|
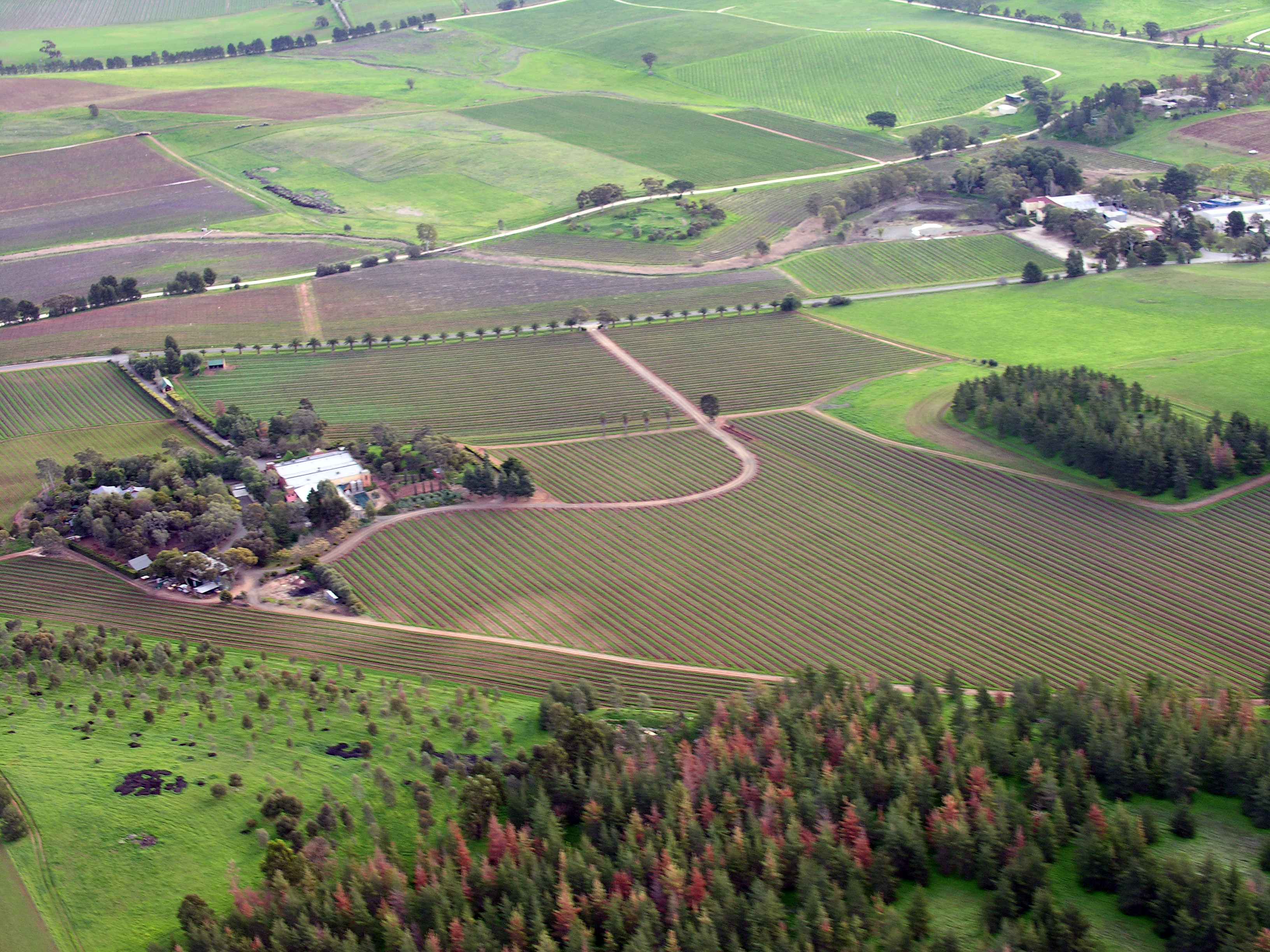
Bethune, Saskatchewan
Bethune ( 2016 population: ) is a village in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan within the Rural Municipality of Dufferin No. 190 and Census Division No. 6. The village is north-west of Regina on Highway 11 (Louis Riel Trail). Arm River flows along a river valley north of Bethune, which features camping sites, and the Qu'Appelle River is a short way south. Last Mountain Lake or Long Lake is north-east of Bethune whereas Buffalo Pound Lake is just south-west. The post office of Bethune, Assiniboia, NWT was established on 5 June 1905, three months before Saskatchewan became a province. History Bethune incorporated as a village on 2 August 1912. The village takes its name from C.B. Bethune, the engineer on the first train to travel the railway in 1887. Demographics In the 2021 Census of Population conducted by Statistics Canada, Bethune had a population of living in of its total private dwellings, a change of from its 2016 population of . With a land area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Villages In Saskatchewan
A village is a type of incorporated urban municipality in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. A village is created from an organized hamlet by the Minister of Municipal Affairs by ministerial order via section 51 of ''The Municipalities Act'' if the community has: *been an organized hamlet for three or more years; *a population of 100 or more; *50 or more dwellings or businesses; and *a taxable assessment base that meets a prescribed minimum. Saskatchewan has 250 villages that had a cumulative population of 41,514 and an average population of 166 in the 2016 Census. Saskatchewan's largest village is Caronport with a population of 994, while Ernfold Ernfold ( 2016 population: ) is a village in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan within the Rural Municipality of Morse No. 165 and Census Division No. 7. Initially situated alongside the original two-lane highway, the village was enclosed b ..., Keeler, Krydor, Valparaiso and Waldron are the province's small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postal Code
A postal code (also known locally in various English-speaking countries throughout the world as a postcode, post code, PIN or ZIP Code) is a series of letters or digits or both, sometimes including spaces or punctuation, included in a postal address for the purpose of sorting mail. the Universal Postal Union lists 160 countries which require the use of a postal code. Although postal codes are usually assigned to geographical areas, special codes are sometimes assigned to individual addresses or to institutions that receive large volumes of mail, such as government agencies and large commercial companies. One example is the French CEDEX system. Terms There are a number of synonyms for postal code; some are country-specific; * CAP: The standard term in Italy; CAP is an acronym for ''codice di avviamento postale'' (postal expedition code). * CEP: The standard term in Brazil; CEP is an acronym for ''código de endereçamento postal'' (postal addressing code). * Eircode: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
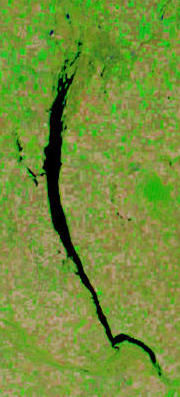
Buffalo Pound Lake
Buffalo Pound Lake is a eutrophic prairie lake in Saskatchewan, Canada, formed from glaciation about 10,000 years ago, on the Qu'Appelle River approximately north of Moose Jaw and north-east of Tuxford. The lake gets its name from the method used by First Nations people to capture the bison using the natural topography as corrals or buffalo pounds. Bison, once numbering more than 60 million on the prairies but almost extinct by 1900, were reintroduced into the area in 1972. The lake provides drinking water for the cities of Regina, Moose Jaw, and the Mosaic Company potash mine at Belle Plaine, approximately 25% of the province's population. It is also used for recreational purposes such as camping, boating, and fishing and is home to a host of fish species including walleye, sauger, yellow perch, northern pike, cisco, mooneye, lake whitefish, white sucker, channel catfish, burbot, bigmouth buffalo, and common carp. Buffalo Pound Provincial Park is located on the sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Last Mountain Lake
Last Mountain Lake, also known as Long Lake, is a prairie lake formed from glaciation 11,000 years ago. It is located in south central Saskatchewan, Canada, about north-west of the city of Regina. It flows into the Qu'Appelle River via Last Mountain Creek, which flows past Craven. It is approximately long, and wide at its widest point. It is the largest naturally occurring body of water in southern Saskatchewan. Only Lake Diefenbaker, which is man-made, is larger. The lake is a popular resort area for residents of south-eastern Saskatchewan. History In the late 1800s, access to the area for farming and settlement was opened up by the Qu'Appelle, Long Lake and Saskatchewan Railroad and Steamboat Company which also operated steamships on the lake. Until 1974, the lake was known as ''Long Lake''. It was renamed ''Last Mountain Lake'' in honour of a Plains Cree legend about the Great Spirit shovelling dirt from the valley the lake now occupies and forming Last Mounta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qu'Appelle River
The Qu'Appelle River is a river in the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba that flows east from Lake Diefenbaker in south-western Saskatchewan to join the Assiniboine River in Manitoba, just south of Lake of the Prairies, near the village of St. Lazare. It is located in a region called the Prairie Pothole Region of North America, which extends throughout three Canadian provinces and five U.S. states. It is also within Palliser's Triangle and the Great Plains ecoregion. With the construction of the Qu'Appelle River Dam and Gardiner Dam upstream, water flow was significantly increased and regulated. Most of the Qu'Appelle's present flow is actually water diverted from the South Saskatchewan River. Upper and lower watersheds According to the Saskatchewan Water Security Agency, the Qu'Appelle Valley is made up of two watersheds with the dividing point being Craven Dam on the east side of Craven: Lower Qu'Appelle Watershed The Lower Qu'Appelle Valley is lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arm River No
In human anatomy, the arm refers to the upper limb in common usage, although academically the term specifically means the upper arm between the glenohumeral joint (shoulder joint) and the elbow joint. The distal part of the upper limb between the elbow and the radiocarpal joint (wrist joint) is known as the forearm or "lower" arm, and the extremity beyond the wrist is the hand. By anatomical definitions, the bones, ligaments and skeletal muscles of the shoulder girdle, as well as the axilla between them, is considered parts of the upper limb, and thus also components of the arm. The Latin term ''brachium'', which serves as a root word for naming many anatomical structures, may refer to either the upper limb as a whole or to the upper arm on its own. Anatomy Bones The humerus is one of the three long bones of the arm. It joins with the scapula at the shoulder joint and with the other long bones of the arm, the ulna and radius at the elbow joint. The elbow is a complex hin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Riel
Louis Riel (; ; 22 October 1844 – 16 November 1885) was a Canadian politician, a founder of the province of Manitoba, and a political leader of the Métis people. He led two resistance movements against the Government of Canada and its first prime minister John A. Macdonald. Riel sought to defend Métis rights and identity as the Northwest Territories came progressively under the Canadian sphere of influence. The first resistance movement led by Riel was the Red River Resistance of 1869–1870. The provisional government established by Riel ultimately negotiated the terms under which the new province of Manitoba entered the Canadian Confederation. However, while carrying out the resistance, Riel had a Canadian nationalist, Thomas Scott, executed. Riel soon fled to the United States to escape prosecution. He was elected three times as member of the House of Commons, but, fearing for his life, he could never take his seat. During these years in exile he came to believe that h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saskatchewan Highway 11
Highway 11 is a major north-south highway in Saskatchewan, Canada that connects the province's three largest cities: Regina, Saskatoon and Prince Albert. It is a structural pavement major arterial highway which is approximately long. It is also known as the Louis Riel Trail (LRT) after the 19th century Métis leader. It runs from Highway 1 (Trans-Canada Highway) in Regina until Highway 2 south of Prince Albert. Historically the southern portion between Regina and Saskatoon was Provincial Highway 11, and followed the Dominion Survey lines on the square, and the northern portion between Saskatoon and Prince Albert was Provincial Highway 12. From Regina to Saskatoon, Highway 11 is a four-lane divided highway except in the village of Chamberlain, where the road narrows to two lanes through the community, including its intersection with Highway 2 south to Moose Jaw. All intersections in this segment are at-grade except for two interchanges in the Lumsden valley and in Saskatoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regina, Saskatchewan
Regina () is the capital city of the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. The city is the second-largest in the province, after Saskatoon, and is a commercial centre for southern Saskatchewan. As of the 2021 census, Regina had a city population of 226,404, and a Metropolitan Area population of 249,217. It is governed by Regina City Council. The city is surrounded by the Rural Municipality of Sherwood No. 159. Regina was previously the seat of government of the North-West Territories, of which the current provinces of Saskatchewan and Alberta originally formed part, and of the District of Assiniboia. The site was previously called Wascana ("Buffalo Bones" in Cree), but was renamed to Regina (Latin for "Queen") in 1882 in honour of Queen Victoria. This decision was made by Queen Victoria's daughter Princess Louise, who was the wife of the Governor General of Canada, the Marquess of Lorne. Unlike other planned cities in the Canadian West, on its treeless flat plain Regina ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rural Municipality Of Dufferin No
In general, a rural area or a countryside is a geographic area that is located outside towns and cities. Typical rural areas have a low population density and small settlements. Agricultural areas and areas with forestry typically are described as rural. Different countries have varying definitions of ''rural'' for statistical and administrative purposes. In rural areas, because of their unique economic and social dynamics, and relationship to land-based industry such as agriculture, forestry and resource extraction, the economics are very different from cities and can be subject to boom and bust cycles and vulnerability to extreme weather or natural disasters, such as droughts. These dynamics alongside larger economic forces encouraging to urbanization have led to significant demographic declines, called rural flight, where economic incentives encourage younger populations to go to cities for education and access to jobs, leaving older, less educated and less wealthy popul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Village
A village is a clustered human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town (although the word is often used to describe both hamlets and smaller towns), with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Though villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighborhoods. Villages are normally permanent, with fixed dwellings; however, transient villages can occur. Further, the dwellings of a village are fairly close to one another, not scattered broadly over the landscape, as a dispersed settlement. In the past, villages were a usual form of community for societies that practice subsistence agriculture, and also for some non-agricultural societies. In Great Britain, a hamlet earned the right to be called a village when it built a church. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada 2016 Census
The 2016 Canadian census was an enumeration of Canadian residents, which counted a population of 35,151,728, a change from its 2011 population of 33,476,688. The census, conducted by Statistics Canada, was Canada's seventh quinquennial census. The official census day was May 10, 2016. Census web access codes began arriving in the mail on May 2, 2016. The 2016 census marked the reinstatement of the mandatory long-form census, which had been dropped in favour of the voluntary National Household Survey for the 2011 census. With a response rate of 98.4%, this census is said to be the best one ever recorded since the 1666 census of New France. This census was succeeded by Canada's 2021 census. Planning Consultation with census data users, clients, stakeholders and other interested parties closed in November 2012. Qualitative content testing, which involved soliciting feedback regarding the questionnaire and tests responses to its questions, was scheduled for the fall of 2013, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |