|
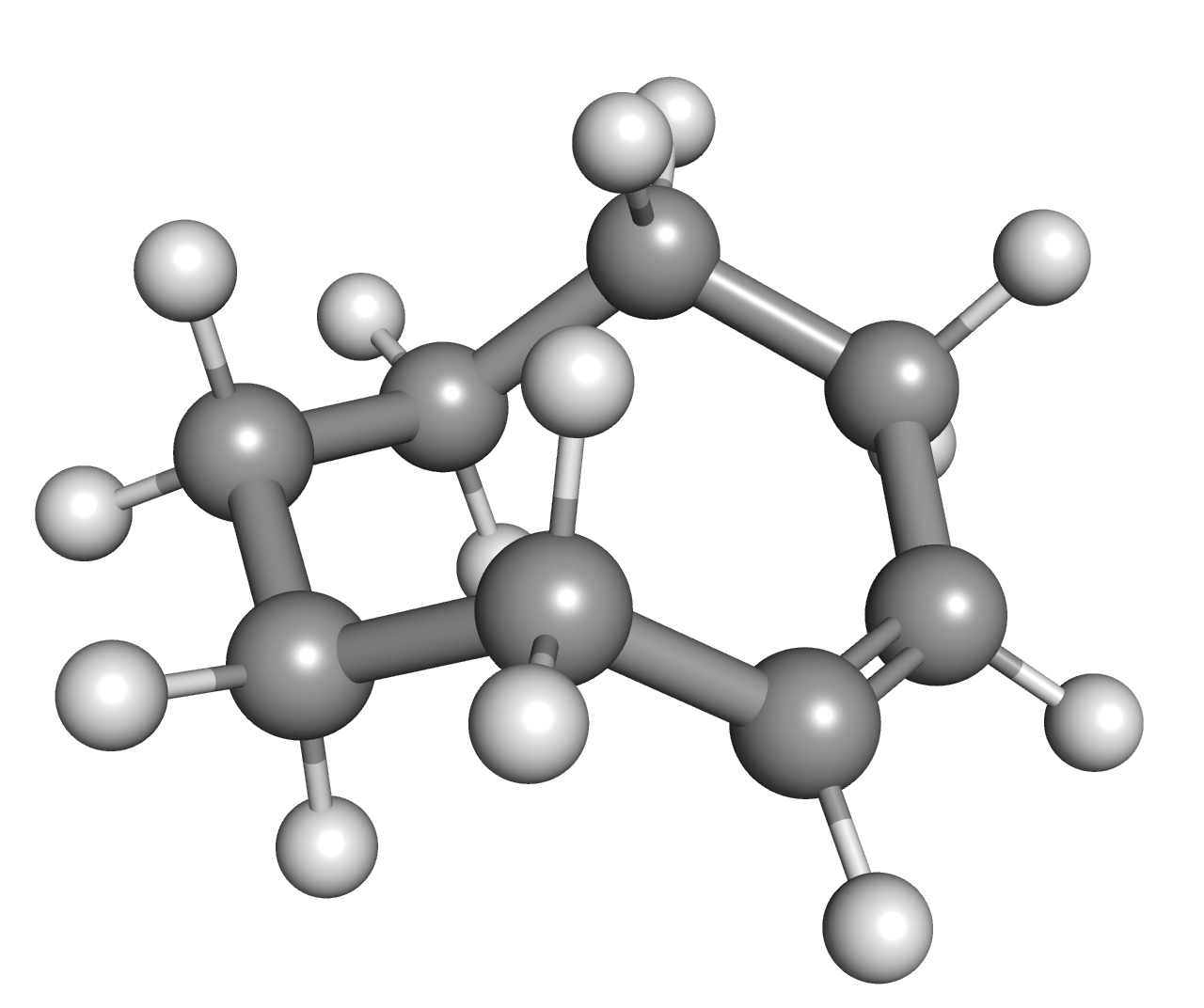
Bicyclooctane
The molecular formula C8H14 (molar mass: 110.20 g/mol) may refer to: * Allylcyclopentane * Biisobutenyl * Bimethallyl * Cyclooctenes ** cis-Cyclooctene, ''cis''-Cyclooctene ** trans-Cyclooctene, ''trans''-Cyclooctene * Methylcycloheptene * Methylenecycloheptane * 1,7-Octadiene * Octynes ** 1-Octyne ** 2-Octyne ** 3-Octyne ** 4-Octyne * Bicyclooctane ** Bicyclo[2.2.2]octane ** Polyquinane, Bicyclo[3.3.0]octane (polyquinane) ** Bicyclo[3.2.1]octane References {{MolFormDisambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Formula
In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and ''plus'' (+) and ''minus'' (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae. The simplest types of chemical formulae are called ''empirical formulae'', which use letters and numbers indicating the numerical ''proportions'' of atoms o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allylcyclopentane
Allylcyclopentane is a hydrocarbon that has the formula C8H14. This compound is a colourless liquid at room temperature. It has been prepared from cyclopentylmagnesium bromide and allyl bromide. References {{Reflist Allyl compounds Cyclopentyl compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclooctene
Cyclooctene is the cycloalkene with a formula . Its molecule has a ring of 8 carbon atoms, connected by seven single bonds and one double bond. Cyclooctene is notable because it is the smallest cycloalkene that can exist stably as either the ''cis'' or ''trans'' stereoisomer, with ''cis''-cyclooctene being the most common. Theoretical analysis implies a total of 16 conformational and configurational isomers, all chiral, forming 8 enantiomeric In chemistry, an enantiomer ( /ɪˈnænti.əmər, ɛ-, -oʊ-/ ''ih-NAN-tee-ə-mər''; from Ancient Greek ἐνάντιος ''(enántios)'' 'opposite', and μέρος ''(méros)'' 'part') – also called optical isomer, antipode, or optical ant ... pairs. The ''cis'' isomer can adopt various conformations, the most stable one being shaped like a ribbon. The most stable conformation of ''trans''-cyclooctene is shaped like the 8-carbon equivalent of the chair conformation of cyclohexane. Longer cycloalkene rings such as the ten-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cis-Cyclooctene
''cis''-Cyclooctene is a cycloalkene with the formula (CH2)6(CH)2. It is a colorless liquid that is used industrially to produce a polymer. It is also a ligand in organometallic chemistry. Cyclooctene is the smallest cycloalkene that can be isolated as both the ''cis''- and ''trans''-isomer. ''cis''-Cyclooctene is shaped like the 8-carbon equivalent chair conformation of cyclohexane. Uses and reactions Cyclooctene undergoes ring-opening metathesis polymerization to give polyoctenamers, which are marketed under the name Vestenamer. ''cis''-Cyclooctene (COE) is a substrate known for quite selectively forming the epoxide, as compared to other cycloalkenes, e.g. cyclohexene. Low amounts of radical by-products are found only. This behaviour is attributed to the difficulty of functionalizing allylic CH centers, which almost orthogonal allylic C-H bonds. Therefore, if radicals are around, they tend to form epoxide via an addition-elimination mechanism. It is used as an easily d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans-Cyclooctene
''trans''-Cyclooctene is a cyclic hydrocarbon with the formula ��(CH2)6CH=CH– where the two C–C single bonds adjacent to the double bond are on opposite sides of the latter's plane. It is a colorless liquid with a disagreeable odor. Cyclooctene is notable as the smallest cycloalkene that is readily isolated as its ''trans''-isomer. The ''cis''-isomer is much more stable; the ring-strain energies being 16.7 and 7.4 kcal/mol, respectively.Ron Walker, Rosemary M. Conrad, and Robert H. Grubbs (2009): "The living ROMP of ''trans''-cyclooctene". ''Macromolecules'', volume 42, issue 3, pages 599–605. A planar arrangement of the ring carbons would be too strained, and therefore the stable conformations of the ''trans'' form have a bent (non-planar) ring. Computations indicate that the most stable "crown" conformation has the carbon atoms alternately above and below the plane of the ring. A "half-chair" conformation, with about 6 kcal/mol higher energy, has carbons 2,3,5,6, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octyne
Octynes are alkynes with one triple bond and the molecular formula C8H14. The isomers are: * 1-Octyne * 2-Octyne * 3-Octyne * 4-Octyne 4-Octyne, also known as dipropylethyne, is a type of alkyne with a triple bond at its fourth carbon (the '4-' indicates the location of the triple bond in the chain). Its formula is C8H14. 4-Octyne forms with 5-decyne, 3-hexyne, and 2-butyne ... Alkynes {{Chemistry index ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |