|
Bilingual Lexical Access
Bilingual lexical access is an area of psycholinguistics that studies the activation or retrieval process of the mental lexicon for bilingual people. Bilingual lexical access can be understood as all aspects of the word processing, including all of the mental activity from the time when a word from one language is perceived to the time when all its lexical knowledge from the target language is available.De Groot, A. M. (2011). Language and cognition in bilinguals and multilingual: An introduction. New York, NY, US: Psychology Press Research in this field seeks to fully understand these mental processes. Bilingual individuals have two mental lexical representations for an item or concept and can successfully select words from one language without significant interference from the other language. It is the field's goal to understand whether these dual representations interact or affect one another. Bilingual lexical access researchers focus on the control mechanisms bilinguals use to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psycholinguistics
Psycholinguistics or psychology of language is the study of the interrelation between linguistic factors and psychological aspects. The discipline is mainly concerned with the mechanisms by which language is processed and represented in the mind and brain; that is, the psychological and neurobiological factors that enable humans to acquire, use, comprehend, and produce language. Psycholinguistics is concerned with the cognitive faculties and processes that are necessary to produce the grammatical constructions of language. It is also concerned with the perception of these constructions by a listener. Initial forays into psycholinguistics were in the philosophical and educational fields, due mainly to their location in departments other than applied sciences (e.g., cohesive data on how the human brain functioned). Modern research makes use of biology, neuroscience, cognitive science, linguistics, and information science to study how the mind-brain processes language, and less so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexical Entries
In lexicography, a lexical item is a single word, a part of a word, or a chain of words (catena (linguistics), catena) that forms the basic elements of a language's lexicon (≈ vocabulary). Examples are ''cat'', ''traffic light'', ''take care of'', ''by the way'', and ''it's raining cats and dogs''. Lexical items can be generally understood to convey a single meaning, much as a lexeme, but are not limited to single words. Lexical items are like seme (semantics), semes in that they are "natural units" translating between languages, or in learning a new language. In this last sense, it is sometimes said that language consists of grammaticalized lexis, and not lexicalized grammar. The entire store of lexical items in a language is called its lexis (linguistics), lexis. Lexical items composed of more than one word are also sometimes called ''lexical chunks'', ''gambits'', ''lexical phrases'', ''lexicalized stems'', or ''speech formulae''. The term ''polyword listemes'' is also s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word Recognition
Word recognition, according to Literacy Information and Communication System (LINCS) is "the ability of a reader to recognize written words correctly and virtually effortlessly". It is sometimes referred to as "isolated word recognition" because it involves a reader's ability to recognize words individually from a list without needing similar words for contextual help. LINCS continues to say that "rapid and effortless word recognition is the main component of fluent reading" and explains that these skills can be improved by "practic ngwith flashcards, lists, and word grids". In her 1990 review of the science of learning to read, psychologist Marilyn Jager Adams wrote that "the single immutable and nonoptional fact about skilful reading is that it involves relatively complete processing of the individual letters of print." The article "The Science of Word Recognition" says that "evidence from the last 20 years of work in cognitive psychology indicates that we use the letters with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction Time
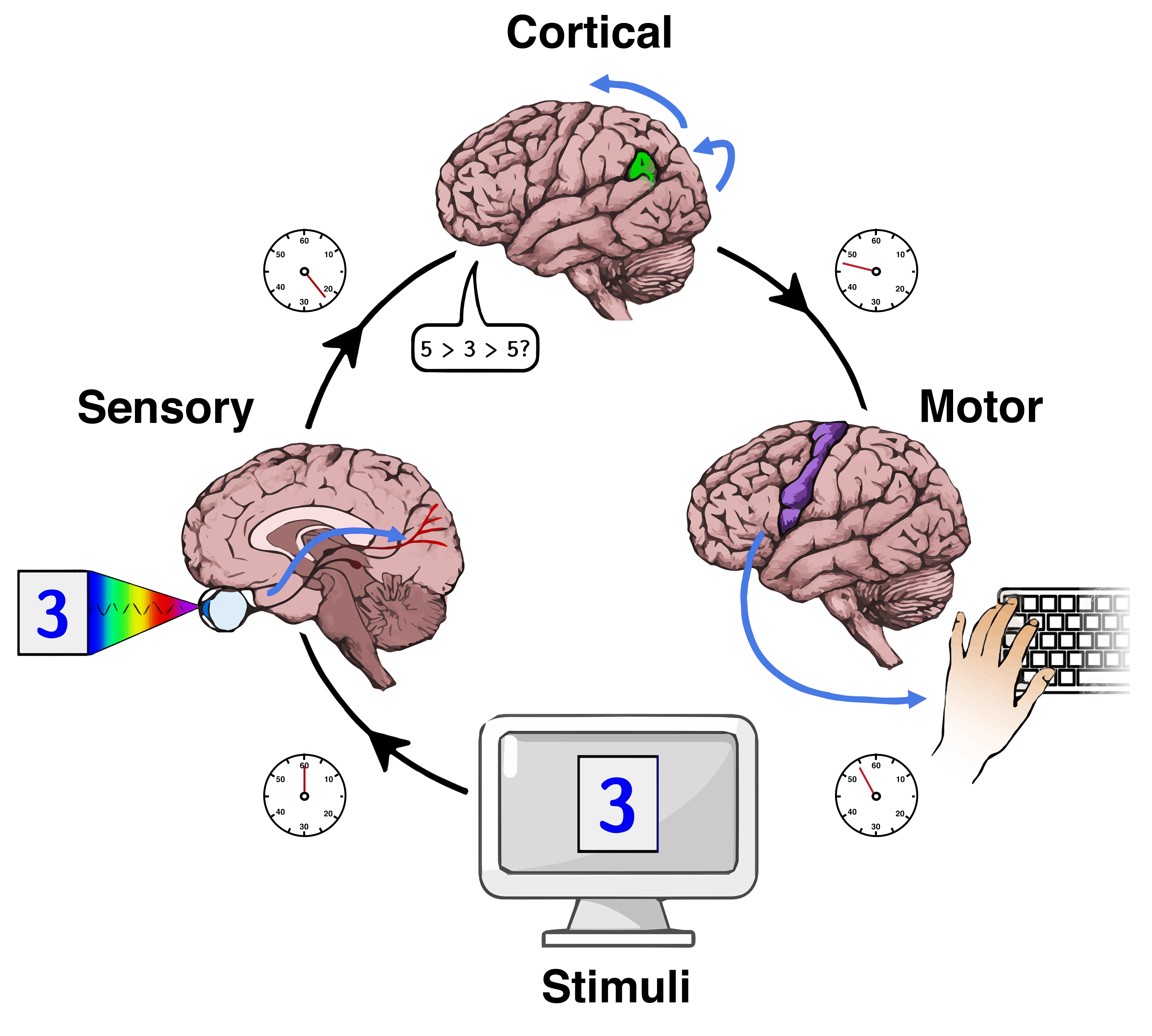
Mental chronometry is the scientific study of processing speed or reaction time on cognitive tasks to infer the content, duration, and temporal sequencing of mental operations. Reaction time (RT; sometimes referred to as "response time") is measured by the elapsed time between stimulus onset and an individual's response on elementary cognitive tasks (ETCs), which are relatively simple perceptual-motor tasks typically administered in a laboratory setting. Mental chronometry is one of the core methodological paradigms of human experimental, cognitive, and differential psychology, but is also commonly analyzed in psychophysiology, cognitive neuroscience, and behavioral neuroscience to help elucidate the biological mechanisms underlying perception, attention, and decision-making in humans and other species. Mental chronometry uses measurements of elapsed time between sensory stimulus onsets and subsequent behavioral responses to study the time course of information processing in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonology
Phonology is the branch of linguistics that studies how languages or dialects systematically organize their sounds or, for sign languages, their constituent parts of signs. The term can also refer specifically to the sound or sign system of a particular language variety. At one time, the study of phonology related only to the study of the systems of phonemes in spoken languages, but may now relate to any linguistic analysis either: Sign languages have a phonological system equivalent to the system of sounds in spoken languages. The building blocks of signs are specifications for movement, location, and handshape. At first, a separate terminology was used for the study of sign phonology ('chereme' instead of 'phoneme', etc.), but the concepts are now considered to apply universally to all human languages. Terminology The word 'phonology' (as in 'phonology of English') can refer either to the field of study or to the phonological system of a given language. This is one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognates
In historical linguistics, cognates or lexical cognates are sets of words in different languages that have been inherited in direct descent from an etymological ancestor in a common parent language. Because language change can have radical effects on both the sound and the meaning of a word, cognates may not be obvious, and often it takes rigorous study of historical sources and the application of the comparative method to establish whether lexemes are cognate or not. Cognates are distinguished from loanwords, where a word has been borrowed from another language. The term ''cognate'' derives from the Latin noun '' cognatus blood relative'. Characteristics Cognates need not have the same meaning, which may have changed as the languages developed independently. For example English '' starve'' and Dutch '' sterven'' 'to die' or German '' sterben'' 'to die' all descend from the same Proto-Germanic verb, '' *sterbaną'' 'to die'. Cognates also do not need to look or sound simila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homographs
A homograph (from the el, ὁμός, ''homós'', "same" and γράφω, ''gráphō'', "write") is a word that shares the same written form as another word but has a different meaning. However, some dictionaries insist that the words must also be pronounced differently, while the Oxford English Dictionary says that the words should also be of "different origin". In this vein, ''The Oxford Guide to Practical Lexicography'' lists various types of homographs, including those in which the words are discriminated by being in a different ''word class'', such as ''hit'', the verb ''to strike'', and ''hit'', the noun ''a blow''. If, when spoken, the meanings may be distinguished by different pronunciations, the words are also heteronyms. Words with the same writing ''and'' pronunciation (i.e. are both homographs and homophones) are considered homonyms. However, in a looser sense the term "homonym" may be applied to words with the same writing ''or'' pronunciation. Homograph disambiguat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroscience Of Multilingualism
Neuroscience of multilingualism is the study of multilingualism within the field of neurology. These studies include the representation of different language systems in the brain, the effects of multilingualism on the brain's structural plasticity, aphasia in multilingual individuals, and bimodal bilinguals (people who can speak one sign language and one oral language). Neurological studies of multilingualism are carried out with functional neuroimaging, electrophysiology, and through observation of people who have suffered brain damage. The brain contains areas that are specialized to deal with language, located in the perisylvian cortex of the left hemisphere. These areas are crucial for performing language tasks, but they are not the only areas that are used; disparate parts of both the right and left brain hemispheres are active during language production. In multilingual individuals, there is a great deal of similarity in the brain areas used for each of their languages. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphasic
Aphasia is an inability to comprehend or formulate language because of damage to specific brain regions. The major causes are stroke and head trauma; prevalence is hard to determine but aphasia due to stroke is estimated to be 0.1–0.4% in the Global North. Aphasia can also be the result of brain tumors, brain infections, or neurodegenerative diseases (such as dementias). To be diagnosed with aphasia, a person's speech or language must be significantly impaired in one (or more) of the four aspects of communication following acquired brain injury. Alternatively, in the case of progressive aphasia, it must have significantly declined over a short period of time. The four aspects of communication are auditory comprehension, verbal expression, reading and writing, and functional communication. The difficulties of people with aphasia can range from occasional trouble finding words, to losing the ability to speak, read, or write; intelligence, however, is unaffected. Expressive la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypotheses
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it. Scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on previous observations that cannot satisfactorily be explained with the available scientific theories. Even though the words "hypothesis" and "theory" are often used interchangeably, a scientific hypothesis is not the same as a scientific theory. A working hypothesis is a provisionally accepted hypothesis proposed for further research in a process beginning with an educated guess or thought. A different meaning of the term ''hypothesis'' is used in formal logic, to denote the antecedent of a proposition; thus in the proposition "If ''P'', then ''Q''", ''P'' denotes the hypothesis (or antecedent); ''Q'' can be called a consequent. ''P'' is the assumption in a (possibly counterfactual) ''What If'' question. The adjective ''hypothetical'', meaning "havin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexical Access
A lexicon is the vocabulary of a language or branch of knowledge (such as nautical or medical). In linguistics, a lexicon is a language's inventory of lexemes. The word ''lexicon'' derives from Greek word (), neuter of () meaning 'of or for words'. Linguistic theories generally regard human languages as consisting of two parts: a lexicon, essentially a catalogue of a language's words (its wordstock); and a grammar, a system of rules which allow for the combination of those words into meaningful sentences. The lexicon is also thought to include bound morphemes, which cannot stand alone as words (such as most affixes). In some analyses, compound words and certain classes of idiomatic expressions, collocations and other phrases are also considered to be part of the lexicon. Dictionaries are lists of the lexicon, in alphabetical order, of a given language; usually, however, bound morphemes are not included. Size and organization Items in the lexicon are called lexemes, lexical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Modeling
Computer simulation is the process of mathematical modelling, performed on a computer, which is designed to predict the behaviour of, or the outcome of, a real-world or physical system. The reliability of some mathematical models can be determined by comparing their results to the real-world outcomes they aim to predict. Computer simulations have become a useful tool for the mathematical modeling of many natural systems in physics (computational physics), astrophysics, climatology, chemistry, biology and manufacturing, as well as human systems in economics, psychology, social science, health care and engineering. Simulation of a system is represented as the running of the system's model. It can be used to explore and gain new insights into new technology and to estimate the performance of systems too complex for analytical solutions. Computer simulations are realized by running computer program A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |