|
Biuret Protein Assay
Biuret is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a white solid that is soluble in hot water. A variety of organic derivatives are known. The term "biuret" also describes a family of organic compounds with the chemical formula , where are hydrogen, organyl or other groups. Also known as carbamylurea, it results from the condensation of two equivalents of urea. As such, it is an undesirable impurity in urea-based fertilizers. As biuret is toxic to plants, its percentage in fertilizers must be kept low. Preparation and structure The parent compound can be prepared by heating urea at 150 °C for ~6 hours until it gets slightly cloudy, then recrystallizing from water. After that, it can be recrystallized repeatedly from 2% sodium hydroxide solution and water to finally get base-free crystalline needles of the monohydrate which are free of cyanuric acid. While heating, a lot of ammonia is expelled: : Under related conditions, pyrolysis of urea affords triuret . In general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Chemistry
The Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) is a learned society (professional association) in the United Kingdom with the goal of "advancing the chemistry, chemical sciences". It was formed in 1980 from the amalgamation of the Chemical Society, the Royal Institute of Chemistry, the Faraday Society, and the Society for Analytical Chemistry with a new Royal Charter and the dual role of learned society and professional body. At its inception, the Society had a combined membership of 34,000 in the UK and a further 8,000 abroad. The headquarters of the Society are at Burlington House, Piccadilly, London. It also has offices in Thomas Graham House in Cambridge (named after Thomas Graham (chemist), Thomas Graham, the first president of the Chemical Society) where ''RSC Publishing'' is based. The Society has offices in the United States, on the campuses of The University of Pennsylvania and Drexel University, at the University City Science Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in both Beijing a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allophanic Acid
Allophanic acid is the organic compound with the formula H2NC(O)NHCO2H. It is a carbamic acid, the carboxylated derivative of urea. Biuret can be viewed as the amide of allophanic acid. The compound can be prepared by treating urea with sodium bicarbonate: :H2NC(O)NH2 + NaHCO3 → H2NC(O)NHCO2H + NaOH The anionicconjugate base, H2NC(O)NHCO2−, is called allophanate. Salt of this anion have been characterized by X-ray crystallography.{{cite journal , doi=10.1080/10610279608233970, title=A Novel Inclusion Compound Consolidated by Host-host and Host-guest Hydrogen Bonding: (2-hydro-xyethyl)trimethylammonium Ions Included in a Channel Host Lattice Built of Urea Molecules and Allophanate Ions, year=1996, last1=Li, first1=Qi, last2=Mak, first2=Thomas C. W., journal=Supramolecular Chemistry, volume=8, pages=73–80 The anion allophonate is the substrate for the enzyme allophanate hydrolase. Allophonate esters arise from the condensation of carbamates. References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanuric Acid
Cyanuric acid or 1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triol is a chemical compound with the formula (CNOH)3. Like many industrially useful chemicals, this triazine has many synonyms. This white, odorless solid finds use as a precursor or a component of bleaches, disinfectants, and herbicides. In 1997, worldwide production was 160 000 tonnes.Klaus Huthmacher, Dieter Most "Cyanuric Acid and Cyanuric Chloride" Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry" 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi 10.1002/14356007.a08 191 Properties and synthesis Properties Cyanuric acid can be viewed as the cyclic trimer of the elusive species cyanic acid, HOCN. The ring can readily interconvert between several structures via lactam-lactim tautomerism. Although the triol tautomer may have aromatic character, the keto form predominates in solution. The hydroxyl (-OH) groups assume phenolic character. Deprotonation with base affords a series of cyanurate salts: : (O)NHsub>3 ⇌ (O)NHsub>2 (O)Nsup>− + H+ (pKa = 6. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustav Heinrich Wiedemann
Gustav Heinrich Wiedemann (; 2 October 1826 – 24 March 1899) was a German physicist and scientific author. Life Wiedemann was born in Berlin the son of a merchant who died two years later. Following the death of his mother in 1842 he lived with his grandparents. After attending a private school as well as the Cölnische Humanistische Gymnasium, he entered the University of Berlin in 1844 where took his doctor's degree three years later under the supervision of Heinrich Gustav Magnus. His thesis on that occasion was devoted to a question in organic chemistry, for he held the opinion that the study of chemistry is an indispensable preliminary to the pursuit of physics, which was his ultimate aim. In Berlin he made the acquaintance of Hermann von Helmholtz at the house of Heinrich Gustav Magnus and was one of the founders of the Berlin Physical Society. In 1854 he left Germany to take on the role of Professor of Physics in Basel, nine years later he moved to Braunschweig and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
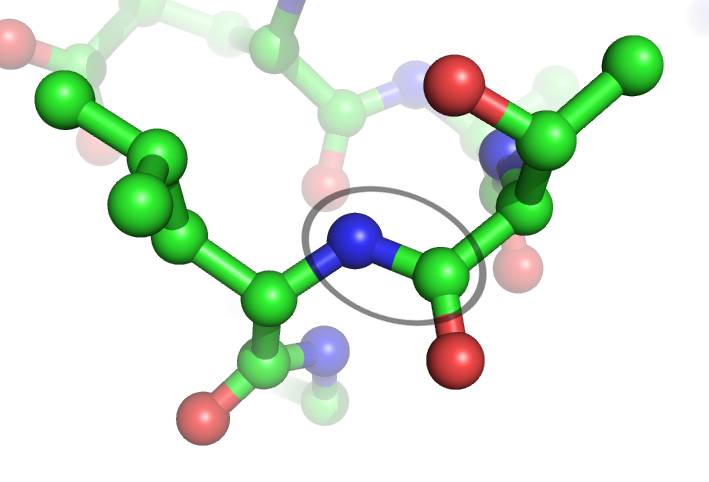
Peptide Bond
In organic chemistry, a peptide bond is an amide type of covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive alpha-amino acids from C1 (carbon number one) of one alpha-amino acid and N2 (nitrogen number two) of another, along a peptide or protein chain. It can also be called a eupeptide bond to distinguish it from an isopeptide bond, which is another type of amide bond between two amino acids. Synthesis When two amino acids form a ''dipeptide'' through a ''peptide bond'', it is a type of condensation reaction. In this kind of condensation, two amino acids approach each other, with the non-side chain (C1) carboxylic acid moiety of one coming near the non-side chain (N2) amino moiety of the other. One loses a hydrogen and oxygen from its carboxyl group (COOH) and the other loses a hydrogen from its amino group (NH2). This reaction produces a molecule of water (H2O) and two amino acids joined by a peptide bond (−CO−NH−). The two joined amino acids are called a dipeptide. The am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biuret Reagent
Biuret is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a white solid that is soluble in hot water. A variety of organic derivatives are known. The term "biuret" also describes a family of organic compounds with the chemical formula , where are hydrogen, organyl or other groups. Also known as carbamylurea, it results from the condensation of two equivalents of urea. As such, it is an undesirable impurity in urea-based fertilizers. As biuret is toxic to plants, its percentage in fertilizers must be kept low. Preparation and structure The parent compound can be prepared by heating urea at 150 °C for ~6 hours until it gets slightly cloudy, then recrystallizing from water. After that, it can be recrystallized repeatedly from 2% sodium hydroxide solution and water to finally get base-free crystalline needles of the monohydrate which are free of cyanuric acid. While heating, a lot of ammonia is expelled: : Under related conditions, pyrolysis of urea affords triuret . In general, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polypeptides
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Hence, peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. A polypeptide that contains more than approximately 50 amino acids is known as a protein. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, or to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cyclic peptides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Test
In chemistry, a chemical test is a qualitative property, qualitative or Quantitative property, quantitative procedure designed to identify, quantify, or characterise a chemical compound or substituent, chemical group. Purposes Chemical testing might have a variety of purposes, such as to: * Determine if, or verify that, the requirements of a specification, regulation, or contract are met * Decide if a new product development program is on track: Demonstrate proof of concept * Demonstrate the utility of a proposed patent * Determine the interactions of a sample with other known substances * Determine the composition of a sample * Provide Technical standard, standard data for other scientific, medical, and Quality assurance functions * Validate suitability for end-use * Provide a basis for Technical communication * Provide a technical means of comparison of several options * Provide evidence in legal proceedings Biochemical tests * Clinistrips quantitatively test for sugar in uri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biuret Test
Biuret is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a white solid that is soluble in hot water. A variety of organic derivatives are known. The term "biuret" also describes a family of organic compounds with the chemical formula , where are hydrogen, organyl or other groups. Also known as carbamylurea, it results from the condensation of two equivalents of urea. As such, it is an undesirable impurity in urea-based fertilizers. As biuret is toxic to plants, its percentage in fertilizers must be kept low. Preparation and structure The parent compound can be prepared by heating urea at 150 °C for ~6 hours until it gets slightly cloudy, then recrystallizing from water. After that, it can be recrystallized repeatedly from 2% sodium hydroxide solution and water to finally get base-free crystalline needles of the monohydrate which are free of cyanuric acid. While heating, a lot of ammonia is expelled: : Under related conditions, pyrolysis of urea affords triuret . In general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Animal Science
The ''Journal of Animal Science'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal in the field of animal science. It is published by the American Society of Animal Science. External links * Monthly journals Publications established in 1910 English-language journals Animal science journals Academic journals associated with learned and professional societies of the United States {{zoo-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |