|
Bison Occidentalis
''Bison occidentalis'' is an extinct species of bison that lived in North America, and in continental EurasiaC. G Van Zyll de Jong , 1986, A systematic study of recent bison, with particular consideration of the wood bison (Bison bison athabascae Rhoads 1898), p.53, National Museum of Natural Sciences and the Japanese archipelago from about 11,700 to 5,000 years ago, spanning the end of the Pleistocene to the mid-Holocene. Characteristics Likely evolving from ''Bison antiquus'', ''B. occidentalis'' was smaller overall from its most direct ancestor, but was similar to the distant ancestor the steppe bison (''Bison priscus'') in size. ''B. occidentalis'' had a highly variable morphology, and their horns, which pointed rearward, were much thinner and pointed than other Pleistocene species of bison. ''B. occidentalis'', like other bison species, may have existed in small, scattered populations and been unable to increase in numbers until after the Pleistocene epoch ended 10,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing Great American Interchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
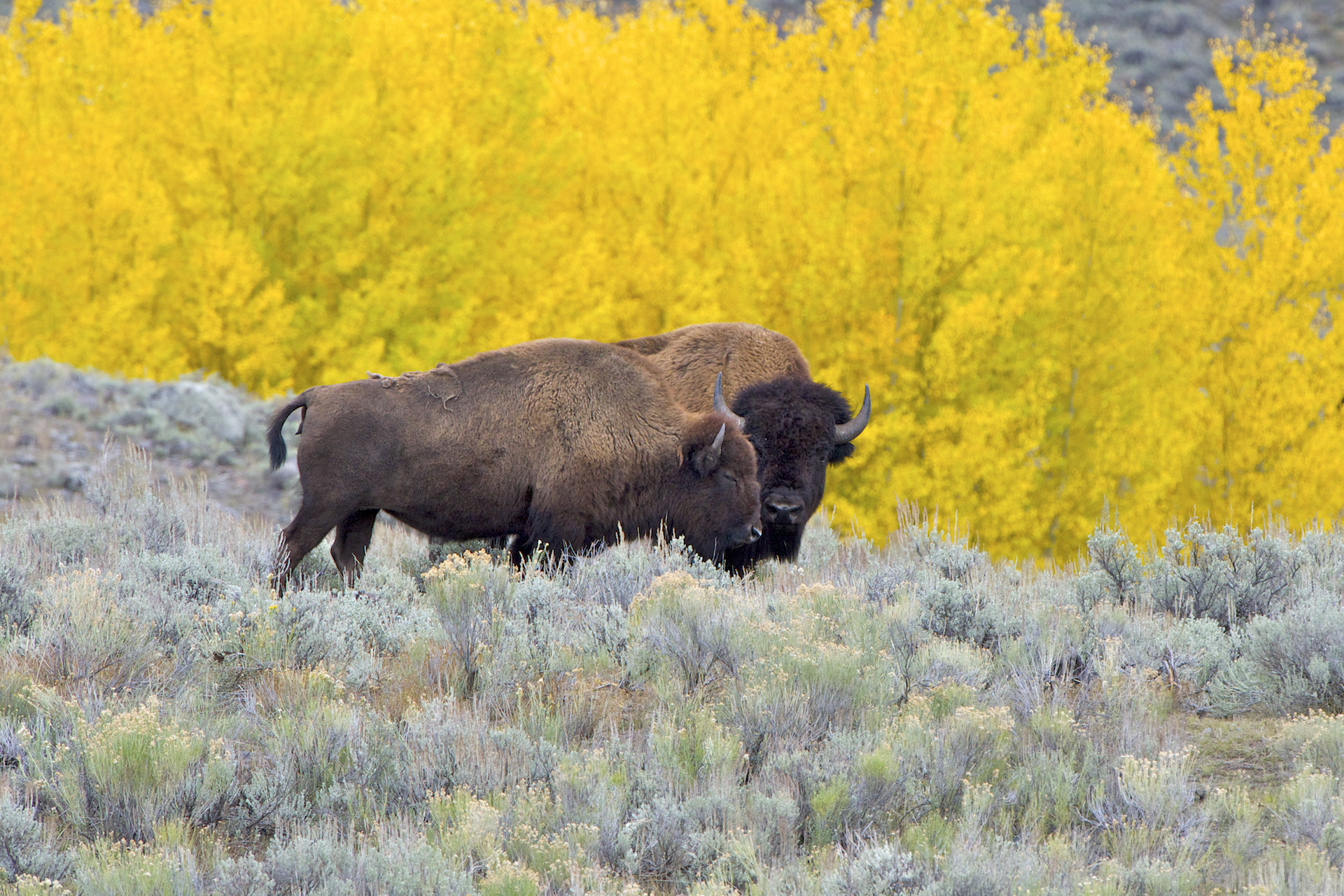
American Bison
The American bison (''Bison bison'') is a species of bison native to North America. Sometimes colloquially referred to as American buffalo or simply buffalo (a different clade of bovine), it is one of two extant species of bison, alongside the European bison. Its historical range, by 9000 BC, is described as the great bison belt, a tract of rich grassland that ran from Alaska to the Gulf of Mexico, east to the Atlantic Seaboard (nearly to the Atlantic tidewater in some areas) as far north as New York, south to Georgia and, according to some sources, further south to Florida, with sightings in North Carolina near Buffalo Ford on the Catawba River as late as 1750. Once roaming in vast herds, the species nearly became extinct by a combination of commercial hunting and slaughter in the 19th century and introduction of bovine diseases from domestic cattle. With a population in excess of 60 million in the late 18th century, the species was culled down to just 541 animals by 1889. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Mammals Of North America
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene Even-toed Ungulates
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing a faunal interchange between the two r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Bovids
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bison
Bison are large bovines in the genus ''Bison'' (Greek: "wild ox" (bison)) within the tribe Bovini. Two extant and numerous extinct species are recognised. Of the two surviving species, the American bison, ''B. bison'', found only in North America, is the more numerous. Although colloquially referred to as a buffalo in the United States and Canada, it is only distantly related to the true buffalo. The North American species is composed of two subspecies, the Plains bison, ''B. b. bison'', and the wood bison, ''B. b. athabascae'', which is the namesake of Wood Buffalo National Park in Canada. A third subspecies, the eastern bison (''B. b. pennsylvanicus'') is no longer considered a valid taxon, being a junior synonym of ''B. b. bison''. References to "woods bison" or "wood bison" from the eastern United States refer to this subspecies, not ''B. b. athabascae'', which was not found in the region. The European bison, ''B. bonasus'', or wisent, or zubr, or colloquially European buff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steppe Bison
The steppe bisonSeveral literatures address the species as ''primeval bison''. or steppe wisent (''Bison'' ''priscus'') – Yukon Beringia Interpretive Centre. Beringia.com. Retrieved on 2013-05-31. is an extinct species of that was once found on the where its range included , , [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Bison Belt
The great bison belt is a tract of rich grassland that ran from Alaska to the Gulf of Mexico from around 9000 BC. The great bison belt was supported by spring and early summer rainfall that allowed short grasses to grow. These grasses retain their moisture at the roots which allowed for grazing ungulates such as bison to find high-quality nutritious food in autumn. These grasses are what allowed the bison population to thrive, as they were able to receive all of their nutrients from the short grasses, unlike other Ice Age animals which expanded in the postglacial period. This area was important to the Plains Paleo-Indians, who around 8500 BC turned to bison hunting instead of hunting a broader range of food. Early history About 50–75 million years ago, surging molten rock formed the mountain ranges of the west, including the Black Hills. About 10 million years ago, geological forces shaped the rest of the Great Bison Belt, the largest terrestrial biome in North America. Whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronospecies
A chronospecies is a species derived from a anagenesis, sequential development pattern that involves continual and uniform changes from an extinct ancestral form on an evolutionary scale. The sequence of alterations eventually produces a population that is physically, Comparative anatomy, morphologically, and/or Genetics, genetically distinct from the original ancestors. Throughout the change, there is only one species in the lineage at any point in time, as opposed to cases where divergent evolution produces contemporary species with a common ancestor. The related term paleospecies (or palaeospecies) indicates an extinct species only identified with fossil material. That identification relies on distinct similarities between the earlier fossil specimens and some proposed descendant although the exact relationship to the later species is not always defined. In particular, the range of variation within all the early fossil specimens does not exceed the observed range that exists in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient DNA
Ancient DNA (aDNA) is DNA isolated from ancient specimens. Due to degradation processes (including cross-linking, deamination and fragmentation) ancient DNA is more degraded in comparison with contemporary genetic material. Even under the best preservation conditions, there is an upper boundary of 0.4–1.5 million years for a sample to contain sufficient DNA for sequencing technologies. The oldest sample ever sequenced is estimated to be 1.65 million years old. Genetic material has been recovered from paleo/archaeological and historical skeletal material, mummified tissues, archival collections of non-frozen medical specimens, preserved plant remains, ice and from permafrost cores, marine and lake sediments and excavation dirt. On 7 December 2022, ''The New York Times'' reported that two-million year old genetic material was found in Greenland, and is currently considered the oldest DNA discovered so far. History of ancient DNA studies 1980s The first study of what would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plains Bison
The Plains bison (''Bison bison bison'') is one of two subspecies/ecotypes of the American bison, the other being the wood bison (''B. b. athabascae''). A natural population of Plains bison survives in Yellowstone National Park (the Yellowstone Park bison herd consisting of an estimated 4,800 bison) and multiple smaller reintroduced herds of bison in many places in the United States as well as southern portions of the Canadian Prairies. Near-extinction and reintroduction of herds At one time, at least 25 million American bison were spread across the United States and Canada. However, by the late 1880s, the total number of bison in the United States had been reduced to fewer than 600. Most of these were collected onto various private ranches, and the last known free-roaming population of bison consisted of fewer than 30 in the area which later became Yellowstone National Park. Although farmers and ranchers considered bison to be a nuisance, some people were concerned about the dem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood Bison
The wood bison (''Bison bison athabascae'') or mountain bison (often called the wood buffalo or mountain buffalo), is a distinct northern subspecies or ecotype of the American bison. Its original range included much of the boreal forest regions of Alaska, Yukon, western Northwest Territories, northeastern British Columbia, northern Alberta, and northwestern Saskatchewan.Wood Bison Restoration in Alaska Alaska Department of Fish & Game, Division of Wildlife Conservation Name The term "buffalo" is considered to be a for this animal, as it is only distantly related to either of the two "true buffalo", the Asian |







.jpg)