|
BioModels Database, Logo 2014
BioModels is a free and open-source repository for storing, exchanging and retrieving quantitative models of biological interest created in 2006. All the models in the curated section of BioModels Database have been described in peer-reviewed scientific literature. The models stored in BioModels' curated branch are compliant with MIRIAM, the standard of model curation and annotation. The models have been simulated by curators to check that when run in simulations, they provide the same results as described in the publication. Model components are annotated, so the users can conveniently identify each model element and retrieve further information from other resources. Modellers can submit the models in SBML and CellML. Models can subsequently be downloaded in SBMLVCML |
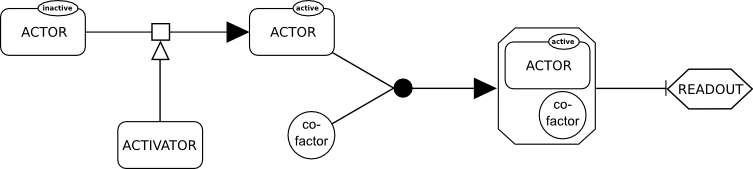
Systems Biology Graphical Notation
The Systems Biology Graphical Notation (SBGN) is a standard graphical representation intended to foster the efficient storage, exchange and reuse of information about signaling pathways, metabolic networks, and gene regulatory networks amongst communities of biochemists, biologists, and theoreticians. The system was created over several years by a community of biochemists, modelers and computer scientists. SBGN is made up of three orthogonal languages for representing different views of biological systems: ''Process Descriptions'', ''Entity Relationships'' and ''Activity Flows''. Each language defines a comprehensive set of symbols with precise semantics, together with detailed syntactic rules regarding the construction and interpretation of maps. Using these three notations, a life scientist can represent in an unambiguous way networks of interactions (for example biochemical interactions). These notations make use of an idea and symbols similar to that used by electrical and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Center For Research Resources
The National Center for Research Resources (NCRR) was a center within the National Institutes of Health a United States government agency. NCRR provided funding to laboratory scientists and researchers for facilities and tools in the goal of curing and treating diseases. Organization and history The National Center for Research Resources (NCRR) was one of the 27 institutes and centers that make up the National Institutes of Health (NIH) within the Department of Health and Human Services of the federal government of the United States. The NIH is one of eight agencies under the Public Health Service (PHS) in the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). In 1990 the Division of Research Resources and the Division of Research Services were merged to form the ''National Center for Research Resources''. Its mission statement declares that it "provides laboratory scientists and clinical researchers with environments and tools that they can use to prevent, detect, and treat a wide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DARPA
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military. Originally known as the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA), the agency was created on February 7, 1958, by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in response to the Soviet launching of Sputnik 1 in 1957. By collaborating with academia, industry, and government partners, DARPA formulates and executes research and development projects to expand the frontiers of technology and science, often beyond immediate U.S. military requirements.Dwight D. Eisenhower and Science & Technology, (2008). Dwight D. Eisenhower Memorial CommissionSource '' The Economist'' has called DARPA the agency "that shaped the modern world," and pointed out that " Moderna's COVID-19 vaccine sits alongside weather satellites, GPS, drones, stealth technology, voice interfaces, the personal comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute Of General Medical Sciences
The National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS) supports basic research that increases understanding of biological processes and lays the foundation for advances in disease diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. NIGMS-funded scientists investigate how living systems work at a range of levels, from molecules and cells to tissues and organs, in research organisms, humans, and populations. Additionally, to ensure the vitality and continued productivity of the research enterprise, NIGMS provides leadership in training the next generation of scientists, in enhancing the diversity of the scientific workforce, and in developing research capacity throughout the country. NIGMS is one of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the principal medical research agency of the Federal Government. NIH is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. All NIH Institutes and Centers support basic research that is relevant to the diseases, organ systems, stages of li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Framework Programmes For Research And Technological Development
The Framework Programmes for Research and Technological Development, also called Framework Programmes or abbreviated FP1 to FP9, are funding programmes created by the European Union/European Commission to support and foster research in the European Research Area (ERA). Starting in 2014, the funding programmes were named Horizon. The funding programmes began in 1984 and continue to the present day. The most recent programme, Horizon Europe, has a budget of 95.5 billion Euros to be distributed over 7 years. The specific objectives and actions vary between funding periods. In FP6 and FP7, focus was on technological research. In Horizon 2020, the focus was on innovation, delivering economic growth faster, and delivering solutions to end users that are often governmental agencies. Background Conducting European research policies and implementing European research programmes is an obligation under the Amsterdam Treaty, which includes a chapter on research and technological developme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innovative Medicines Initiative
The Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI) is a European initiative to improve the competitive situation of the European Union in the field of pharmaceutical research. The IMI is a joint initiative ( public-private partnership) of the DG Research of the European Commission, representing the European Communities, and the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations (EFPIA). IMI is laid out as a Joint Technology Initiative within the Seventh Framework Programme. Michel Goldman was the first executive director, from September 2009 until December 2014. The Innovative Medicines Initiative is aimed towards removing research bottlenecks in the current drug development process. The IMI Joint Technology Initiative (IMI JTI), to be implemented by the IMI Joint Undertaking is meant to address these research bottlenecks. Its €2bn budget makes it the largest biomedical public-private partnership in the world. The funding scheme has been criticised, requiring unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotechnology And Biological Sciences Research Council
Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC), part of UK Research and Innovation, is a non-departmental public body (NDPB), and is the largest UK public funder of non-medical bioscience. It predominantly funds scientific research institutes and university research departments in the UK. Purpose Receiving its funding through the science budget of the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS), BBSRC's mission is to "promote and support, by any means, high-quality basic, strategic and applied research and related postgraduate training relating to the understanding and exploitation of biological systems". Structure BBSRC's head office is at Polaris House in Swindon - the same building as the other councils of UK Research and Innovation, AHRC EPSRC, ESRC, Innovate UK, MRC, NERC, Research England and STFC, as well as the UKSA. Funded by Government, BBSRC invested over £498 million in bioscience in 2017–18. BBSRC also manages t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Molecular Biology Laboratory
The European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) is an intergovernmental organization dedicated to molecular biology research and is supported by 27 member states, two prospect states, and one associate member state. EMBL was created in 1974 and is funded by public research money from its member states. Research at EMBL is conducted by approximately 110 independent research and service groups and teams covering the spectrum of molecular biology and bioinformatics. The list of Groups and Teams at EMBL can be found at . The Laboratory operates from six sites: the main laboratory in Heidelberg, and sites in Hinxton (the European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI), in England), Grenoble (France), Hamburg (Germany), Rome (Italy) and Barcelona (Spain). EMBL groups and laboratories perform basic research in molecular biology and molecular medicine as well as train scientists, students, and visitors. The organization aids in the development of services, new instruments and methods, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EMBL
The European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) is an intergovernmental organization dedicated to molecular biology research and is supported by 27 member states, two prospect states, and one associate member state. EMBL was created in 1974 and is funded by public research money from its member states. Research at EMBL is conducted by approximately 110 independent research and service groups and teams covering the spectrum of molecular biology and bioinformatics. The list of Groups and Teams at EMBL can be found at . The Laboratory operates from six sites: the main laboratory in Heidelberg, and sites in Hinxton (the European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI), in England), Grenoble (France), Hamburg (Germany), Rome (Italy) and Barcelona (Spain). EMBL groups and laboratories perform basic research in molecular biology and molecular medicine as well as train scientists, students, and visitors. The organization aids in the development of services, new instruments and methods, and tech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Chemistry
The Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) is a learned society (professional association) in the United Kingdom with the goal of "advancing the chemistry, chemical sciences". It was formed in 1980 from the amalgamation of the Chemical Society, the Royal Institute of Chemistry, the Faraday Society, and the Society for Analytical Chemistry with a new Royal Charter and the dual role of learned society and professional body. At its inception, the Society had a combined membership of 34,000 in the UK and a further 8,000 abroad. The headquarters of the Society are at Burlington House, Piccadilly, London. It also has offices in Thomas Graham House in Cambridge (named after Thomas Graham (chemist), Thomas Graham, the first president of the Chemical Society) where ''RSC Publishing'' is based. The Society has offices in the United States, on the campuses of The University of Pennsylvania and Drexel University, at the University City Science Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in both Beijing a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BioMed Central
BioMed Central (BMC) is a United Kingdom-based, for-profit scientific open access publisher that produces over 250 scientific journals. All its journals are published online only. BioMed Central describes itself as the first and largest open access science publisher. It was founded in 2000 and has been owned by Springer, now Springer Nature, since 2008. History BioMed Central was founded in 2000 as part of the Current Science Group (now Science Navigation Group, SNG), a nursery of scientific publishing companies. SNG chairman Vitek Tracz developed the concept for the company after NIH director Harold Varmus's PubMed Central concept for open-access publishing was scaled back. The first director of the company was Jan Velterop. Chemistry Central was established in 2006 and the PhysMath Central journal imprint in 2007. In 2002, the company introduced article processing charges, and these have since been the primary source of revenue. In 2007 Yale University Libraries stopped s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |