|
Billy Budd, Sailor
''Billy Budd, Sailor (An Inside Narrative)'' is a novella by American writer Herman Melville, left unfinished at his death in 1891. Acclaimed by critics as a masterpiece when a hastily transcribed version was finally published in 1924, it quickly took its place as a classic second only to ''Moby-Dick'' among Melville's works. Billy Budd is a "handsome sailor" who strikes and inadvertently kills his false accuser, Master-at-arms John Claggart. The ship's Captain, Edward Vere, recognizes Billy's lack of intent, but claims that the law of mutiny requires him to sentence Billy to be hanged. Melville began work on the novella in November 1886, revising and expanding it from time to time, but he left the manuscript in disarray. Melville's widow Elizabeth began to edit the manuscript for publication, but was not able to discern her husband's intentions at key points, even as to the book's title. Raymond M. Weaver, Melville's first biographer, was given the manuscript and published t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herman Melville
Herman Melville (Name change, born Melvill; August 1, 1819 – September 28, 1891) was an American people, American novelist, short story writer, and poet of the American Renaissance (literature), American Renaissance period. Among his best-known works are ''Moby-Dick'' (1851); ''Typee'' (1846), a romanticized account of his experiences in Polynesia; and ''Billy Budd, Billy Budd, Sailor'', a posthumously published novella. Although his reputation was not high at the time of his death, the 1919 centennial of his birth was the starting point of a #Melville revival and Melville studies, Melville revival, and ''Moby-Dick'' grew to be considered one of the great American novels. Melville was born in New York City, the third child of a prosperous merchant whose death in 1832 left the family in dire financial straits. He took to sea in 1839 as a common sailor on a merchant ship and then on the whaler ''Acushnet'', but he jumped ship in the Marquesas Islands. ''Typee'', his first b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rights Of Man
''Rights of Man'' (1791), a book by Thomas Paine, including 31 articles, posits that popular political revolution is permissible when a government does not safeguard the natural rights of its people. Using these points as a base it defends the French Revolution against Edmund Burke's attack in ''Reflections on the Revolution in France'' (1790). It was published in two parts in March 1791 and February 1792. Background Paine was a very strong supporter of the French Revolution that began in 1789; he visited France the following year. Many British thinkers supported it, including Richard Price, who initiated the Revolution Controversy with his sermon and pamphlet drawing favourable parallels between the Glorious Revolution of 1688 and the French Revolution. Conservative intellectual Edmund Burke responded with a counter-revolutionary attack entitled ''Reflections on the Revolution in France'' (1790), which strongly appealed to the landed class and sold 30,000 copies.Mark Philp, " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herman Melville 1885
Herman may refer to: People * Herman (name), list of people with this name * Saint Herman (other) * Peter Noone (born 1947), known by the mononym Herman Places in the United States * Herman, Arkansas * Herman, Michigan * Herman, Minnesota * Herman, Nebraska * Herman, Pennsylvania * Herman, Dodge County, Wisconsin * Herman, Shawano County, Wisconsin * Herman, Sheboygan County, Wisconsin Place in India * Herman (Village) Other uses * ''Herman'' (comic strip) * ''Herman'' (film), a 1990 Norwegian film * Herman the Bull, a bull used for genetic experiments in the controversial lactoferrin project of GenePharming, Netherlands * Herman the Clown ( fi, Pelle Hermanni), a Finnish TV clown from children's TV show performed by Veijo Pasanen * Herman's Hermits, a British pop combo * Herman cake (also called Hermann), a type of sourdough bread starter or Amish Friendship Bread starter * ''Herman'' (album) by 't Hof Van Commerce See also * Hermann (other) * Arman (na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darbies
Handcuffs are Physical restraint, restraint devices designed to secure an individual's wrists in proximity to each other. They comprise two parts, linked together by a Link chain, chain, a hinge, or rigid bar. Each cuff has a rotating arm which engages with a ratchet (device), ratchet that prevents it from being opened once closed around a person's wrist. Without the key, the handcuffs cannot be removed without specialist knowledge, and the handcuffed person cannot move their wrists more than a few centimetres or inches apart, making many tasks difficult or impossible. Handcuffs are frequently used by law enforcement agencies worldwide to prevent Suspect, suspected criminals from escaping from Arrest, police custody. Styles Metal handcuffs There are three main types of contemporary metal handcuffs: chain (cuffs are held together by a short chain), hinged (since hinged handcuffs permit less movement than a chain cuff, they are generally considered to be more secure), and ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Articles Of War
The Articles of War are a set of regulations drawn up to govern the conduct of a country's military and naval forces. The first known usage of the phrase is in Robert Monro's 1637 work ''His expedition with the worthy Scot's regiment called Mac-keyes regiment etc.'' (in the form "Articles of warres") and can be used to refer to military law in general. In Swedish, the equivalent term ''Krigsartiklar'', is first mentioned in 1556. However, the term is usually used more specifically and with the modern spelling and capitalisation to refer to the British regulations drawn up in the wake of the Glorious Revolution and the United States regulations later based on them. United Kingdom Throughout the Articles' existence, there were separate sets for the army and navy. Royal Navy England's first Articles of War were written for the Royal Navy. They formed the statutory provisions regulating and governing the behaviour of members of the Royal Navy. They were prominently displayed in all n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
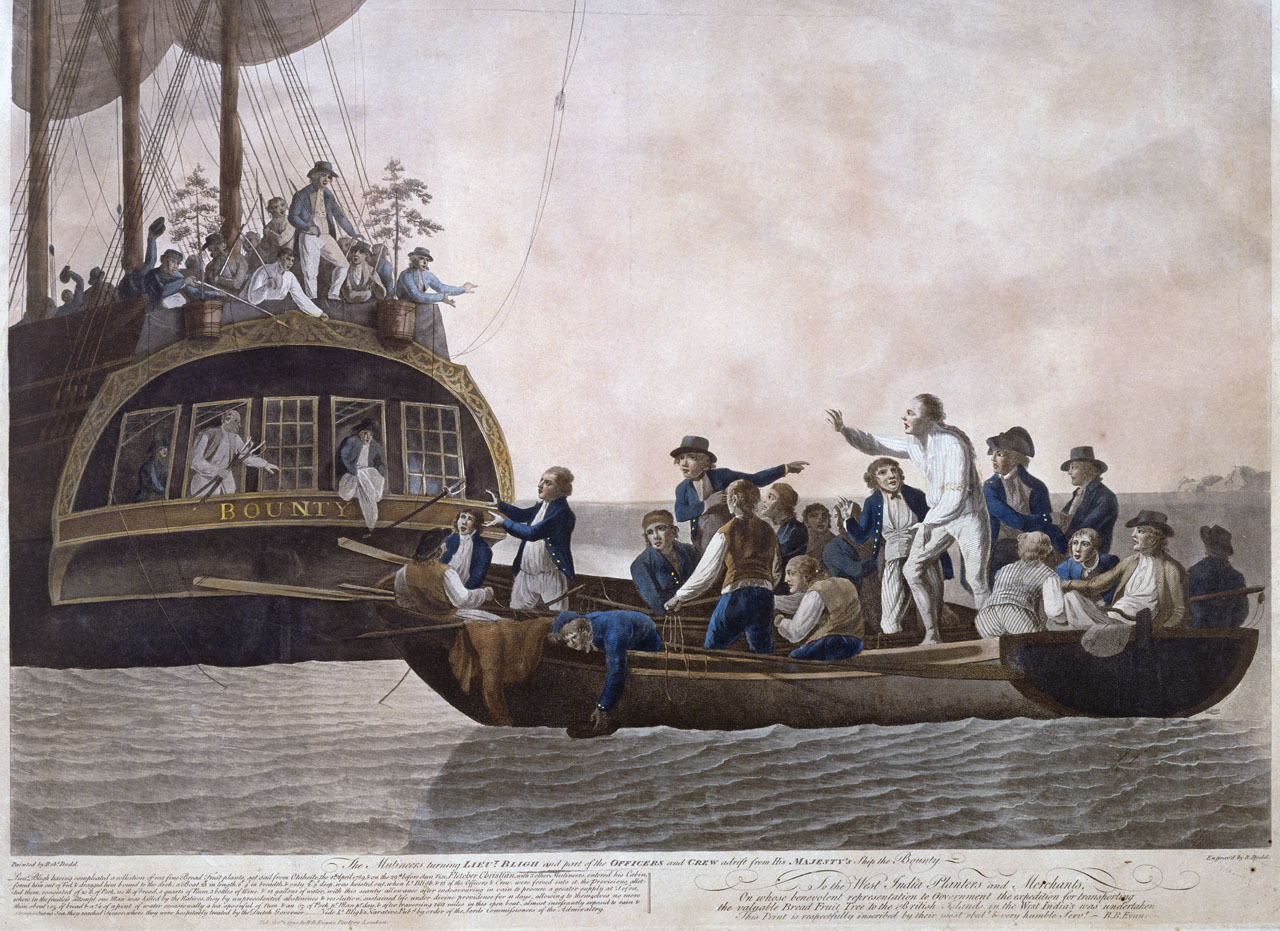
Mutiny Act
Mutiny is a revolt among a group of people (typically of a military, of a crew or of a crew of pirates) to oppose, change, or overthrow an organization to which they were previously loyal. The term is commonly used for a rebellion among members of the military against an internal force, but it can also sometimes mean any type of rebellion against any force. Mutiny does not necessarily need to refer to a military force and can describe a political, economic, or power structure in which there is a change of power. During the Age of Discovery, mutiny particularly meant open rebellion against a ship's captain. This occurred, for example, during Ferdinand Magellan's journeys around the world, resulting in the killing of one mutineer, the execution of another, and the marooning of others; on Henry Hudson's ''Discovery'', resulting in Hudson and others being set adrift in a boat; and the notorious mutiny on the ''Bounty''. Penalty Those convicted of mutiny often faced capital punish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defense Counsel
In a civil proceeding or criminal prosecution under the common law or under statute, a defendant may raise a defense (or defence) in an effort to avert civil liability or criminal conviction. A defense is put forward by a party to defeat a suit or action brought against the party, and may be based on legal grounds or on factual claims. Besides contesting the accuracy of an allegation made against the defendant in the proceeding, the defendant may also make allegations against the prosecutor or plaintiff or raise a defense, arguing that, even if the allegations against the defendant are true, the defendant is nevertheless not liable. Acceptance of a defense by the court completely exonerates the defendant and not merely mitigates the liability. The defense phase of a trial occurs after the prosecution phase, that is, after the prosecution "rests". Other parts of the defense include the opening and closing arguments and the cross-examination during the prosecution phase. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosecutor
A prosecutor is a legal representative of the prosecution in states with either the common law adversarial system or the Civil law (legal system), civil law inquisitorial system. The prosecution is the legal party responsible for presenting the case in a Criminal law, criminal jury trial, trial against an individual accused of breaking the law. Typically, the prosecutor represents the state or the government in the case brought against the accused person. Prosecutor as a legal professional Prosecutors are typically lawyers who possess a law degree, and are recognised as suitable legal professionals by the court in which they are acting. This may mean they have been Admission to the bar, admitted to the bar, or obtained a comparable qualification where available - such as Solicitor advocate, solicitor advocates in English law, England and Wales. They become involved in a criminal case once a suspect has been identified and Indictment, charges need to be filed. They are employe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convening Authority
The term convening authority is used in United States military law to refer to an individual with certain legal powers granted under either the Uniform Code of Military Justice (i.e. the regular military justice system) or the Military Commissions Act of 2009 (for the Guantanamo military commissions). Uniform Code of Military Justice The term "convening authority" is used in the Uniform Code of Military Justice (UCMJ) when referring to an individual whose function is of critical importance in the US military justice system. The persons who may exercise this authority are defined in article 22 () for general court-martial, article 23 () for special court-martial, and article 24 () for summary court-martial. The convening authority decides on the disposition of cases to investigation and trial, and also selects the members of a court-martial. The appointees serve as the military judge and members of the "panel", which decides the guilt or innocence of a person standing trial before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drumhead Court-martial
A drumhead court-martial is a court-martial held in the field to hear urgent charges of offences committed in action. The term sometimes has connotations of summary justice. The term is said to originate from the use of a drum as an improvised table, the drumhead forming the writing surface. Origins The earliest recorded usage is in an English memoir of the Peninsular War (1807). The term sometimes has connotations of summary justice, with an implied lack of judicial impartiality, as noted in the transcripts of the trial at Nuremberg of Josef Bühler. According to Sir Arthur Wynne Morgan Bryant, such courts-martial have ordered lashings or hangings to punish soldiers (and their officers) who were cowardly, disobedient, or, conversely, acted rashly; and especially as a discouragement to drunkenness. It is also used as a reference to a kangaroo court in its derogatory form. World War II Nazi Germany From 1934, every division of the German Army had a court martial. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Master-at-arms
A Master-at-Arms (US: MA; UK & some Commonwealth: MAA) may be a naval rating, responsible for law enforcement, regulating duties, security, anti-terrorism/force protection (AT/FP) for/of a country's navy; an army officer responsible for physical training; or a member of the crew of a merchant ship (usually a passenger vessel) responsible for security and law enforcement. In some navies, a ship's corporal is a position—not the rank—of a petty officer who assists the master-at-arms in his various duties. Historically, a master-at-arms was responsible for the training of soldiers during peace time, or actively involved in leading the defense of a fortification during war time. In some countries, the term "Navy Police" is used for an institution part of a navy responsible for law enforcement, such as the Royal Navy Police, known as the Royal Navy Regulating Branch until 2007. South Africa United Kingdom Royal Navy The master-at-arms (MAA) is a ship's senior rating, normal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stutter
Stuttering, also known as stammering, is a speech disorder in which the flow of speech is disrupted by involuntary repetitions and prolongations of sounds, syllables, words, or phrases as well as involuntary silent pauses or blocks in which the person who stutters is unable to produce sounds. The term ''stuttering'' is most commonly associated with involuntary sound repetition, but it also encompasses the abnormal hesitation or pausing before speech, referred to by people who stutter as ''blocks'', and the prolongation of certain sounds, usually vowels or semivowels. According to Watkins et al., stuttering is a disorder of "selection, initiation, and execution of motor sequences necessary for fluent speech production". arlson, N. (2013). Human Communication. In Physiology of behavior (11th ed., pp. 497–500). Boston: Allyn and Bacon./ref> For many people who stutter, repetition is the main concern. The term "stuttering" covers a wide range of severity, from barely perceptible imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |