslim minister and human rights activist who was a prominent figure during the civil rights movement. A spokesman for the Nation of Islam until 1964, he was a vocal advocate for Black empowerment and the promotion of Islam within the Black community. A posthumous autobiography, on which he collaborated with Alex Haley, was published in 1965. Malcolm spent his adolescence living in a series of foster homes or with relatives after his father's death and his mother's hospitalization. He committed various crimes, being sentenced to 10 years in prison in 1946 for larceny and burglary. In prison he joined the Nation of Islam (adopting the name MalcolmX to symbolize his unknown African ancestral surname while discarding "the White slavemaster name of 'Little'"), and after his parole in 1952 quickly became one of the organization's most influential leaders. He was the public ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
How Europe Underdeveloped Africa
''How Europe Underdeveloped Africa'' is a 1972 book written by Walter Rodney that describes how Africa was deliberately exploited and underdeveloped by European colonial regimes. One of his main arguments throughout the book is that Africa developed Europe at the same rate that Europe underdeveloped Africa. Rodney argues that a combination of power politics and economic exploitation of Africa by Europeans led to the poor state of African political and economic development evident in the late 20th century. Though, he did not intend "to remove the ultimate responsibility for development from the shoulders of Africans... e believes thatevery African has a responsibility to understand the apitalistsystem and work for its overthrow." This book, along with Frantz Fanon's ''The Wretched of the Earth'', is a popular example of 20th century books concerning African development and post-colonial theory. Background First published in London by Bogle-L'Ouverture Publications in 1972 (in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Rodney
Walter Anthony Rodney (23 March 1942 – 13 June 1980) was a Guyanese historian, political activist and academic. His notable works include ''How Europe Underdeveloped Africa'', first published in 1972. Rodney was assassinated in Georgetown, Guyana, in 1980. Early career Walter Rodney was born in 1942 into a working-class family in Georgetown, Guyana. He attended the University College of the West Indies in 1960 and was awarded a first-class honours degree in history in 1963. He earned a PhD in African History in 1966 at the School of Oriental and African Studies in London, England at the age of 24. His dissertation, which focused on the slave trade on the Upper Guinea Coast, was published by the Oxford University Press in 1970 under the title ''A History of the Upper Guinea Coast 1545–1800'' and was widely acclaimed for its originality in challenging the conventional wisdom on the topic. Rodney travelled widely and became known internationally as an activist, scholar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Caribbean Times
''The Caribbean Times'' was a British weekly newspaper that was first published in 1981 by Hansib Publications, a publishing house for Caribbean, African and Asian writers and their communities, founded in London by Guyanese-born businessman Arif Ali in 1970.Marika Sherwoodreview of ''Caribbean Publishing in Britain. A Tribute to Arif Ali'' by Asher Hoyles and Martin Hoyles (review no. 1106) Reviews in History. The newspaper covered news, sport and social developments in the Caribbean, targeting the UK's West Indian and African-Caribbean population. It was "an important anti-racist campaigning organ" and the UK's oldest Black weekly newspaper. Hansib brought out other publications, including the weekly ''Asian Times'' in 1983 and the ''African Times'' in 1984, but in 1997 sold off the newspapers in order to concentrate on producing books. The ''Caribbean Times'' was subsequently published by Ethnic Media Group Ltd, and in 2006 was merged with the ''New Nation ''New Nation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Voice (British Newspaper)
''The Voice'', founded in 1982, is a British national African-Caribbean newspaper operating in the United Kingdom. The paper is based in London and was published every Thursday until 2019 when it became monthly. It is available in a paper version by subscription and also online. History ''The Voice'' was founded in 1982 by Val McCalla, who was working on a London local paper called the ''East End News'' in 1981. He and a group of businesspeople and journalists created a weekly newspaper to cater for the interests of British-born African-Caribbean people. Until then, relevant publications had mastheads such as the '' West Indian Gazette'', ''West Indian World'', ''The Caribbean Times'' and ''West Africa''. This was in order to address the interests of a generation of immigrants, by passing on news from their countries of origin in the Caribbean and Africa, rather than addressing the concerns of generations born in the UK. According to Beulah Ainley, who worked with McCalla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |