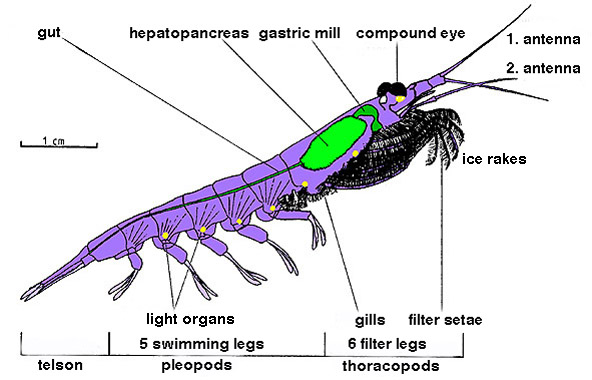
|
Berryteuthis Magister Magister
''Berryteuthis magister'', also known as the magister armhook squid, commander squid or schoolmaster gonate squid, is a medium-sized squid in the family Gonatidae. It is found in cold, high latitude waters of the North Pacific where it is among the most numerous squid species recorded. There are three recognised subspecies of ''B. magister''. The type locality of all three is Japan, although specimens have been recorded as far east as the Aleutian Islands. Description The cylindrical bodies of magister armhook squid are muscular with very soft reddish brown skin. Like all gonatids, the suckers of their arms are arranged in four rows or ''series''. But unlike other gonatids it is in females only that the suckers are modified into hooks; these hooks are on the mesial rows of the dorsal arms only. The clubs at the end of both tentacles are covered in 20 rows of suckers; these are smaller in ''B. magister nipponensis''. The wing-like fins at the rear of the body are rather large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Stillman Berry
Samuel Stillman Berry (March 16, 1887 – April 9, 1984) was an American marine zoologist specialized in cephalopods. Early life Berry was born in Unity, Maine, but the family home was the Winnecook Ranch in Montana, which had been founded by his father Ralph in 1880. In 1897, he moved with his mother to Redlands, California. Berry received a B.S. (1909) from Stanford and his M.S. (1910) from Harvard. He then returned to Stanford for his Ph.D. work on cephalopods and got his doctorate in 1913. Career From 1913 until 1915, he worked as a librarian and research assistant at the Scripps Institution for Biological Research in La Jolla, California. This was the last paid employment he ever held in academia—all his later studies and expeditions were financed by the profits from the family ranch in Montana. From November 1946 to December 1969, Berry published his own journal, ''Leaflets in Malacology'', which primary contained articles which he had written himself. Desp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelagic Zone
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean, and can be further divided into regions by depth (as illustrated on the right). The word ''pelagic'' is derived . The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or water column between the surface of the sea and the bottom. Conditions in the water column change with depth: pressure increases; temperature and light decrease; salinity, oxygen, micronutrients (such as iron, magnesium and calcium) all change. Marine life is affected by bathymetry (underwater topography) such as the seafloor, shoreline, or a submarine seamount, as well as by proximity to the boundary between the ocean and the atmosphere at the ocean surface, which brings light for photosynthesis, predation from above, and wind stirring up waves and setting currents in motion. The pelagic zone refers to the open, free waters away from the shore, where marine life can swim freely in any direction unhindered by topographical constraints. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baird's Beaked Whale
Baird's beaked whale (''Berardius bairdii''), also known as the northern giant bottlenose whale, North Pacific bottlenose whale, giant four-toothed whale, northern four-toothed whale and the North Pacific four-toothed whale, is a species of whale from the genus ''Berardius''. Baird's and Arnoux's beaked whales are so similar that researchers have debated whether or not they are simply two populations of the same species. However, genetic evidence and their wide geographical separation has led them to be classified as separate. Baird’s beaked whale is the second largest living species of toothed whale after the sperm whale. Taxonomy Baird's beaked whales were first described in 1883 by American zoologist Leonhard Stejneger based on a skull from a specimen that had been found stranded on the eastern shore of Bering Island the previous fall. The species was named after Spencer Fullerton Baird, the then Secretary of the Smithsonian. A few months after Stejneger's description was pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannibalism
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species. Human cannibalism is well documented, both in ancient and in recent times. The rate of cannibalism increases in nutritionally poor environments as individuals turn to members of their own species as an additional food source.Elgar, M.A. & Crespi, B.J. (1992) ''Cannibalism: ecology and evolution among diverse taxa'', Oxford University Press, Oxford ngland New York. Cannibalism regulates population numbers, whereby resources such as food, shelter and territory become more readily available with the decrease of potential competition. Although it may benefit the individual, it has been shown that the presence of cannibalism decreases the expected survival rate of the whole population and increases the risk of consuming a relative. Other negative effects may include the increased r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphipod
Amphipoda is an order of malacostracan crustaceans with no carapace and generally with laterally compressed bodies. Amphipods range in size from and are mostly detritivores or scavengers. There are more than 9,900 amphipod species so far described. They are mostly marine animals, but are found in almost all aquatic environments. Some 1,900 species live in fresh water, and the order also includes the terrestrial sandhoppers such as ''Talitrus saltator''. Etymology and names The name ''Amphipoda'' comes, via New Latin ', from the Greek roots 'on both/all sides' and 'foot'. This contrasts with the related Isopoda, which have a single kind of thoracic leg. Particularly among anglers, amphipods are known as ''freshwater shrimp'', ''scuds'', or ''sideswimmers''. Description Anatomy The body of an amphipod is divided into 13 segments, which can be grouped into a head, a thorax and an abdomen. The head is fused to the thorax, and bears two pairs of antennae and one pair of se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphausiid
Krill are small crustaceans of the order Euphausiacea, and are found in all the world's oceans. The name "krill" comes from the Norwegian word ', meaning "small fry of fish", which is also often attributed to species of fish. Krill are considered an important trophic level connection – near the bottom of the food chain. They feed on phytoplankton and (to a lesser extent) zooplankton, yet also are the main source of food for many larger animals. In the Southern Ocean, one species, the Antarctic krill, ''Euphausia superba'', makes up an estimated biomass of around 379,000,000 tonnes, making it among the species with the largest total biomass. Over half of this biomass is eaten by whales, seals, penguins, seabirds, squid, and fish each year. Most krill species display large daily vertical migrations, thus providing food for predators near the surface at night and in deeper waters during the day. Krill are fished commercially in the Southern Ocean and in the waters around Jap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans (Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
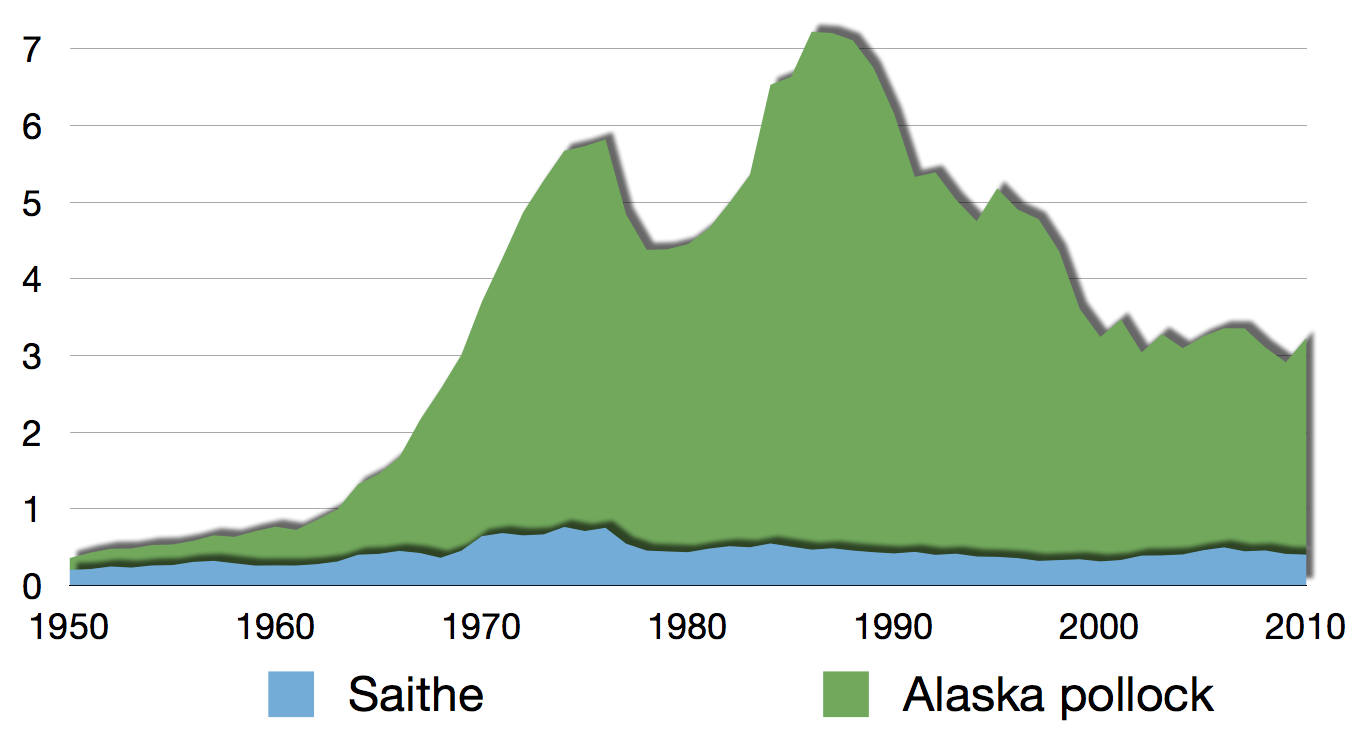
Pollock
Pollock or pollack (pronounced ) is the common name used for either of the two species of North Atlantic marine fish in the genus ''Pollachius''. ''Pollachius pollachius'' is referred to as pollock in North America, Ireland and the United Kingdom, while ''Pollachius virens'' is usually known as saithe or coley in Great Britain and Ireland (derived from the older name coalfish). Other names for ''P. pollachius'' include the Atlantic pollock, European pollock, ''lieu jaune'', and lythe; while ''P. virens'' is also known as Boston blue (distinct from bluefish), silver bill, or saithe. Species The recognized species in this genus are: * ''Pollachius pollachius'' (Linnaeus, 1758) (pollack) * ''Pollachius virens'' (Linnaeus, 1758) (coalfish) Description Both species can grow to and can weigh up to . ''P. virens'' has a strongly defined, silvery lateral line running down the sides. Above the lateral line, the colour is a greenish black. The belly is white, while '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sablefish
The sablefish (''Anoplopoma fimbria'') is one of two members of the fish family Anoplopomatidae and the only species in the genus ''Anoplopoma''. In English, common names for it include sable (US), butterfish (US), black cod (US, UK, Canada), blue cod (UK), bluefish (UK), candlefish (UK), coal cod (UK), snowfish (; Thailand), coalfish (Canada), beshow, and skil (Canada), although many of these names also refer to other, unrelated, species. The US Food and Drug Administration accepts only "sablefish" as the Acceptable Market Name in the United States; "black cod" is considered a vernacular (regional) name and should not be used as a Statement of Identity for this species. The sablefish is found in muddy sea beds in the North Pacific Ocean at depths of and is commercially important to Japan. Description The sablefish is a species of deep-sea fish common to the North Pacific Ocean. Adult sablefish are opportunistic feeders, preying on fish, including Alaskan pollock, eulachon, ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of living fish species are ray-finned fish, belonging to the class Actinopterygii, with around 99% of those being teleosts. The earliest organisms that can be classified as fish were soft-bodied chordates that first appeared during the Cambrian period. Although they lacked a true spine, they possessed notochords which allowed them to be more agile than their invertebrate counterparts. Fish would continue to evolve through the Paleozoic era, diversifying into a wide variety of forms. Many fish of the Paleozoic developed external armor that protected them from predators. The first fish with jaws appeared in the Silurian period, after which many (such as sharks) became formidable marine predators rather than just the prey of arthropods. Mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sculpin
A sculpin is a type of fish that belongs to the superfamily Cottoidea in the order Scorpaeniformes.Kane, E. A. and T. E. Higham. (2012)Life in the flow lane: differences in pectoral fin morphology suggest transitions in station-holding demand across species of marine sculpin.''Zoology'' (Jena) 115(4), 223-32. As of 2006, this superfamily contains 7 families, 94 genera, and 387 species. Sculpins occur in many types of habitat, including ocean and freshwater zones. They live in rivers, submarine canyons, kelp forests, and shallow littoral habitat types, such as tidepools. Sculpins are benthic fish, dwelling on the bottoms of water bodies. Their pectoral fins are smooth on the upper edge and webbed with sharp rays along the lower edge, a modification that makes them specialized for gripping the substrate. This adaptation helps the fish anchor in fast-flowing water. The sculpin normally grows to about four inches long. Families and subfamilies Families include: * Jordaniidae Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benthos
Benthos (), also known as benthon, is the community of organisms that live on, in, or near the bottom of a sea, river, lake, or stream, also known as the benthic zone.Benthos from the Census of Antarctic Marine Life website This community lives in or near marine or freshwater sedimentary environments, from s along the , out to the , and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |