|
Bicyclic
In chemistry, a bicyclic molecule () is a molecule that features two joined rings. Bicyclic structures occur widely, for example in many biologically important molecules like α-thujene and camphor. A bicyclic compound can be carbocyclic (all of the ring atoms are carbons), or heterocyclic (the rings' atoms consist of at least two elements), like DABCO. Moreover, the two rings can both be aliphatic (''e.g.'' decalin and norbornane), or can be aromatic (''e.g.'' naphthalene), or a combination of aliphatic and aromatic (''e.g.'' tetralin). Three modes of ring junction are possible for a bicyclic compound: * In spirocyclic compounds, the two rings share only one single atom, the spiro atom, which is usually a quaternary carbon. An example of a spirocyclic compound is the photochromic switch spiropyran. * In fused/condensed bicyclic compounds, two rings share two adjacent atoms. In other words, the rings share one covalent bond, ''i.e.'' the so-called bridgehead atoms are directly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridged Compounds
In chemistry, a bicyclic molecule () is a molecule that features two joined rings. Bicyclic structures occur widely, for example in many biologically important molecules like α-thujene and camphor. A bicyclic compound can be carbocyclic (all of the ring atoms are carbons), or heterocyclic (the rings' atoms consist of at least two elements), like DABCO. Moreover, the two rings can both be aliphatic (''e.g.'' decalin and norbornane), or can be aromatic (''e.g.'' naphthalene), or a combination of aliphatic and aromatic (''e.g.'' tetralin). Three modes of ring junction are possible for a bicyclic compound: * In spirocyclic compounds, the two rings share only one single atom, the spiro atom, which is usually a quaternary carbon. An example of a spirocyclic compound is the photochromic switch spiropyran. * In fused/condensed bicyclic compounds, two rings share two adjacent atoms. In other words, the rings share one covalent bond, ''i.e.'' the so-called bridgehead atoms are direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiro Compounds
In organic chemistry, spiro compounds are compounds that have at least two molecular rings with only one common atom. The simplest spiro compounds are bicyclic (having just two rings), or have a bicyclic portion as part of the larger ring system, in either case with the two rings connected through the defining single common atom. The one common atom connecting the participating rings distinguishes spiro compounds from other bicyclics: from ''isolated ring compounds'' like biphenyl that have no connecting atoms, from ''fused ring compounds'' like decalin having two rings linked by two adjacent atoms, and from ''bridged ring compounds'' like norbornane with two rings linked by two non-adjacent atoms.For all four categories, see The specific chapters can be found aan respectively, same access date. For the description featuring adjacent atoms for all but the isolated category, see Clayden, op. cit. Spiro compounds may be fully carbocyclic (all carbon) or heterocyclic (havi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Compound
A cyclic compound (or ring compound) is a term for a compound in the field of chemistry in which one or more series of atoms in the compound is connected to form a ring. Rings may vary in size from three to many atoms, and include examples where all the atoms are carbon (i.e., are carbocycles), none of the atoms are carbon (inorganic cyclic compounds), or where both carbon and non-carbon atoms are present (heterocyclic compounds). Depending on the ring size, the bond order of the individual links between ring atoms, and their arrangements within the rings, carbocyclic and heterocyclic compounds may be aromatic or non-aromatic; in the latter case, they may vary from being fully saturated to having varying numbers of multiple bonds between the ring atoms. Because of the tremendous diversity allowed, in combination, by the valences of common atoms and their ability to form rings, the number of possible cyclic structures, even of small size (e.g., < 17 total atoms) numbers in the many b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norbornane
Norbornane (also known as bicyclo .2.1eptane) is an organic compound and a saturated hydrocarbon with chemical formula C7H12. It is a crystalline compound with a melting point of 88 °C. The carbon skeleton is derived from cyclohexane ring with a methylene bridge in the 1,4- position, and is a bridged bicyclic compound. The compound is a prototype of a class of strained bicyclic hydrocarbons. The compound was originally synthesized by reduction of norcamphor. The name norbornane is derived from bornane, which is 1,7,7-trimethylnorbornane, being a derivative of camphor (bornanone). The prefix ''nor'' refers to the stripping of the methyl groups from the parent molecule bornane. See also * 2-Norbornyl cation * Norbornene * Norbornadiene * Bornane * endo-Norborneol * exo-Norborneol * Norcamphor Norcamphor is an organic compound, classified as a bicyclic ketone. It is an analog of camphor, but without the three methyl groups. A colorless solid, it is used as a building block ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dabco
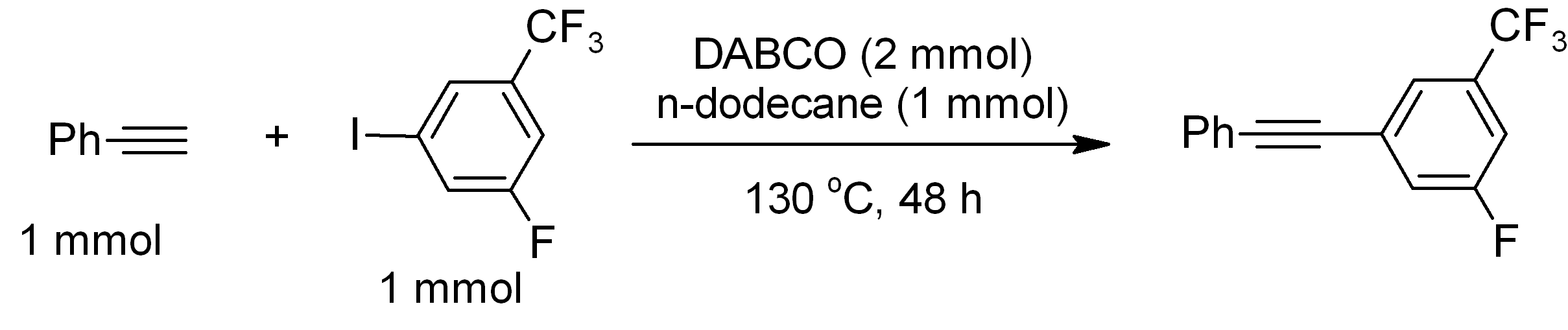
DABCO (1,4-diazabicyclo .2.2ctane), also known as triethylenediamine or TEDA, is a bicyclic organic compound with the formula N2(C2H4)3. This colorless solid is a highly nucleophilic tertiary amine base, which is used as a catalyst and reagent in polymerization and organic synthesis. It is similar in structure to quinuclidine, but the latter has one of the nitrogen atoms replaced by a carbon atom. Reactions The p''K''a of DABCOsup>+ (the protonated derivative) is 8.8, which is almost the same as ordinary alkylamines. The nucleophilicity of the amine is high because the amine centers are unhindered. It is sufficiently basic to promote C–C coupling of terminal acetylenes, for example, phenylacetylene couples with electron-deficient iodoarenes. : Catalyst DABCO is used as a base-catalyst for: *formation of polyurethane from alcohol and isocyanate functionalized monomers and pre-polymers. * Baylis-Hillman reactions of aldehydes and unsaturated ketones and aldehydes. : Lewis ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DABCO
DABCO (1,4-diazabicyclo .2.2ctane), also known as triethylenediamine or TEDA, is a bicyclic organic compound with the formula N2(C2H4)3. This colorless solid is a highly nucleophilic tertiary amine base, which is used as a catalyst and reagent in polymerization and organic synthesis. It is similar in structure to quinuclidine, but the latter has one of the nitrogen atoms replaced by a carbon atom. Reactions The p''K''a of DABCOsup>+ (the protonated derivative) is 8.8, which is almost the same as ordinary alkylamines. The nucleophilicity of the amine is high because the amine centers are unhindered. It is sufficiently basic to promote C–C coupling of terminal acetylenes, for example, phenylacetylene couples with electron-deficient iodoarenes. : Catalyst DABCO is used as a base-catalyst for: *formation of polyurethane from alcohol and isocyanate functionalized monomers and pre-polymers. * Baylis-Hillman reactions of aldehydes and unsaturated ketones and aldehydes. : Lewis ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclopentane
Cyclopentane (also called C pentane) is a highly flammable alicyclic hydrocarbon with chemical formula C5H10 and CAS number 287-92-3, consisting of a ring of five carbon atoms each bonded with two hydrogen atoms above and below the plane. It occurs as a colorless liquid with a petrol-like odor. Its melting point is −94 °C and its boiling point is 49 °C. Cyclopentane is in the class of cycloalkanes, being alkanes that have one or more rings of carbon atoms. It is formed by cracking cyclohexane in the presence of alumina at a high temperature and pressure. It was first prepared in 1893 by the German chemist Johannes Wislicenus. Production, occurrence and use Cycloalkanes are formed by catalytic reforming. For example, when passed over a hot platinum surfact, 2-methylbutane converts into cyclopentane. Cyclopentane has no particular use. No commercial products are made from cyclopentane itself. As a volatile hydrocarbon it is an incidental component of some fuels and blowing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decalin
Decalin (decahydronaphthalene, also known as bicyclo .4.0ecane and sometimes decaline), a bicyclic organic compound, is an industrial solvent. A colorless liquid with an aromatic odor, it is used as a solvent for many resins or fuel additives. Isomers Decalin occurs in ''cis'' and ''trans'' forms. The ''trans'' form is energetically more stable because of fewer steric interactions. ''cis''-Decalin is a chiral molecule without a chiral center; it has a two-fold rotational symmetry axis, but no reflective symmetry. However, the chirality is canceled through a chair-flipping process that turns the molecule into its mirror image. Image:Cis-trans isomerism of decahydronaphthalene.svg, Image:cis-decalin double chair.png, 2: Image:trans-decalin double chair.png, 3: File:Cisdecalin conformations.png, 4: ''trans''-Decalin The only possible way to join the two six-membered rings in the ''trans'' position means the second ring needs to start from two equatorial bonds (blue) of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Chemistry
The Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) is a learned society (professional association) in the United Kingdom with the goal of "advancing the chemistry, chemical sciences". It was formed in 1980 from the amalgamation of the Chemical Society, the Royal Institute of Chemistry, the Faraday Society, and the Society for Analytical Chemistry with a new Royal Charter and the dual role of learned society and professional body. At its inception, the Society had a combined membership of 34,000 in the UK and a further 8,000 abroad. The headquarters of the Society are at Burlington House, Piccadilly, London. It also has offices in Thomas Graham House in Cambridge (named after Thomas Graham (chemist), Thomas Graham, the first president of the Chemical Society) where ''RSC Publishing'' is based. The Society has offices in the United States, on the campuses of The University of Pennsylvania and Drexel University, at the University City Science Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in both Beijing a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
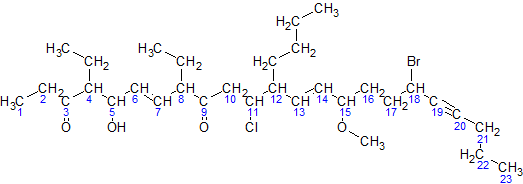
IUPAC Nomenclature Of Organic Chemistry
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic chemical compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published in the ''Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry'' (informally called the Blue Book). Ideally, every possible organic compound should have a name from which an unambiguous structural formula can be created. There is also an IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry. To avoid long and tedious names in normal communication, the official IUPAC naming recommendations are not always followed in practice, except when it is necessary to give an unambiguous and absolute definition to a compound. IUPAC names can sometimes be simpler than older names, as with ethanol, instead of ethyl alcohol. For relatively simple molecules they can be more easily understood than non-systematic names, which must be learnt or looked over. However, the common or trivial name is often substantially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |