|
Binary Alignment Map
Binary Alignment Map (BAM) is the comprehensive raw data of genome sequencing; it consists of the lossless, compressed binary Binary may refer to: Science and technology Mathematics * Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two digits (0 and 1) * Binary function, a function that takes two arguments * Binary operation, a mathematical operation that ta ... representation of the Sequence Alignment Map-files. BAM is the compressed binary representation of SAM (Sequence Alignment Map), a compact and index-able representation of nucleotide sequence alignments. The goal of indexing is to retrieve alignments that overlap a specific location quickly without having to go through all of them. Before indexing, BAM must be sorted by reference ID and then leftmost coordinate. BAM is in compressed BGZF format. The structure of BAM files include a header section and an alignment section: * Header—The sample name, sample length, and alignment method are all included in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome Sequencing
Whole genome sequencing (WGS), also known as full genome sequencing, complete genome sequencing, or entire genome sequencing, is the process of determining the entirety, or nearly the entirety, of the DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a single time. This entails sequencing all of an organism's chromosomal DNA as well as DNA contained in the mitochondria and, for plants, in the chloroplast. Whole genome sequencing has largely been used as a research tool, but was being introduced to clinics in 2014. In the future of personalized medicine, whole genome sequence data may be an important tool to guide therapeutic intervention. The tool of gene sequencing at SNP level is also used to pinpoint functional variants from association studies and improve the knowledge available to researchers interested in evolutionary biology, and hence may lay the foundation for predicting disease susceptibility and drug response. Whole genome sequencing should not be confused with DNA profili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lossless
Lossless compression is a class of data compression that allows the original data to be perfectly reconstructed from the compressed data with no loss of information. Lossless compression is possible because most real-world data exhibits statistical redundancy. By contrast, lossy compression permits reconstruction only of an approximation of the original data, though usually with greatly improved compression rates (and therefore reduced media sizes). By operation of the pigeonhole principle, no lossless compression algorithm can efficiently compress all possible data. For this reason, many different algorithms exist that are designed either with a specific type of input data in mind or with specific assumptions about what kinds of redundancy the uncompressed data are likely to contain. Therefore, compression ratios tend to be stronger on human- and machine-readable documents and code in comparison to entropic binary data (random bytes). Lossless data compression is used in man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Code
A binary code represents text, computer processor instructions, or any other data using a two-symbol system. The two-symbol system used is often "0" and "1" from the binary number system. The binary code assigns a pattern of binary digits, also known as bits, to each character, instruction, etc. For example, a binary string of eight bits (which is also called a byte) can represent any of 256 possible values and can, therefore, represent a wide variety of different items. In computing and telecommunications, binary codes are used for various methods of encoding data, such as character strings, into bit strings. Those methods may use fixed-width or variable-width strings. In a fixed-width binary code, each letter, digit, or other character is represented by a bit string of the same length; that bit string, interpreted as a binary number, is usually displayed in code tables in octal, decimal or hexadecimal notation. There are many character sets and many character encodings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
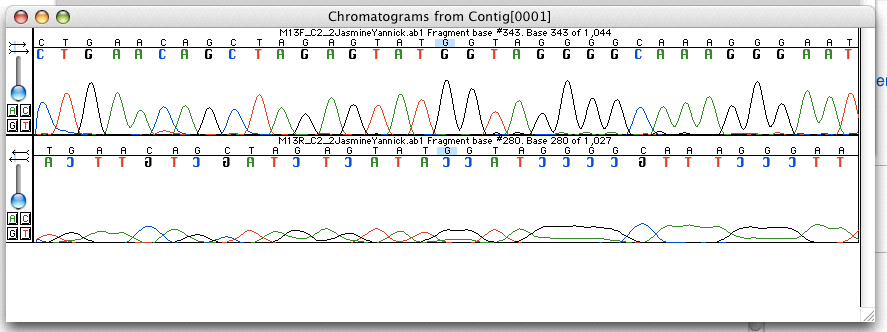
SAM (file Format)
Sequence Alignment Map (SAM) is a text-based format originally for storing biological sequences aligned to a reference sequence developed by Heng Li and Bob Handsaker ''et al''. It was developed when the 1000 Genomes Project wanted to move away from the MAQ mapper format and decided to design a new format. The overall TAB-delimited flavour of the format came from an earlier format inspired by BLAT’s PSL. The name of SAM came from Gabor Marth from University of Utah, who originally had a format under the same name but with a different syntax more similar to a BLAST output. It is widely used for storing data, such as nucleotide sequences, generated by next generation sequencing technologies, and the standard has been broadened to include unmapped sequences. The format supports short and long reads (up to 128 Mbp) produced by different sequencing platforms and is used to hold mapped data within the Genome Analysis Toolkit (GATK) and across the Broad Institute, the Wellcome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordinate System
In geometry, a coordinate system is a system that uses one or more numbers, or coordinates, to uniquely determine the position of the points or other geometric elements on a manifold such as Euclidean space. The order of the coordinates is significant, and they are sometimes identified by their position in an ordered tuple and sometimes by a letter, as in "the ''x''-coordinate". The coordinates are taken to be real numbers in elementary mathematics, but may be complex numbers or elements of a more abstract system such as a commutative ring. The use of a coordinate system allows problems in geometry to be translated into problems about numbers and ''vice versa''; this is the basis of analytic geometry. Common coordinate systems Number line The simplest example of a coordinate system is the identification of points on a line with real numbers using the '' number line''. In this system, an arbitrary point ''O'' (the ''origin'') is chosen on a given line. The coordinate of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FASTQ Format
FASTQ format is a text-based format for storing both a biological sequence (usually nucleotide sequence) and its corresponding quality scores. Both the sequence letter and quality score are each encoded with a single ASCII character for brevity. It was originally developed at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute to bundle a FASTA formatted sequence and its quality data, but has recently become the ''de facto'' standard for storing the output of high-throughput sequencing instruments such as the Illumina Genome Analyzer. Format A FASTQ file has four line-separated fields per sequence: * Field 1 begins with a '@' character and is followed by a sequence identifier and an ''optional'' description (like a FASTA title line). * Field 2 is the raw sequence letters. * Field 3 begins with a '+' character and is ''optionally'' followed by the same sequence identifier (and any description) again. * Field 4 encodes the quality values for the sequence in Field 2, and must contain the same num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAMtools
SAMtools is a set of utilities for interacting with and post-processing short DNA sequence read alignments in the SAM (Sequence Alignment/Map), BAM (Binary Alignment/Map) and CRAM formats, written by Heng Li. These files are generated as output by short read aligners like BWA. Both simple and advanced tools are provided, supporting complex tasks like variant calling and alignment viewing as well as sorting, indexing, data extraction and format conversion. SAM files can be very large (10s of Gigabytes is common), so compression is used to save space. SAM files are human-readable text files, and BAM files are simply their binary equivalent, whilst CRAM files are a restructured column-oriented binary container format. BAM files are typically compressed and more efficient for software to work with than SAM. SAMtools makes it possible to work directly with a compressed BAM file, without having to uncompress the whole file. Additionally, since the format for a SAM/BAM file is somewha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRAM (file Format)
Compressed Reference-oriented Alignment Map (CRAM) is a compressed columnar file format for storing biological sequences aligned to a reference sequence A reference genome (also known as a reference assembly) is a digital nucleic acid sequence database, assembled by scientists as a representative example of the set of genes in one idealized individual organism of a species. As they are assemble ..., initially devised by Markus Hsi-Yang Fritz ''et al''. CRAM was designed to be an efficient reference-based alternative to the Sequence Alignment Map (SAM) and Binary Alignment Map (BAM) file formats. It optionally uses a genomic reference to describe differences between the aligned sequence fragments and the reference sequence, reducing storage costs. Additionally each column in the SAM format is separated into its own blocks, improving compression ratio. CRAM files typically vary from 30 to 60% smaller than BAM, depending on the data held within them. Implementations of CRA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of File Formats
This is a list of file formats used by computers, organized by type. Filename extension it is usually noted in parentheses if they differ from the file format name or abbreviation. Many operating systems do not limit filenames to one extension shorter than 4 characters, as was common with some operating systems that supported the File Allocation Table (FAT) file system. Examples of operating systems that do not impose this limit include Unix-like systems, and Microsoft Windows NT, 95- 98, and ME which have no three character limit on extensions for 32-bit or 64-bit applications on file systems other than pre-Windows 95 and Windows NT 3.5 versions of the FAT file system. Some filenames are given extensions longer than three characters. While MS-DOS and NT always treat the suffix after the last period in a file's name as its extension, in UNIX-like systems, the final period does not necessarily mean that the text after the last period is the file's extension. Some file forma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |