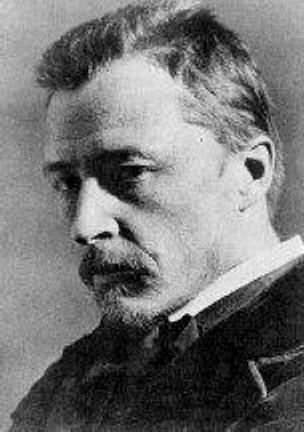|
Biedemeier
The ''Biedermeier'' period was an era in Central Europe between 1815 and 1848 during which the middle class grew in number and the arts appealed to common sensibilities. It began with the Congress of Vienna at the end of the Napoleonic Wars in 1815 and ended with the onset of the Revolutions of 1848. Although the term itself derives from a literary reference from the period, it is used mostly to denote the artistic styles that flourished in the fields of literature, music, the visual arts and interior design. It has influenced later styles, especially those originating in Vienna. Background The ''Biedermeier'' period does not refer to the era as a whole, but to a particular mood and set of trends that grew out of the unique underpinnings of the time in Central Europe. There were two driving forces for the development of the period. One was the growing urbanization and industrialization leading to a new urban middle class, which created a new kind of audience for the arts. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Spitzweg 036
Carl may refer to: *Carl, Georgia, city in USA *Carl, West Virginia, an unincorporated community *Carl (name), includes info about the name, variations of the name, and a list of people with the name *Carl², a TV series * "Carl", an episode of television series ''Aqua Teen Hunger Force'' * An informal nickname for a student or alum of Carleton College CARL may refer to: *Canadian Association of Research Libraries *Colorado Alliance of Research Libraries See also *Carle (other) *Charles *Carle, a surname *Karl (other) *Karle (other) Karle may refer to: Places * Karle (Svitavy District), a municipality and village in the Czech Republic * Karli, India, a town in Maharashtra, India ** Karla Caves, a complex of Buddhist cave shrines * Karle, Belgaum, a settlement in Belgaum d ... {{disambig ja:カール zh:卡尔 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annette Von Droste-Hülshoff
Baroness Anna Elisabeth Franziska Adolphine Wilhelmine Louise Maria von Droste zu Hülshoff, known as Annette von Droste-Hülshoff (; 10 January 179724 May 1848), was a 19th-century German poet, novelist, and composer of Classical music. She was also the author of the novella '' Die Judenbuche''. In an article for the 1913 Catholic Encyclopedia, Francis Joste wrote, "The fame of the poetess rests chiefly on her lyric poems, her pastorales, and her ballads. In the poetic representation of nature, few can equal her. The poetical works of Annette von Droste-Hülshoff are imperishable. What makes them so is their originality, the proof that they are the works of a genius. It is this too that gained for their author the well-earned title of 'Germany's greatest poetess.'" Biography Early years Annette von Droste-Hülshoff was born at the castle of Burg Hülshoff (now a part of Havixbeck) in the Prince-Bishopric of Münster. Her family, the Barons Droste zu Hülshoff, belonged to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Mann
Paul Thomas Mann ( , ; ; 6 June 1875 – 12 August 1955) was a German novelist, short story writer, social critic, philanthropist, essayist, and the 1929 Nobel Prize in Literature laureate. His highly symbolic and ironic epic novels and novellas are noted for their insight into the psychology of the artist and the intellectual. His analysis and critique of the European and German soul used modernized versions of German and Biblical stories, as well as the ideas of Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, Friedrich Nietzsche, and Arthur Schopenhauer. Mann was a member of the Hanseatic Mann family and portrayed his family and class in his first novel, ''Buddenbrooks''. His older brother was the radical writer Heinrich Mann and three of Mann's six children – Erika Mann, Klaus Mann and Golo Mann – also became significant German writers. When Adolf Hitler came to power in 1933, Mann fled to Switzerland. When World War II broke out in 1939, he moved to the United States, then returned to Swit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Black Spider
''The Black Spider'' is a novella by the Swiss writer Jeremias Gotthelf written in 1842. Set in an idyllic frame story, old legends are worked into a Christian-humanist allegory about ideas of good and evil. Though the novel is initially divided, what is originally the internal story later spills over into the frame story as well. The story is characterized by its complex narrative structure, its conservative Christian motifs and symbolism and its precise descriptions of the social dynamics of the village. Plot The novella begins with a christening party at a farm, during the course of which a few of the guests in front of the house go for a walk. It catches the godmother's eye that although the house is newly built, an old black post is built into it. At her inquiry, the grandfather tells everyone the story of the post. First internal narrative The grandfather tells how a few centuries before, the village had been ruled by a Teutonic Knight named Hans von Stoffeln, who wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press A university press is an academic publishing house specializing in monographs and scholarly journals. Most are nonprofit organizations and an integral component of a large research university. They publish work that has been reviewed by schola ... in the world. It is also the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press is a department of the University of Cambridge and is both an academic and educational publisher. It became part of Cambridge University Press & Assessment, following a merger with Cambridge Assessment in 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 Country, countries, it publishes over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publishing includes more than 380 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Emil Schorske
Carl Emil Schorske (March 15, 1915 – September 13, 2015), known professionally as Carl E. Schorske, was an American cultural historian and professor emeritus at Princeton University. In 1981 he won the Pulitzer Prize for General Non-Fiction for his book '' Fin-de-Siècle Vienna: Politics and Culture'' (1980), which remains significant to modern European intellectual history. He was a recipient of the first year of MacArthur Fellows Program awards in 1981 and made an honorary citizen of Vienna in 2012. Biography Born in the Bronx, New York City, to Theodore Schorske and Gertrude Goldsmith, Schorske received his B.A. from Columbia in 1936 and a Ph.D. from Harvard. He served in the Office of Strategic Services, the precursor to the CIA, during World War II, as chief of political intelligence for Western Europe. His first book, ''German Social Democracy'', published by Harvard University Press in 1955, describes the schism of the Social Democratic Party of Germany into a reformist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Der Nachsommer
''Der Nachsommer'' ( en, Indian Summer, italic=yes; subtitled ''A Tale''; 1857) is a novel in three volumes by Adalbert Stifter. A 19th century ''Bildungsroman'' that describes the journey of an idealistic, sheltered young man from childhood to maturity, it combines aspects of Biedermeier thought with elements of German humanism to create what is generally considered to be a great work of German bourgeois realism. Plot summary This first-person narrative describes the main character Heinrich's maturation in the regimented household of his father and his subsequent encounter and involvement with the owner of the Rosenhaus, the home, and part of the estate, of a wise, but mysterious older man who becomes a mentor to Heinrich. Heinrich accepts his regimented upbringing without criticism. His father is a merchant who has planned out Heinrich's early education at home in the minutest detail. When it is time for Heinrich to head out on his own, his father allows his son to choose his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adalbert Stifter
Adalbert Stifter (; 23 October 1805 – 28 January 1868) was an Austrian writer, poet, painter, and pedagogue. He was notable for the vivid natural landscapes depicted in his writing and has long been popular in the German-speaking world, while remaining almost entirely unknown to English readers. Life Born in Oberplan in Bohemia (now Horní Planá in the Czech Republic), he was the eldest son of Johann Stifter, a wealthy linen weaver, and his wife, Magdalena. Johann died in 1817 after being crushed by an overturned wagon. Stifter was educated at the '' Benedictine Gymnasium'' at Kremsmünster, and went to the University of Vienna in 1826 to study law. In 1828 he fell in love with Fanny Greipl, but after a relationship lasting five years, her parents forbade further correspondence, a loss from which he never recovered. In 1835 he became engaged to Amalia Mohaupt, and they married in 1837, but the marriage was not a happy one. Stifter and his wife, unable to conceive, tried a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Schubert
Franz Peter Schubert (; 31 January 179719 November 1828) was an Austrian composer of the late Classical and early Romantic eras. Despite his short lifetime, Schubert left behind a vast ''oeuvre'', including more than 600 secular vocal works (mainly lieder), seven complete symphonies, sacred music, opera Opera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a libr ...s, incidental music, and a large body of piano and chamber music. His major works include "Erlkönig (Schubert), Erlkönig" (D. 328), the Trout Quintet, Piano Quintet in A major, D. 667 (''Trout Quintet''), the Symphony No. 8 (Schubert), Symphony No. 8 in B minor, D. 759 (''Unfinished Symphony''), the Symphony No. 9 (Schubert), "Great" Symphony No. 9 in C major, D. 944, the String Quintet (Schubert), String Quintet (D. 956), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugo Wolf
Hugo Philipp Jacob Wolf (13 March 1860 – 22 February 1903) was an Austrian composer of Slovene origin, particularly noted for his art songs, or Lieder. He brought to this form a concentrated expressive intensity which was unique in late Romantic music, somewhat related to that of the Second Viennese School in concision but diverging greatly in technique. Though he had several bursts of extraordinary productivity, particularly in 1888 and 1889, depression frequently interrupted his creative periods, and his last composition was written in 1898, before he suffered a mental collapse caused by syphilis. Early life (1860–1887) Hugo Wolf was born in Windischgrätz in the Duchy of Styria (now Slovenj Gradec, Slovenia), then a part of the Austrian Empire. Herbert von Karajan was related to him on his maternal side. He spent most of his life in Vienna, becoming a representative of a "New German" trend in Lieder, a trend which followed from the expressive, chromatic and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schumann
Robert Schumann (; 8 June 181029 July 1856) was a German composer, pianist, and influential music critic. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest composers of the Romantic era. Schumann left the study of law, intending to pursue a career as a virtuoso pianist. His teacher, Friedrich Wieck, a German pianist, had assured him that he could become the finest pianist in Europe, but a hand injury ended this dream. Schumann then focused his musical energies on composing. In 1840, Schumann married Friedrich Wieck's daughter Clara Wieck, after a long and acrimonious legal battle with Friedrich, who opposed the marriage. A lifelong partnership in music began, as Clara herself was an established pianist and music prodigy. Clara and Robert also maintained a close relationship with German composer Johannes Brahms. Until 1840, Schumann wrote exclusively for the piano. Later, he composed piano and orchestral works, and many Lieder (songs for voice and piano). He composed four symphonies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Müller
Johann Ludwig Wilhelm Müller (7 October 1794 – 30 September 1827) was a German lyric poet, best known as the author of ''Die schöne Müllerin'' (1823) and ''Winterreise'' (1828), which Franz Schubert later set to music as song cycles. Life Wilhelm Müller was born on 7 October 1794 at Dessau, the son of a tailor. He was educated at the gymnasium of his native town and at the University of Berlin, where he devoted himself to philological and historical studies. In 1813-1814 he took part, as a volunteer in the Prussian army, in the national rising against Napoleon. He participated in the battles of Lützen, Bautzen, Hanau and Kulm. In 1814 he returned to his studies at Berlin. From 1817 to 1819, he visited southern Germany and Italy, and in 1820 published his impressions of the latter in ''Rom, Römer und Römerinnen''. In 1819, he was appointed teacher of classics in the Gelehrtenschule at Dessau, and in 1820 librarian to the ducal library. He remained there the rest of hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_by_night.jpg)