|
Bilche-Zolote
Bilche-Zolote ( ua, Більче-Золоте ''Bil'che Zolote''; pl, Bilcze Złote; he, בילצ'ה זלוטה, Vilche Zlote) is a Ukrainian village located within the Chortkiv Raion (district) of the Ternopil Oblast (province), about driving distance southwest of Kyiv. It hosts the administration of Bilche-Zolote settlement hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. This rural community is located in a small valley adjacent to the ''Seret'' River, which is surrounded by plateaus covered with farms, broken by occasional stands of mixed forest. Bilche-Zolote is home to a remarkable park of , of which 11 hectares (27 acres) is covered with virgin timber, including some trees up to 400 years old. Bilche-Zolote is also the location of the large gypsum karst ''Verteba'' Cave, as well as a significant Neolithic Cucuteni-Trypillian culture archaeological site, and attracts tourist and spelunker visitors from many countries. History Founded in the early 10th century, Bilche-Zolote ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilche-Zolote Settlement Hromada
Bilche-Zolote ( ua, Більче-Золоте ''Bil'che Zolote''; pl, Bilcze Złote; he, בילצ'ה זלוטה, Vilche Zlote) is a Ukrainian village located within the Chortkiv Raion (district) of the Ternopil Oblast (province), about driving distance southwest of Kyiv. It hosts the administration of Bilche-Zolote settlement hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. This rural community is located in a small valley adjacent to the ''Seret'' River, which is surrounded by plateaus covered with farms, broken by occasional stands of mixed forest. Bilche-Zolote is home to a remarkable park of , of which 11 hectares (27 acres) is covered with virgin timber, including some trees up to 400 years old. Bilche-Zolote is also the location of the large gypsum karst ''Verteba'' Cave, as well as a significant Neolithic Cucuteni-Trypillian culture archaeological site, and attracts tourist and spelunker visitors from many countries. History Founded in the early 10th century, Bilche-Zolote has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borshchiv Raion
Borshchiv Raion (, translit. ''Borschivs’kyi raion'') was a raion (a district within Ternopil Oblast (province) in western Ukraine, an area known as Galicia. The administrative center of the raion was Borshchiv. The raion was abolished on 18 July 2020 as part of the administrative reform of Ukraine, which reduced the number of raions of Ternopil Oblast to three. The area of Borshchiv Raion was merged into Chortkiv Raion. The last estimate of the raion population was Subdivisions At the time of disestablishment, the raion consisted of five hromadas: * Bilche-Zolote rural hromada with the administration in the selo of Bilche-Zolote; * Borshchiv urban hromada with the administration in Borshchiv; * Ivane-Puste rural hromada with the administration in the selo of Ivane-Puste; * Melnytsia-Podilska settlementl hromada with the administration in the urban-type settlement of Melnytsia-Podilska; * Skala-Podilska settlementl hromada with the administration in the urban-type settlemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chortkiv Raion
Chortkiv Raion ( uk, Чортківський район) is a raion in Ternopil Oblast in western Ukraine. Its administrative center is the city of Chortkiv. It has a population of On 18 July 2020, as part of the administrative reform of Ukraine, the number of raions of Ternopil Oblast was reduced to three, and the area of Chortkiv Raion was significantly expanded. Five abolished raions, Borshchiv, Buchach, Husiatyn, Monastyryska, and Zalishchyky Raions, as well as the city of Chortkiv, which was previously incorporated as a city of oblast significance and did not belong to the raion, were merged into Chortkiv Raion. The January 2020 estimate of the raion population was Subdivisions Current After the reform in July 2020, the raion consisted of 22 hromadas: * Bilche-Zolote rural hromada with the administration in the selo of Bilche-Zolote, transferred from Borshchiv Raion; * Bilobozhnytsia rural hromada with the administration in the selo of Bilobozhnytsia, retained from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countries Of The World
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, 2 United Nations General Assembly observers#Present non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (2 states, both in associated state, free association with New Zealand). Compi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of Russia'' (Penguin, 1995), p.14–16.Kievan Rus Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encompassing a variety of polities and peoples, including East Slavic, Norse, and Finnic, it was ruled by the , fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moonmilk
Moonmilk (sometimes called mondmilch, also known as montmilch or as cave milk) is a white, creamy substance found inside limestone, dolomite, and possibly other types of caves. It is a precipitate from limestone comprising aggregates of fine crystals of varying composition usually made of carbonates such as calcite, aragonite, hydromagnesite, and/or monohydrocalcite. There are several hypotheses concerning the origin of moonmilk. One of these explains moonmilk to be the result of bacterial action rather than from chemical reactions. According to this particular hypothesis, moonmilk is thought to have been created by the bacterium ''Macromonas bipunctata''. However, no microbiological studies have been carried out so far. Moonmilk was originally explained as created by moon rays. It is possible that moonmilk is formed by water that dissolves and softens the karst of caves consisting of carbonates, and carries dissolved nutrients that can be used by microbes, such as Actinomyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
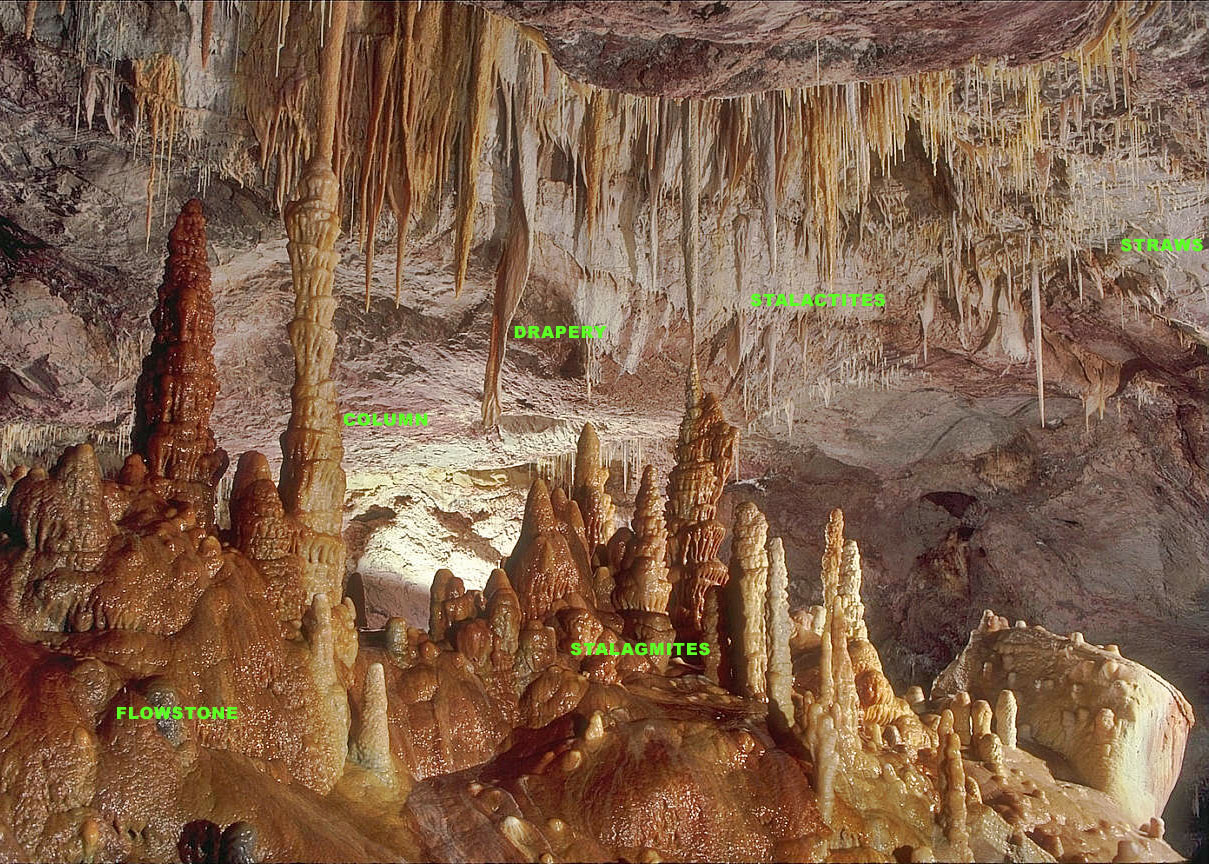
Stalagmites
A stalagmite (, ; from the Greek , from , "dropping, trickling") is a type of rock formation that rises from the floor of a cave due to the accumulation of material deposited on the floor from ceiling drippings. Stalagmites are typically composed of calcium carbonate, but may consist of lava, mud, peat, pitch, sand, sinter, and amberat (crystallized urine of pack rats). The corresponding formation hanging down from the ceiling of a cave is a stalactite. Mnemonics have been developed for which word refers to which type of formation; one is that ''stalactite'' has a C for "ceiling", and ''stalagmite'' has a G for "ground", another is that, as with ants in the pants, the mites go up and the tights (tites) come down. Formation and type Limestone stalagmites The most common stalagmites are speleothems, which usually form in limestone caves. Stalagmite formation occurs only under certain pH conditions within the cavern. They form through deposition of calcium carbonate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stalactites
A stalactite (, ; from the Greek 'stalaktos' ('dripping') via ''stalassein'' ('to drip') is a mineral formation that hangs from the ceiling of caves, hot springs, or man-made structures such as bridges and mines. Any material that is soluble and that can be deposited as a colloid, or is in suspension, or is capable of being melted, may form a stalactite. Stalactites may be composed of lava, minerals, mud, peat, pitch, sand, sinter, and amberat (crystallized urine of pack rats). A stalactite is not necessarily a speleothem, though speleothems are the most common form of stalactite because of the abundance of limestone caves. The corresponding formation on the floor of the cave is known as a stalagmite. Mnemonics have been developed for which word refers to which type of formation; one is that ''stalactite'' has a C for "ceiling", and ''stalagmite'' has a G for "ground". Another example is that ''stalactites'' "hang on ''T''ight" and ''stalagmites'' "''M''ight grow up" � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpatho-Ukraine
Carpatho-Ukraine or Carpathian Ukraine ( uk, Карпа́тська Украї́на, Karpats’ka Ukrayina, ) was an autonomous region within the Second Czechoslovak Republic, created in December 1938 by renaming Subcarpathian Rus' whose full administrative and political autonomy was confirmed by the Constitutional law of 22 November 1938. After the breakup of the Second Czechoslovak Republic, it was proclaimed an independent republic on 15 March 1939, headed by president Avgustyn Voloshyn, who appealed to Hitler for recognition and support. Nazi Germany did not reply, and the short-lived state was returned to the Kingdom of Hungary, crushing all local resistance by 18 March 1939. The region remained under Hungarian control until the End of World War II in Europe, after which it was occupied and annexed by the Soviet Union. The territory is now administered as the Ukrainian Zakarpattia Oblast. History Political autonomy Soon after the implementation of the Munich Agr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of , with a population of almost 84 million within its 16 constituent states. Germany borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the bulk of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |