|
Betavexity
In investment analysis, betavexity is a form of convexity that is specific to the beta coefficient of a long tailed investment (i.e. mortality risk). It is similar in nature to bond convexity In finance, bond convexity is a measure of the non-linear relationship of bond prices to changes in interest rates, the second derivative of the price of the bond with respect to interest rates ( duration is the first derivative). In general, the ... or gamma that are exhibited in financial products such as bonds or options but is specific to portfolios replicating indices of shorter maturities. Investment horizon Certain investors such as insurance companies have longer-term investment horizons than hedge funds, which allow for investments in assets that have longer maturities. As a result, these investors can invest in assets that have an inherent return component linked to the dynamic of the term of the investment. References {{Finance-stub Convex geometry Financial risk modelin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Coefficient
In finance, the beta (β or market beta or beta coefficient) is a measure of how an individual asset moves (on average) when the overall stock market increases or decreases. Thus, beta is a useful measure of the contribution of an individual asset to the risk of the market portfolio when it is added in small quantity. Thus, beta is referred to as an asset's non-diversifiable risk, its systematic risk, market risk, or hedge ratio. Beta is ''not'' a measure of idiosyncratic risk. Interpretation of values By definition, the value-weighted average of all market-betas of all investable assets with respect to the value-weighted market index is 1. If an asset has a beta above (below) 1, it indicates that its return moves more (less) than 1-to-1 with the return of the market-portfolio, on average. In practice, few stocks have negative betas (tending to go up when the market goes down). Most stocks have betas between 0 and 3. Treasury bills (like most fixed income instruments) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convexity In Economics
Convexity is an important topic in economics. In the Arrow–Debreu model of general economic equilibrium, agents have convex budget sets and convex preferences: At equilibrium prices, the budget hyperplane supports the best attainable indifference curve. The profit function is the convex conjugate of the cost function. Convex analysis is the standard tool for analyzing textbook economics. Non‑convex phenomena in economics have been studied with nonsmooth analysis, which generalizes convex analysis. Preliminaries The economics depends upon the following definitions and results from convex geometry. Real vector spaces A real vector space of two dimensions may be given a Cartesian coordinate system in which every point is identified by a list of two real numbers, called "coordinates", which are conventionally denoted by ''x'' and ''y''. Two points in the Cartesian plane can be '' added'' coordinate-wise : (''x''1, ''y''1) + (''x''2, ''y''2) = (''x''1+''x''2, ''y' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Tail
In statistics and business, a long tail of some probability distribution, distributions of numbers is the portion of the distribution having many occurrences far from the "head" or central part of the distribution. The distribution could involve popularities, random numbers of occurrences of events with various probabilities, etc. The term is often used loosely, with no definition or an arbitrary definition, but precise definitions are possible. In statistics, the term ''long-tailed distribution'' has a narrow technical meaning, and is a subtype of heavy-tailed distribution. Intuitively, a distribution is (right) long-tailed if, for any fixed amount, when a quantity exceeds a high level, it almost certainly exceeds it by at least that amount: large quantities are probably even larger. Note that there is no sense of ''the'' "long tail" of a distribution, but only the ''property'' of a distribution being long-tailed. In business, the term ''long tail'' is applied to rank-size dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bond Convexity
In finance, bond convexity is a measure of the non-linear relationship of bond prices to changes in interest rates, the second derivative of the price of the bond with respect to interest rates (duration is the first derivative). In general, the higher the duration, the more sensitive the bond price is to the change in interest rates. Bond convexity is one of the most basic and widely used forms of convexity in finance. Convexity was based on the work of Hon-Fei Lai and popularized by Stanley Diller. Calculation of convexity Duration is a linear measure or 1st derivative of how the price of a bond changes in response to interest rate changes. As interest rates change, the price is not likely to change linearly, but instead it would change over some curved function of interest rates. The more curved the price function of the bond is, the more inaccurate duration is as a measure of the interest rate sensitivity. Convexity is a measure of the curvature or 2nd derivative of how ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
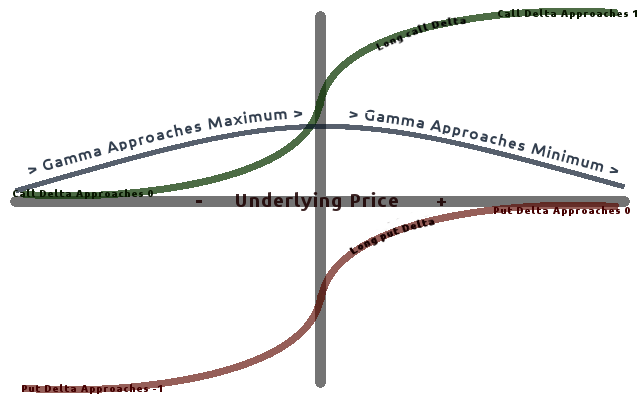
Gamma (finance)
In mathematical finance, the Greeks are the quantities representing the sensitivity of the price of derivatives such as options to a change in underlying parameters on which the value of an instrument or portfolio of financial instruments is dependent. The name is used because the most common of these sensitivities are denoted by Greek letters (as are some other finance measures). Collectively these have also been called the risk sensitivities, risk measures or hedge parameters. Use of the Greeks The Greeks are vital tools in risk management. Each Greek measures the sensitivity of the value of a portfolio to a small change in a given underlying parameter, so that component risks may be treated in isolation, and the portfolio rebalanced accordingly to achieve a desired exposure; see for example delta hedging. The Greeks in the Black–Scholes model are relatively easy to calculate, a desirable property of financial models, and are very useful for derivatives traders, espec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bond (finance)
In finance, a bond is a type of security under which the issuer ( debtor) owes the holder ( creditor) a debt, and is obliged – depending on the terms – to repay the principal (i.e. amount borrowed) of the bond at the maturity date as well as interest (called the coupon) over a specified amount of time. The interest is usually payable at fixed intervals: semiannual, annual, and less often at other periods. Thus, a bond is a form of loan or IOU. Bonds provide the borrower with external funds to finance long-term investments or, in the case of government bonds, to finance current expenditure. Bonds and stocks are both securities, but the major difference between the two is that (capital) stockholders have an equity stake in a company (i.e. they are owners), whereas bondholders have a creditor stake in a company (i.e. they are lenders). As creditors, bondholders have priority over stockholders. This means they will be repaid in advance of stockholders, but will rank behind s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Option (finance)
In finance, an option is a contract which conveys to its owner, the ''holder'', the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific quantity of an underlying asset or instrument at a specified strike price on or before a specified date, depending on the style of the option. Options are typically acquired by purchase, as a form of compensation, or as part of a complex financial transaction. Thus, they are also a form of asset and have a valuation that may depend on a complex relationship between underlying asset price, time until expiration, market volatility, the risk-free rate of interest, and the strike price of the option. Options may be traded between private parties in ''over-the-counter'' (OTC) transactions, or they may be exchange-traded in live, public markets in the form of standardized contracts. Definition and application An option is a contract that allows the holder the right to buy or sell an underlying asset or financial instrument at a specified strike ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convex Geometry
In mathematics, convex geometry is the branch of geometry studying convex sets, mainly in Euclidean space. Convex sets occur naturally in many areas: computational geometry, convex analysis, discrete geometry, functional analysis, geometry of numbers, integral geometry, linear programming, probability theory, game theory, etc. Classification According to the Mathematics Subject Classification MSC2010, the mathematical discipline ''Convex and Discrete Geometry'' includes three major branches: * general convexity * polytopes and polyhedra * discrete geometry (though only portions of the latter two are included in convex geometry). General convexity is further subdivided as follows: *axiomatic and generalized convexity *convex sets without dimension restrictions *convex sets in topological vector spaces *convex sets in 2 dimensions (including convex curves) *convex sets in 3 dimensions (including convex surfaces) *convex sets in ''n'' dimensions (including convex hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
