|
Big Mo
The Big Mo ("Big Momentum") is behavioral momentum that operates on a large scale. The concept originally applied to sporting events in the 1960s in the United States, as momentum appeared to have an effect on a team's performance. Successful teams were said to have "The Big Mo" on their side. This has since extended situations in which momentum is a driving factor, such as during political campaigns, social upheavals, economic cycles, and financial bubbles. In modern history The term was used by George H. W. Bush during his quest for the Republican nomination to run for President in 1980. After he won the Iowa caucuses, and was facing further contests, Bush Senior said: "Now they will be after me, howling and yowling at my heels. What we will have is momentum. We will look forward to Big Mo being on our side, as they say in athletics." Eventually, Bush lost to Ronald Reagan who went on to become the 40th President of the United States, with Bush as his Vice President. Impact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behavioral Momentum
Behavioral momentum is a theory in quantitative analysis of behavior and is a behavioral metaphor based on physical momentum. It describes the general relation between resistance to change (persistence of behavior) and the rate of reinforcement obtained in a given situation. B. F. Skinner (1938) proposed that all behavior is based on a fundamental unit of behavior called the discriminated operant. The discriminated operant, also known as the three-term contingency, has three components: an antecedent discriminative stimulus, a response, and a reinforcing or punishing consequence. The organism responds in the presence of the stimulus because past responses in the presence of that stimulus have produced reinforcement. Resistance to change According to behavioral momentum theory, there are two separable factors that independently govern the rate with which a discriminated operant occurs and the persistence of that response in the face of disruptions such as punishment, extinction, or t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Professor Emeritus
''Emeritus'' (; female: ''emerita'') is an adjective used to designate a retired chair, professor, pastor, bishop, pope, director, president, prime minister, rabbi, emperor, or other person who has been "permitted to retain as an honorary title the rank of the last office held". In some cases, the term is conferred automatically upon all persons who retire at a given rank, but in others, it remains a mark of distinguished service awarded selectively on retirement. It is also used when a person of distinction in a profession retires or hands over the position, enabling their former rank to be retained in their title, e.g., "professor emeritus". The term ''emeritus'' does not necessarily signify that a person has relinquished all the duties of their former position, and they may continue to exercise some of them. In the description of deceased professors emeritus listed at U.S. universities, the title ''emeritus'' is replaced by indicating the years of their appointmentsThe Protoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
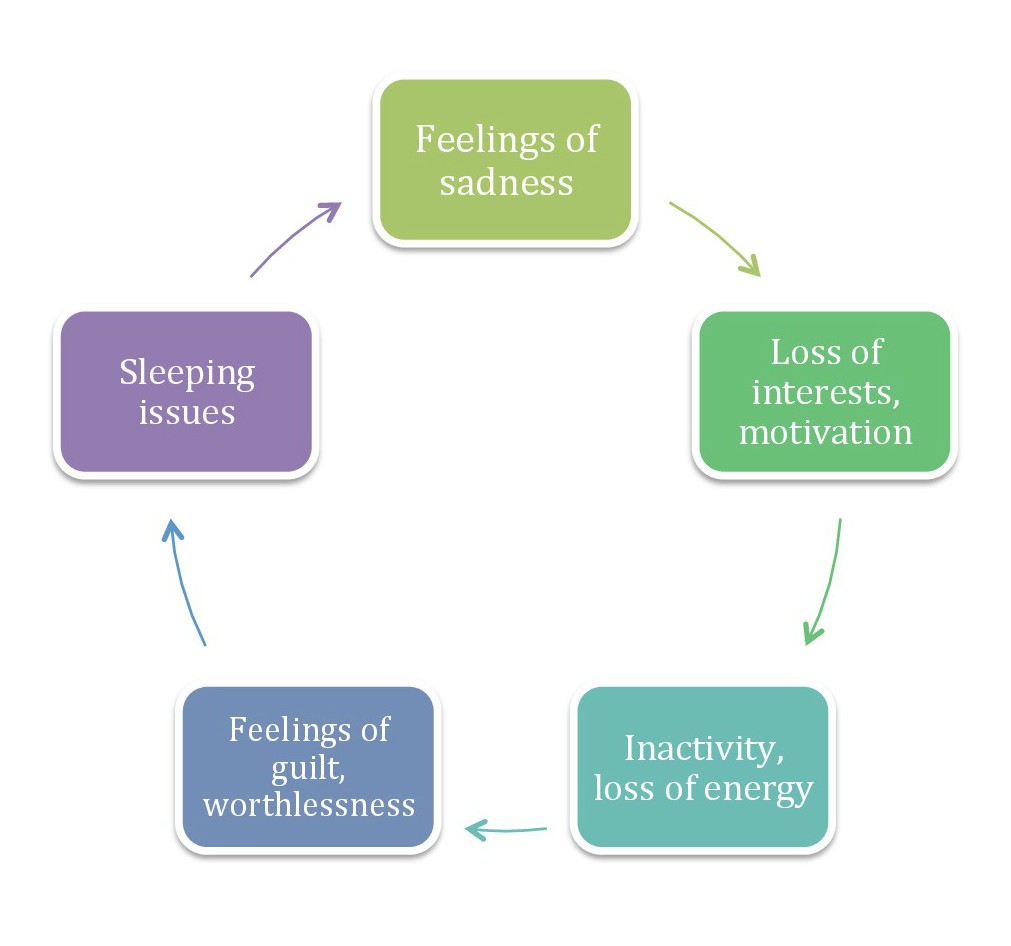
Virtuous Circle And Vicious Circle
A vicious circle (or cycle) is a complex chain of events that reinforces itself through a feedback loop, with detrimental results. It is a system with no tendency toward equilibrium (social, economic, ecological, etc.), at least in the short run. Each iteration of the cycle reinforces the previous one, in an example of positive feedback. A vicious circle will continue in the direction of its momentum until an external factor intervenes to break the cycle. A well-known example of a vicious circle in economics is hyperinflation. A virtuous circle is an equivalent system with a favorable outcome. Examples Vicious circles in the subprime mortgage crisis The contemporary subprime mortgage crisis is a complex group of vicious circles, both in its genesis and in its manifold outcomes, most notably the late 2000s recession. A specific example is the circle related to housing. As housing prices decline, more homeowners go " underwater", when the market value of a home drops below ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Effect
In economics, a network effect (also called network externality or demand-side economies of scale) is the phenomenon by which the value or utility a user derives from a good or service depends on the number of users of compatible products. Network effects are typically positive, resulting in a given user deriving more value from a product as more users join the same network. The adoption of a product by an additional user can be broken into two effects: an increase in the value to all other users ( "total effect") and also the enhancement of other non-users' motivation for using the product ("marginal effect"). Network effects can be direct or indirect. Direct network effects arise when a given user's utility increases with the number of other users of the same product or technology, meaning that adoption of a product by different users is complementary. This effect is separate from effects related to price, such as a benefit to existing users resulting from price decreases as m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domino Effect
A domino effect or chain reaction is the cumulative effect generated when a particular event triggers a chain of similar events. This term is best known as a mechanical effect and is used as an analogy to a falling row of dominoes. It typically refers to a linked sequence of events where the time between successive events is relatively small. It can be used literally (an observed series of actual collisions) or metaphorically (causal linkages within systems such as global finance or politics). The term ''domino effect'' is used both to imply that an event is inevitable or highly likely (as it has already started to happen), and conversely to imply that an event is impossible or highly unlikely (the one domino left standing). Demonstration of the effect The domino effect can easily be visualized by placing a row of dominoes upright, each separated by a small distance. Upon pushing the first domino, the next domino in line will be knocked over, and so on, thus firing a linear ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Critical Mass (sociodynamics)
In social dynamics, critical mass is a sufficient number of adopters of a new idea, technology or innovation in a social system so that the rate of adoption becomes self-sustaining and creates further growth. The point at which critical mass is achieved is sometimes referred to as a threshold within the threshold model of statistical modeling. The term critical mass is borrowed from nuclear physics and in that field, it refers to the amount of a substance needed to sustain a chain reaction. Within social sciences, critical mass has its roots in sociology and is often used to explain the conditions under which reciprocal behavior is started within collective groups, and how it becomes self-sustaining. Recent technology research in platform ecosystems shows that apart from the quantitative notion of a “sufficient number” critical mass is also influenced by qualitative properties such as reputation, interests, commitments, capabilities, goals, consensuses, and decisions, all of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandwagon Effect
The bandwagon effect is the tendency for people to adopt certain behaviors, styles, or attitudes simply because others are doing so. More specifically, it is a cognitive bias by which public opinion or behaviours can alter due to particular actions and beliefs rallying amongst the public. It is a psychological phenomenon whereby the rate of uptake of beliefs, ideas, fads and trends increases with respect to the proportion of others who have already done so. As more people come to believe in something, others also "hop on the bandwagon" regardless of the underlying evidence. Following others' actions or beliefs can occur because of conformism or deriving information from others. Much of the influence of the bandwagon effect comes from the desire to 'fit in' with peers; by making similar selections as other people, this is seen as a way to gain access to a particular social group. An example of this is fashion trends wherein the increasing popularity of a certain garment or style ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behavioral Momentum
Behavioral momentum is a theory in quantitative analysis of behavior and is a behavioral metaphor based on physical momentum. It describes the general relation between resistance to change (persistence of behavior) and the rate of reinforcement obtained in a given situation. B. F. Skinner (1938) proposed that all behavior is based on a fundamental unit of behavior called the discriminated operant. The discriminated operant, also known as the three-term contingency, has three components: an antecedent discriminative stimulus, a response, and a reinforcing or punishing consequence. The organism responds in the presence of the stimulus because past responses in the presence of that stimulus have produced reinforcement. Resistance to change According to behavioral momentum theory, there are two separable factors that independently govern the rate with which a discriminated operant occurs and the persistence of that response in the face of disruptions such as punishment, extinction, or t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Field Theory
In theoretical physics, quantum field theory (QFT) is a theoretical framework that combines classical field theory, special relativity, and quantum mechanics. QFT is used in particle physics to construct physical models of subatomic particles and in condensed matter physics to construct models of quasiparticles. QFT treats particles as excited states (also called Quantum, quanta) of their underlying quantum field (physics), fields, which are more fundamental than the particles. The equation of motion of the particle is determined by minimization of the Lagrangian, a functional of fields associated with the particle. Interactions between particles are described by interaction terms in the Lagrangian (field theory), Lagrangian involving their corresponding quantum fields. Each interaction can be visually represented by Feynman diagrams according to perturbation theory (quantum mechanics), perturbation theory in quantum mechanics. History Quantum field theory emerged from the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Physics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent of quantum mechanics, describes many aspects of nature at an ordinary (macroscopic) scale, but is not sufficient for describing them at small (atomic and subatomic) scales. Most theories in classical physics can be derived from quantum mechanics as an approximation valid at large (macroscopic) scale. Quantum mechanics differs from classical physics in that energy, momentum, angular momentum, and other quantities of a bound system are restricted to discrete values ( quantization); objects have characteristics of both particles and waves (wave–particle duality); and there are limits to ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the greatest mathematicians and physicists and among the most influential scientists of all time. He was a key figure in the philosophical revolution known as the Enlightenment. His book (''Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy''), first published in 1687, established classical mechanics. Newton also made seminal contributions to optics, and shares credit with German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for developing infinitesimal calculus. In the , Newton formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation that formed the dominant scientific viewpoint for centuries until it was superseded by the theory of relativity. Newton used his mathematical description of gravity to derive Kepler's laws of planetary motion, account for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of New Hampshire
The University of New Hampshire (UNH) is a public land-grant research university with its main campus in Durham, New Hampshire. It was founded and incorporated in 1866 as a land grant college in Hanover in connection with Dartmouth College, moved to Durham in 1893, and adopted its current name in 1923. The university's Durham campus comprises six colleges. A seventh college, the University of New Hampshire at Manchester, occupies the university's campus in Manchester. The University of New Hampshire School of Law is in Concord, the state's capital. The university is part of the University System of New Hampshire and is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". , its combined campuses made UNH the largest state university system in the state of New Hampshire, with over 15,000 students. It was also the most expensive state-sponsored school in the United States for in-state students. History The Morrill Act of 1862 granted federal land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |