|
Binary Regression
In statistics, specifically regression analysis, a binary regression estimates a relationship between one or more explanatory variables and a single output binary variable. Generally the probability of the two alternatives is modeled, instead of simply outputting a single value, as in linear regression. Binary regression is usually analyzed as a special case of binomial regression, with a single outcome (n = 1), and one of the two alternatives considered as "success" and coded as 1: the value is the count of successes in 1 trial, either 0 or 1. The most common binary regression models are the logit model (logistic regression) and the probit model (probit regression). Applications Binary regression is principally applied either for prediction (binary classification), or for estimating the association between the explanatory variables and the output. In economics, binary regressions are used to model binary choice. Interpretations Binary regression models can be interpreted as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics
Statistics (from German: '' Statistik'', "description of a state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments.Dodge, Y. (2006) ''The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms'', Oxford University Press. When census data cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey samples. Representative sampling assures that inferences and conclusions can reasonably extend from the sample to the population as a whole. An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latent Variable Model
A latent variable model is a statistical model that relates a set of observable variables (also called ''manifest variables'' or ''indicators'') to a set of latent variables. It is assumed that the responses on the indicators or manifest variables are the result of an individual's position on the latent variable(s), and that the manifest variables have nothing in common after controlling for the latent variable ( local independence). Different types of the latent variable models can be grouped according to whether the manifest and latent variables are categorical or continuous: The Rasch model represents the simplest form of item response theory. Mixture models are central to latent profile analysis. In factor analysis and latent trait analysis the latent variables are treated as continuous normally distributed variables, and in latent profile analysis and latent class analysis as from a multinomial distribution. The manifest variables in factor analysis and latent prof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Probability Model
In statistics, a linear probability model (LPM) is a special case of a binary regression model. Here the dependent variable for each observation takes values which are either 0 or 1. The probability of observing a 0 or 1 in any one case is treated as depending on one or more explanatory variables. For the "linear probability model", this relationship is a particularly simple one, and allows the model to be fitted by linear regression. The model assumes that, for a binary outcome (Bernoulli trial), Y, and its associated vector of explanatory variables, X, : \Pr(Y=1 , X=x) = x'\beta . For this model, : E X= \Pr(Y=1, X) =x'\beta, and hence the vector of parameters β can be estimated using least squares. This method of fitting would be inefficient, and can be improved by adopting an iterative scheme based on weighted least squares, in which the model from the previous iteration is used to supply estimates of the conditional variances, \operatorname(Y, X=x), which would vary be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exponential Family
In probability and statistics, an exponential family is a parametric set of probability distributions of a certain form, specified below. This special form is chosen for mathematical convenience, including the enabling of the user to calculate expectations, covariances using differentiation based on some useful algebraic properties, as well as for generality, as exponential families are in a sense very natural sets of distributions to consider. The term exponential class is sometimes used in place of "exponential family", or the older term Koopman–Darmois family. The terms "distribution" and "family" are often used loosely: specifically, ''an'' exponential family is a ''set'' of distributions, where the specific distribution varies with the parameter; however, a parametric ''family'' of distributions is often referred to as "''a'' distribution" (like "the normal distribution", meaning "the family of normal distributions"), and the set of all exponential families is sometimes lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generalized Linear Model
In statistics, a generalized linear model (GLM) is a flexible generalization of ordinary linear regression. The GLM generalizes linear regression by allowing the linear model to be related to the response variable via a ''link function'' and by allowing the magnitude of the variance of each measurement to be a function of its predicted value. Generalized linear models were formulated by John Nelder and Robert Wedderburn as a way of unifying various other statistical models, including linear regression, logistic regression and Poisson regression. They proposed an iteratively reweighted least squares method for maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) of the model parameters. MLE remains popular and is the default method on many statistical computing packages. Other approaches, including Bayesian regression and least squares fitting to variance stabilized responses, have been developed. Intuition Ordinary linear regression predicts the expected value of a given unknown quanti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Log-odds
In statistics, the logit ( ) function is the quantile function associated with the standard logistic distribution. It has many uses in data analysis and machine learning, especially in data transformations. Mathematically, the logit is the inverse of the standard logistic function \sigma(x) = 1/(1+e^), so the logit is defined as :\operatorname p = \sigma^(p) = \ln \frac \quad \text \quad p \in (0,1). Because of this, the logit is also called the log-odds since it is equal to the logarithm of the odds \frac where is a probability. Thus, the logit is a type of function that maps probability values from (0, 1) to real numbers in (-\infty, +\infty), akin to the probit function. Definition If is a probability, then is the corresponding odds; the of the probability is the logarithm of the odds, i.e.: :\operatorname(p)=\ln\left( \frac \right) =\ln(p)-\ln(1-p)=-\ln\left( \frac-1\right)=2\operatorname(2p-1) The base of the logarithm function used is of little importance in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Distribution
In statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is : f(x) = \frac e^ The parameter \mu is the mean or expectation of the distribution (and also its median and mode), while the parameter \sigma is its standard deviation. The variance of the distribution is \sigma^2. A random variable with a Gaussian distribution is said to be normally distributed, and is called a normal deviate. Normal distributions are important in statistics and are often used in the natural and social sciences to represent real-valued random variables whose distributions are not known. Their importance is partly due to the central limit theorem. It states that, under some conditions, the average of many samples (observations) of a random variable with finite mean and variance is itself a random variable—whose distribution converges to a normal d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Errors And Residuals
In statistics and optimization, errors and residuals are two closely related and easily confused measures of the deviation of an observed value of an element of a statistical sample from its "true value" (not necessarily observable). The error of an observation is the deviation of the observed value from the true value of a quantity of interest (for example, a population mean). The residual is the difference between the observed value and the ''estimated'' value of the quantity of interest (for example, a sample mean). The distinction is most important in regression analysis, where the concepts are sometimes called the regression errors and regression residuals and where they lead to the concept of studentized residuals. In econometrics, "errors" are also called disturbances. Introduction Suppose there is a series of observations from a univariate distribution and we want to estimate the mean of that distribution (the so-called location model). In this case, the errors are the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discounted Cash Flow
The discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis is a method in finance of valuing a security, project, company, or asset using the concepts of the time value of money. Discounted cash flow analysis is widely used in investment finance, real estate development, corporate financial management and patent valuation. It was used in industry as early as the 1700s or 1800s, widely discussed in financial economics in the 1960s, and became widely used in U.S. courts in the 1980s and 1990s. Application To apply the method, all future cash flows are estimated and discounted by using cost of capital to give their present values (PVs). The sum of all future cash flows, both incoming and outgoing, is the net present value (NPV), which is taken as the value of the cash flows in question; see aside. For further context see valuation overview; and for the mechanics see valuation using discounted cash flows, which includes modifications typical for startups, private equity and venture cap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is the mathematical function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of different possible outcomes for an experiment. It is a mathematical description of a random phenomenon in terms of its sample space and the probabilities of events (subsets of the sample space). For instance, if is used to denote the outcome of a coin toss ("the experiment"), then the probability distribution of would take the value 0.5 (1 in 2 or 1/2) for , and 0.5 for (assuming that the coin is fair). Examples of random phenomena include the weather conditions at some future date, the height of a randomly selected person, the fraction of male students in a school, the results of a survey to be conducted, etc. Introduction A probability distribution is a mathematical description of the probabilities of events, subsets of the sample space. The sample space, often denoted by \Omega, is the set of all possible outcomes of a rando ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Parameter
In statistics, as opposed to its general use in mathematics, a parameter is any measured quantity of a statistical population that summarises or describes an aspect of the population, such as a mean or a standard deviation. If a population exactly follows a known and defined distribution, for example the normal distribution, then a small set of parameters can be measured which completely describes the population, and can be considered to define a probability distribution for the purposes of extracting samples from this population. A parameter is to a population as a statistic is to a sample; that is to say, a parameter describes the ''true value'' calculated from the full population, whereas a statistic is an estimated measurement of the parameter based on a subsample. Thus a "statistical parameter" can be more specifically referred to as a population parameter..Everitt, B. S.; Skrondal, A. (2010), ''The Cambridge Dictionary of Statistics'', Cambridge University Press. Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
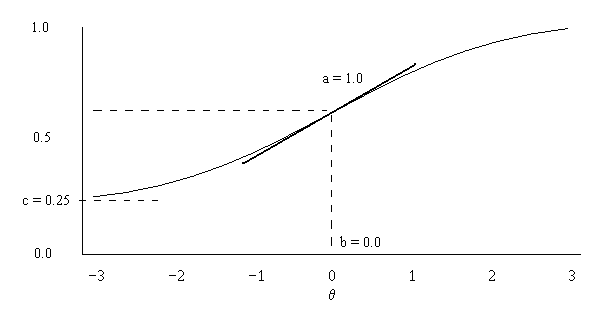
Item Response Theory
In psychometrics, item response theory (IRT) (also known as latent trait theory, strong true score theory, or modern mental test theory) is a paradigm for the design, analysis, and scoring of tests, questionnaires, and similar instruments measuring abilities, attitudes, or other variables. It is a theory of testing based on the relationship between individuals' performances on a test item and the test takers' levels of performance on an overall measure of the ability that item was designed to measure. Several different statistical models are used to represent both item and test taker characteristics. Unlike simpler alternatives for creating scales and evaluating questionnaire responses, it does not assume that each item is equally difficult. This distinguishes IRT from, for instance, Likert scaling, in which ''"''All items are assumed to be replications of each other or in other words items are considered to be parallel instruments".A. van Alphen, R. Halfens, A. Hasman and T. Imbos. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |