|
Bibulous Paper
Blotting paper, called bibulous paper, is a highly absorbent type of paper or other material. It is used to absorb an excess of liquid substances (such as ink or oil) from the surface of writing paper or objects. Blotting paper referred to as bibulous paper is mainly used in microscopy to remove excess liquids from the slide before viewing. Blotting paper has also been sold as a cosmetic to aid in the removal of skin oils and makeup. Manufacture Blotting paper is made from different materials of varying thickness, softness, etc. depending on the application. It is often made of cotton and manufactured on special paper machines. Blotting paper is reputed to be first referred to in the English language in the 15th century but there is a tradition in Norfolk, England that it was invented by accident at Lyng Mill on the River Wensum. It is reported that a Berkshire (England) paper mill worker failed to add sizing to a batch of paper that was being produced. The batch was discarded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysergic Acid Diethylamide
Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), also known colloquially as acid, is a potent psychedelic drug. Effects typically include intensified thoughts, emotions, and sensory perception. At sufficiently high dosages LSD manifests primarily mental, visual, as well as auditory, hallucinations. Dilated pupils, increased blood pressure, and increased body temperature are typical. Effects typically begin within half an hour and can last for up to 20 hours. LSD is also capable of causing mystical experiences and ego dissolution. It is used mainly as a recreational drug or for spiritual reasons. LSD is both the prototypical psychedelic and one of the "classical" psychedelics, being the psychedelics with the greatest scientific and cultural significance. LSD is typically either swallowed or held under the tongue. It is most often sold on blotter paper and less commonly as tablets, in a watery solution or in gelatin squares called panes. LSD is considered to be non-addictive with low potent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
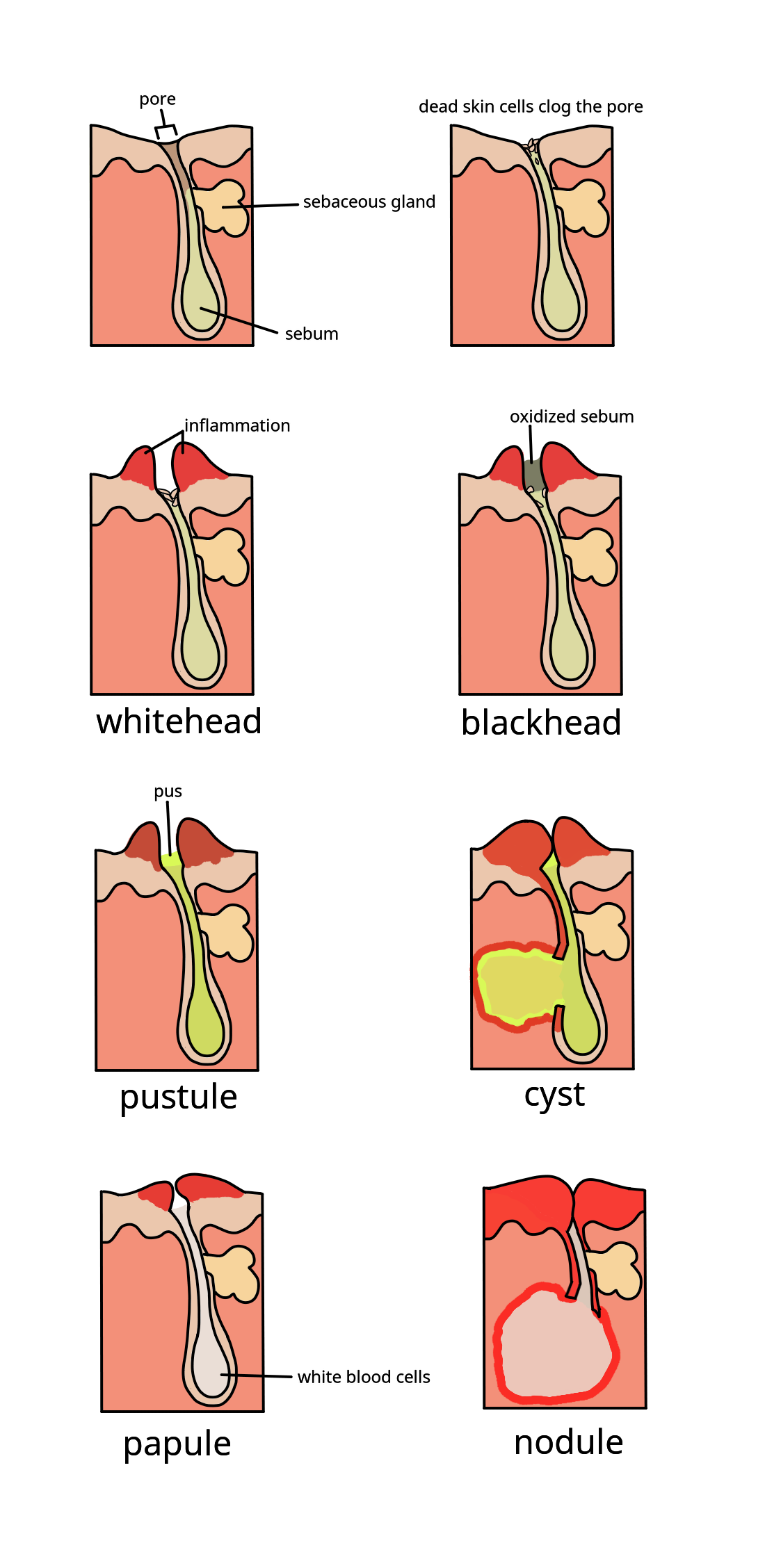
Acne
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term Cutaneous condition, skin condition that occurs when Keratinocyte, dead skin cells and Sebum, oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include comedo, blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and possible scarring. It primarily affects skin with a relatively high number of sebaceous gland, oil glands, including the face, upper part of the chest, and back. The resulting appearance can lead to anxiety (mood), anxiety, reduced self-esteem, and, in extreme cases, clinical depression, depression or suicidal ideations, thoughts of suicide. Susceptibility to acne is primarily genetic in 80% of cases. The roles of diet and cigarette smoking in the condition are unclear, and neither hygiene, cleanliness nor exposure to sunlight appear to play a part. In both sexes, hormones called androgens appear to be part of the underlying mechanism, by causing increased production of sebum. Another common fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
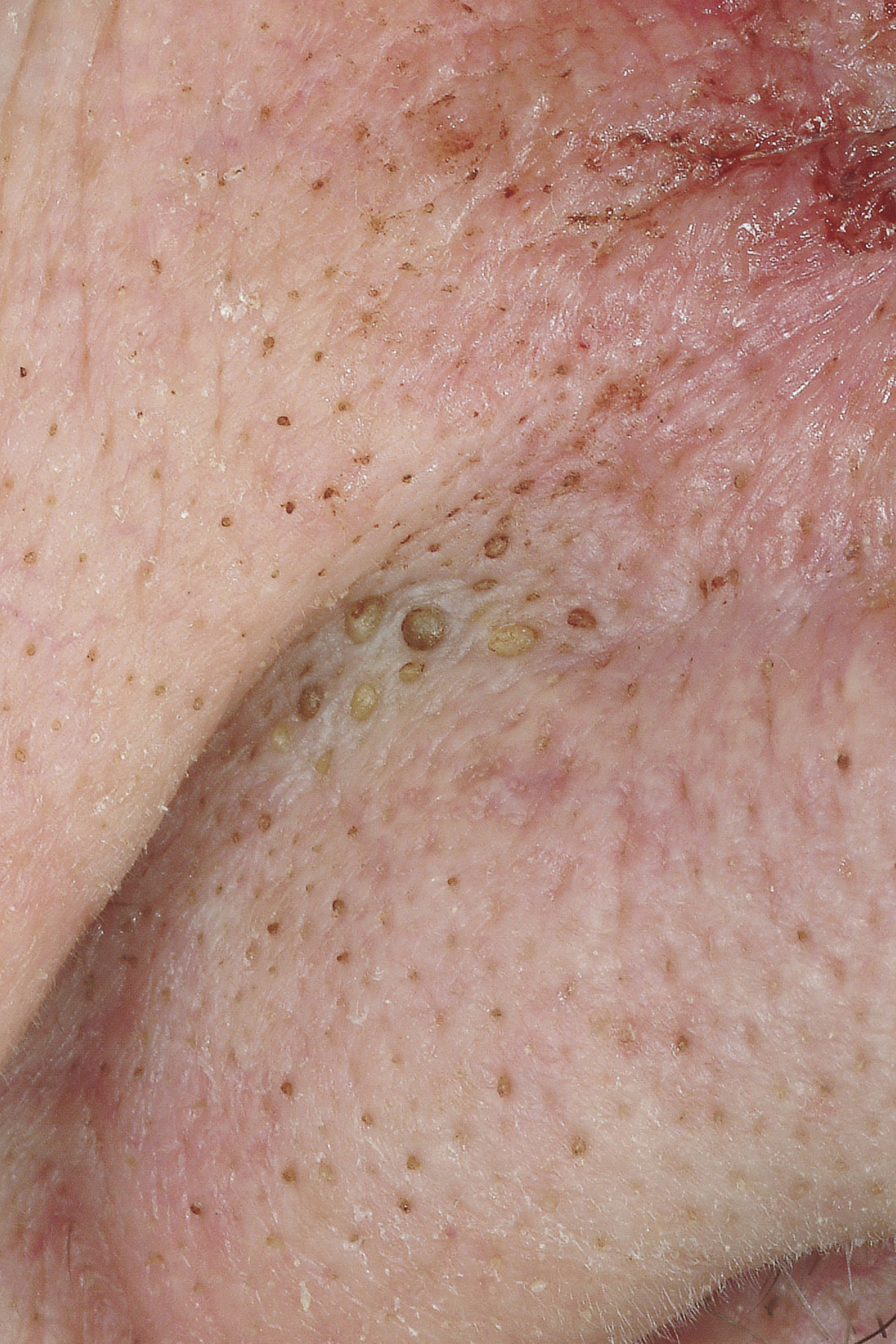
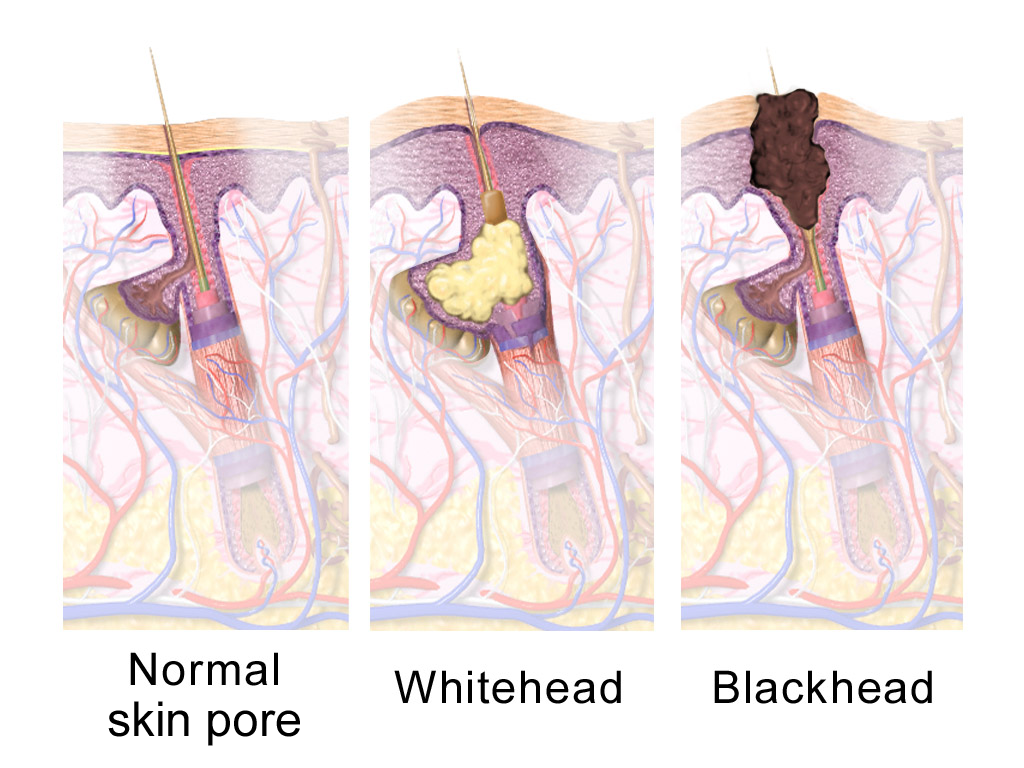
Comedones
A comedo is a clogged hair follicle (pore) in the skin. Keratin (skin debris) combines with oil to block the follicle. A comedo can be open (blackhead) or closed by skin (whitehead) and occur with or without acne. The word "comedo" comes from the Latin ''comedere'', meaning "to eat up", and was historically used to describe parasitic worms; in modern medical terminology, it is used to suggest the worm-like appearance of the expressed material. The chronic inflammatory condition that usually includes comedones, inflamed papules, and pustules (pimples) is called acne. Infection causes inflammation and the development of pus. Whether a skin condition classifies as acne depends on the number of comedones and infection. Comedones should not be confused with sebaceous filaments. Comedo-type ductal carcinoma ''in situ'' (DCIS) is not related to the skin conditions discussed here. DCIS is a noninvasive form of breast cancer, but comedo-type DCIS may be more aggressive, so may be more lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salicylic Acid
Salicylic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4CO2H. A colorless, bitter-tasting solid, it is a precursor to and a metabolite of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid). It is a plant hormone, and has been listed by the EPA Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) Chemical Substance Inventory as an experimental teratogen. The name is from Latin ''salix'' for willow tree. It is an ingredient in some anti-acne products. Salts and esters of salicylic acid are known as salicylates. Uses Medicine Salicylic acid as a medication is commonly used to remove the outer layer of the skin. As such, it is used to treat warts, psoriasis, acne vulgaris, ringworm, dandruff, and ichthyosis. Similar to other hydroxy acids, salicylic acid is an ingredient in many skincare products for the treatment of seborrhoeic dermatitis, acne, psoriasis, calluses, corns, keratosis pilaris, acanthosis nigricans, ichthyosis, and warts. Uses in manufacturing Salicylic acid is used as a food preservative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebum
A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest number on the face and scalp, but also on all parts of the skin except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. In the eyelids, meibomian glands, also called tarsal glands, are a type of sebaceous gland that secrete a special type of sebum into tears. Surrounding the female nipple, areolar glands are specialized sebaceous glands for lubricating the nipple. Fordyce spots are benign, visible, sebaceous glands found usually on the lips, gums and inner cheeks, and genitals. Structure Location Sebaceous glands are found throughout all areas of the skin, except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There are two types of sebaceous glands, those connected to hair follicles and those that exist independently. Sebaceous glands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Adventure Of The Missing Three-Quarter
"The Adventure of the Missing Three-Quarter", one of the 56 Sherlock Holmes short stories written by Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, is one of 13 stories in the cycle collected as ''The Return of Sherlock Holmes'' (1905). It was originally published in ''The Strand Magazine'' in the United Kingdom in August 1904, and was also published in ''Collier's'' in the United States on 26 November 1904. Plot Mr. Cyril Overton of Trinity College, Cambridge, comes to Sherlock Holmes seeking his help in Godfrey Staunton's disappearance. Staunton is the key man on Overton's rugby union team (who plays at the three-quarters position, hence the story's title) and they will not win an important match the following day against Oxford if Staunton cannot be found. Holmes has to admit that sport is outside his field, but he shows the same care he has shown to his other cases. Staunton had seemed a bit pale and bothered earlier in the day, but late in the evening, according to a hotel porter, a rough-look ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plot Device
A plot device or plot mechanism is any narrative technique, technique in a narrative used to move the Plot (narrative), plot forward. A clichéd plot device may annoy the reader and a contrived or arbitrary device may confuse the reader, causing a loss of the suspension of disbelief. However, a well-crafted plot device, or one that emerges naturally from the setting or characters of the story, may be entirely accepted, or may even be unnoticed by the audience. Stories using plot devices Many stories, especially in the fantasy genre, feature an object or objects with some great magical power, such as a crown, sword, or jewel. Often what drives the plot is the hero's need to find the object and use it for good, before the villain can use it for evil, or if the object has been broken by the villains, to retrieve each piece that must be gathered from each antagonist to restore it, or, if the object itself is evil, to destroy it. In some cases destroying the object will lead to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pounce (calligraphy)
Pounce or sand is a fine powder, most often made from powdered cuttlefish bone or sandarac resin, that was used both to dry ink and to sprinkle on a rough writing surface to make it smooth enough for writing. This was especially needed if the paper came " unsized", that is, lacking the thin gelatinous material used to fill the surface of the paper and make it smooth enough for writing with a quill or a steel nib. It was also used to prepare the surface when drafting with Rapidograph pens on mylar, a common drafting medium in the late twentieth century. History In the 19th century the pounce pots or sanders often had a shallow dish round the top so that pounce or sand could be returned to the pot and reused. The process is very effective for quickly drying ink, and although blotting paper has been available since the Tudor period, pounce or sand continued to be used throughout the nineteenth century because it was often cheaper. Application Handwriting and calligraphy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fountain Pen
A fountain pen is a writing instrument which uses a metal nib to apply a water-based ink to paper. It is distinguished from earlier dip pens by using an internal reservoir to hold ink, eliminating the need to repeatedly dip the pen in an inkwell during use. The pen draws ink from the reservoir through a feed to the nib and deposits the ink on paper via a combination of gravity and capillary action. Filling the reservoir with ink may be achieved manually, via the use of an eyedropper or syringe, or via an internal filling mechanism which creates suction (for example, through a piston mechanism) or a vacuum to transfer ink directly through the nib into the reservoir. Some pens employ removable reservoirs in the form of pre-filled ink cartridges. History Early prototypes of reservoir pens According to Qadi al-Nu'man al-Tamimi (d. 974) in his ''Kitab al-Majalis wa 'l-musayarat'', the Fatimid caliph Al-Mu'izz li-Din Allah in Arab Egypt demanded a pen that would not stain his h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dip Pen
A dip pen or nib pen or pen nib usually consists of a metal nib with capillary channels like those of fountain pen nibs, mounted in a handle or holder, often made of wood. Other materials can be used for the holder, including bone, metal and plastic; some pens are made entirely of glass. Generally, dip pens have no ink reservoir, so the user must recharge the ink from an ink bowl or bottle to continue drawing or writing. There are simple, tiny tubular reservoirs that illustrators sometimes clip onto dip pens, which allow drawing for several minutes without recharging the nib. Recharging can be done by dipping into an inkwell, but it is also possible to charge the pen with an eyedropper, a syringe, or a brush, which gives more control over the amount of ink applied. Thus, "dip pens" are not necessarily dipped; many illustrators call them "nib pens". Dip pens emerged in the early 19th century, when they replaced quill pens and, in some parts of the world, reed pens. Dip pens were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
.jpg)