|
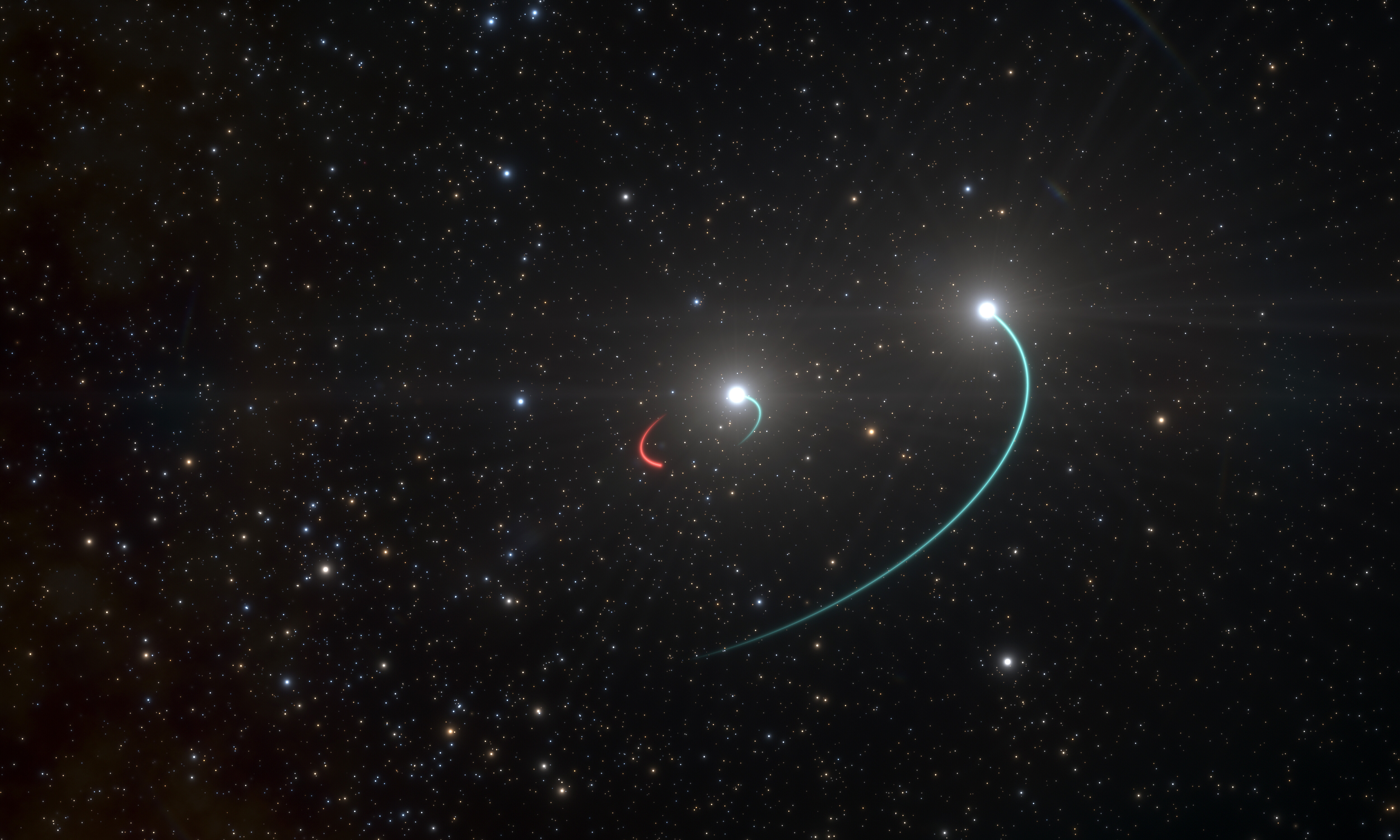
Beta Capricorni
Beta Capricorni (β Capricorni, abbreviated Beta Cap, β Cap) is a multiple star system in the constellation of Capricornus and located 328 light-years from the Sun. Because it is near the ecliptic, Beta Capricorni can be occulted by the Moon, and also (rarely) by planets. The system is believed to consist of five stars. With binoculars or a small telescope, Beta Capricorni can be resolved into a binary pair. The brighter of the two is designated Beta¹ Capricorni or Beta Capricorni A; the dimmer, Beta² Capricorni or Beta Capricorni B. Both are themselves made up of multiple stars. Beta¹ Capricorni has three components; a single star designated Beta Capricorni Aa (formally named Dabih , the traditional name of the system) and a binary pair, Beta Capricorni Ab (whose two components are designated Beta Capricorni Ab1 and Ab2). Beta² Capricorni is also a binary pair, with components designated Beta Capricorni Ba and Bb. Two other nearby stars were discovered by John Hers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J2000
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a instant, moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a Astronomical object, celestial body, as they are subject to Perturbation (astronomy), perturbations and vary with time. These time-varying astronomical quantities might include, for example, the mean longitude or mean anomaly of a body, the node of its orbit relative to a reference plane, the direction of the apogee or Perihelion and aphelion, aphelion of its orbit, or the size of the major axis of its orbit. The main use of astronomical quantities specified in this way is to calculate other relevant parameters of motion, in order to predict future positions and velocities. The applied tools of the disciplines of celestial mechanics or its subfield orbital mechanics (for predicting orbital paths and positions for bodies in motion under the gravitational effects of other bodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Star System
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars that orbit each other, bound by gravitational attraction. A large group of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a '' star cluster'' or '' galaxy'', although, broadly speaking, they are also star systems. Star systems are not to be confused with planetary systems, which include planets and similar bodies (such as comets). A star system of two stars is known as a '' binary star'', ''binary star system'' or ''physical double star''. If there are no tidal effects, no perturbation from other forces, and no transfer of mass from one star to the other, such a system is stable, and both stars will trace out an elliptical orbit around the barycenter of the system indefinitely. ''(See Two-body problem)''. Examples of binary systems are Sirius, Procyon and Cygnus X-1, the last of which probably consists of a star and a black hole. Multiple star systems A multiple star system consists of three or more stars that a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xi2 Capricorni
Xi2 Capricorni (ξ2 Capricorni) is a yellow-white hued star in the southern constellation of Capricornus. It is dimly visible to the naked eye on a dark night, having an apparent visual magnitude of +5.83. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 36.10 mas as seen from Earth, this system is located 90 light years from the Sun. This is an F-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of , where the suffix notation indicates the spectrum displays a mild underabundance of iron. It is around three billion years old with 1.2 times the mass of the Sun. Although considered a single star, there is reason to suspect it forms a wide physical pair with the visual magnitude 10.94 red dwarf star LP 754–50. They have a projected separation of , with LP 754–50 having an estimated 0.55 times the mass of the Sun. If they are gravitationally bound, their orbital period The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha2 Capricorni
Alpha2 Capricorni (α2 Capricorni), or Algedi , is a triple star system in the southern constellation of Capricornus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +3.57. It is separated from the fainter α¹ Capricorni by 0.11° of the sky, a gap just resolvable with the naked eye, similar to Mizar and Alcor. Based on parallax shift as refined from orbits around the sun of the Gaia spacecraft at earth's Lagrange point 2, the star is 101 to 103 light years from the solar system. Properties The primary, component A, is an evolved G-type star with a stellar classification of G8.5III-IV, indicating that the spectrum displays mixed traits of a giant and subgiant star. At the age of 1.3 billion years, is currently on the red giant branch and is generating energy through hydrogen fusion along a shell surrounding an inert helium core. The star has around double the mass of the Sun and has expanded to more than eight times the Sun's radius. The star i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asterism (astronomy)
An asterism is an observed pattern or group of stars in the sky. Asterisms can be any identified pattern or group of stars, and therefore are a more general concept than the formally defined 88 constellations. Constellations are based on asterisms, but unlike asterisms, constellations outline and today completely divide the sky and all its celestial objects into regions around their central asterisms. For example, the asterism known as the Big Dipper comprises the seven brightest stars in the constellation Ursa Major. Another is the asterism of the Southern Cross, within the constellation of Crux. Asterisms range from simple shapes of just a few stars to more complex collections of many stars covering large portions of the sky. The stars themselves may be bright naked-eye objects or fainter, even telescopic, but they are generally all of a similar brightness to each other. The larger brighter asterisms are useful for people who are familiarizing themselves with the night sky. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ox (Chinese Constellation)
The Ox mansion (牛宿, pinyin: Niú Xiù) is one of the Twenty-eight mansions of the Chinese constellations. It is one of the northern mansions of the Black Tortoise. The primary asterism of this mansion is centered on the tail of the constellation known as Capricornus Capricornus is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for "horned goat" or "goat horn" or "having horns like a goat's", and it is commonly represented in the form of a sea goat: a mythical creature that is half goat, half f ... in Western astronomy. Asterisms References {{DEFAULTSORT:Ox (Chinese Constellation) Chinese constellations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Astronomy
Astronomy in China has a long history stretching from the Shang dynasty, being refined over a period of more than 3,000 years. The ancient Chinese people have identified stars from 1300 BCE, as Chinese star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the mid-Shang dynasty. The core of the "mansion" (宿 ''xiù'') system also took shape around this period, by the time of King Wu Ding (1250–1192 BCE). Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BCE) and flourished from the Han period onward. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framework. Joseph Needham has described the ancient Chinese as the most persistent and accurate obser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Star
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars that orbit each other, bound by gravitational attraction. A large group of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a ''star cluster'' or ''galaxy'', although, broadly speaking, they are also star systems. Star systems are not to be confused with planetary systems, which include planets and similar bodies (such as comets). A star system of two stars is known as a ''binary star'', ''binary star system'' or ''physical double star''. If there are no tidal effects, no perturbation from other forces, and no transfer of mass from one star to the other, such a system is stable, and both stars will trace out an elliptical orbit around the barycenter of the system indefinitely. ''(See Two-body problem)''. Examples of binary systems are Sirius, Procyon and Cygnus X-1, the last of which probably consists of a star and a black hole. Multiple star systems A multiple star system consists of three or more stars that appear f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IAU Working Group On Star Names
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) established a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) in May 2016 to catalog and standardize proper names for stars for the international astronomical community. It operates under Division C – Education, Outreach and Heritage. The IAU states that it is keen to make a distinction between the terms ''name'' and ''designation''. To the IAU, ''name'' refers to the (usually colloquial) term used for a star in everyday conversation, while ''designation'' is solely alphanumerical, and used almost exclusively in official catalogues and for professional astronomy. (The WGSN notes that transliterated Bayer designations (e.g., Tau Ceti) are considered a special historical case and are treated as designations.) Terms of reference The terms of reference for the WGSN for the period 2016–2018 were approved by the IAU Executive Committee at its meeting on 6 May 2016. In summary, these are to: * establish IAU guidelines for the proposal and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York (state)
New York, officially the State of New York, is a state in the Northeastern United States. It is often called New York State to distinguish it from its largest city, New York City. With a total area of , New York is the 27th-largest U.S. state by area. With 20.2 million people, it is the fourth-most-populous state in the United States as of 2021, with approximately 44% living in New York City, including 25% of the state's population within Brooklyn and Queens, and another 15% on the remainder of Long Island, the most populous island in the United States. The state is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and Connecticut, Massachusetts, and Vermont to the east; it has a maritime border with Rhode Island, east of Long Island, as well as an international border with the Canadian provinces of Quebec to the north and Ontario to the northwest. New York City (NYC) is the most populous city in the United States, and around two-thirds of the state's popul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the List of United States cities by population density, most densely populated major city in the United States, and is more than twice as populous as second-place Los Angeles. New York City lies at the southern tip of New York (state), New York State, and constitutes the geographical and demographic center of both the Northeast megalopolis and the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban area, urban landmass. With over 20.1 million people in its metropolitan statistical area and 23.5 million in its combined statistical area as of 2020, New York is one of the world's most populous Megacity, megacities, and over 58 million people live within of the city. New York City is a global city, global Culture of New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dover Publications
Dover Publications, also known as Dover Books, is an American book publisher founded in 1941 by Hayward and Blanche Cirker. It primarily reissues books that are out of print from their original publishers. These are often, but not always, books in the public domain. The original published editions may be scarce or historically significant. Dover republishes these books, making them available at a significantly reduced cost. Classic reprints Dover reprints classic works of literature, classical sheet music, and public-domain images from the 18th and 19th centuries. Dover also publishes an extensive collection of mathematical, scientific, and engineering texts. It often targets its reprints at a niche market, such as woodworking. Starting in 2015, the company branched out into graphic novel reprints, overseen by Dover acquisitions editor and former comics writer and editor Drew Ford. Most Dover reprints are photo facsimiles of the originals, retaining the original pagination and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |