|
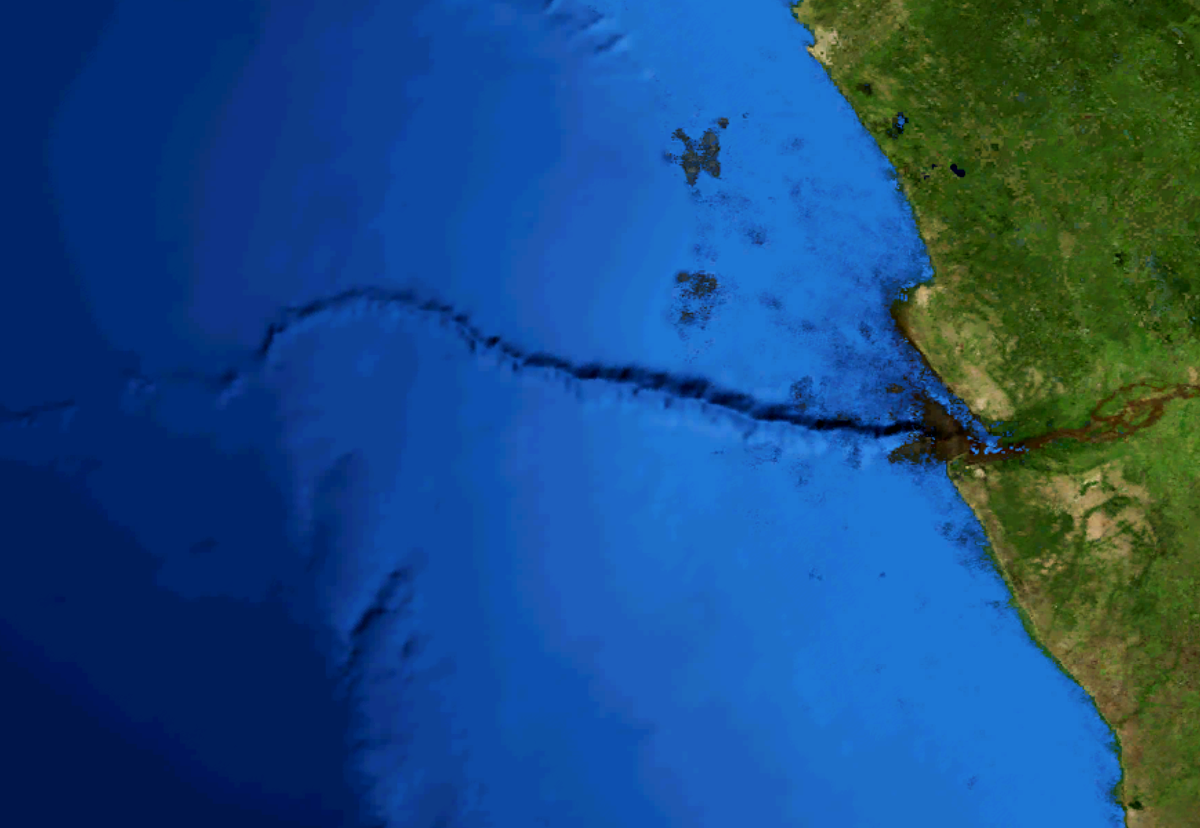
Bering Sea Canyons
The Bering Canyon is the longest of the Bering Sea submarine canyons; it extends about 400 km across the Bering shelf and slope. It is confined at its eastern edge by the Aleutian Islands. The width of the canyon at the shelf break is about 65 km, only about two-thirds that of the Zhemchug Canyon and Navarin Canyons, but because of its great length, the Bering Canyon has the largest area. At a depth of 3200 m, the Bering Canyon thalweg In geography and fluvial geomorphology, a thalweg or talweg () is the line of lowest elevation within a valley or watercourse. Under international law, a thalweg is the middle of the primary navigable channel of a waterway that defines the bounda ... reaches the Aleutian Basin, where a low-relief submarine channel-lobe system has developed. ReferencesGiant submarine canyonsat U.S. Geological Survey Submarine canyons of the Bering Sea {{marine-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarine Canyon
A submarine canyon is a steep-sided valley cut into the seabed of the continental slope, sometimes extending well onto the continental shelf, having nearly vertical walls, and occasionally having canyon wall heights of up to 5 km, from canyon floor to canyon rim, as with the Great Bahama Canyon. Just as above-sea-level canyons serve as channels for the flow of water across land, submarine canyons serve as channels for the flow of turbidity currents across the seafloor. Turbidity currents are flows of dense, sediment laden waters that are supplied by rivers, or generated on the seabed by storms, submarine landslides, earthquakes, and other soil disturbances. Turbidity currents travel down slope at great speed (as much as 70 km/h), eroding the continental slope and finally depositing sediment onto the abyssal plain, where the particles settle out.Continental Margin Sedimentation: From Sediment Transport to Sequence Stratigraphy (Special Publication 37 of the IAS) Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bering Sea
The Bering Sea (, ; rus, Бе́рингово мо́ре, r=Béringovo móre) is a marginal sea of the Northern Pacific Ocean. It forms, along with the Bering Strait, the divide between the two largest landmasses on Earth: Eurasia and The Americas. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelf, continental shelves. The Bering Sea is named for Vitus Bering, a Denmark, Danish navigator in Russian service, who, in 1728, was the first European to systematically explore it, sailing from the Pacific Ocean northward to the Arctic Ocean. The Bering Sea is separated from the Gulf of Alaska by the Alaska Peninsula. It covers over and is bordered on the east and northeast by Alaska, on the west by the Russian Far East and the Kamchatka Peninsula, on the south by the Alaska Peninsula and the Aleutian Islands and on the far north by the Bering Strait, which connects the Bering Sea to the Arctic Ocean's Chukchi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarine Canyon
A submarine canyon is a steep-sided valley cut into the seabed of the continental slope, sometimes extending well onto the continental shelf, having nearly vertical walls, and occasionally having canyon wall heights of up to 5 km, from canyon floor to canyon rim, as with the Great Bahama Canyon. Just as above-sea-level canyons serve as channels for the flow of water across land, submarine canyons serve as channels for the flow of turbidity currents across the seafloor. Turbidity currents are flows of dense, sediment laden waters that are supplied by rivers, or generated on the seabed by storms, submarine landslides, earthquakes, and other soil disturbances. Turbidity currents travel down slope at great speed (as much as 70 km/h), eroding the continental slope and finally depositing sediment onto the abyssal plain, where the particles settle out.Continental Margin Sedimentation: From Sediment Transport to Sequence Stratigraphy (Special Publication 37 of the IAS) Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands (; ; ale, Unangam Tanangin,”Land of the Aleuts", possibly from Chukchi language, Chukchi ''aliat'', "island"), also called the Aleut Islands or Aleutic Islands and known before 1867 as the Catherine Archipelago, are a chain of 14 large volcanic islands and 55 smaller islands. Most of the Aleutian Islands belong to the U.S. state of Alaska, but some belong to the Russian Federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Kamchatka Krai. They form part of the Aleutian Arc in the Northern Pacific Ocean, occupying a land area of 6,821 sq mi (17,666 km2) and extending about westward from the Alaska Peninsula toward the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia, and act as a border between the Bering Sea to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the south. Crossing 180th meridian, longitude 180°, at which point east and west longitude end, the archipelago contains both the westernmost part of the United States by longitude (Amatignak Island) and the easternmost by longitude ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhemchug Canyon
Zhemchug Canyon is an underwater canyon located in the middle of the Bering Sea. It is the deepest submarine canyon in the world, and is also tied for the widest.Normark, W.R. and Carlson, P.R., 2003Giant submarine canyons: Is size any clue to their importance in the rock record? in Chan, M.A., and Archer, A.W., eds., Extreme depositional environments: Mega end members in geologic time: Boulder, Colorado, Geological Society of America Special Paper 370, p. 1–15 Geography It has a vertical relief of dropping from the shallow shelf of the Bering Sea to the depths of the Aleutian Basin. Zhemchug Canyon is deeper than the Grand Canyon which is deep. It has two main branches, each larger than typical continental margin canyons such as the Monterey Canyon. What makes the Zhemchug Canyon the world's largest is not only its great depth, but its immense cross-sectional and drainage area, (11,350 km2) and volume (5800 km3). In 2016, Michelle Ridgeway explored the cany ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navarin Canyon
The Navarin Canyon is a submarine canyon in the Bering Sea. It is just as wide but less than half as deep as the Zhemchug Canyon, which is the largest canyon in the world. The Navarin Canyon is the third-largest to cut through the Beringian margin. It is the second-largest in area. Though these canyons were not directly formed by rivers, it is postulated that when the sea level was low during the Ice Ages, rivers such as the Yukon and the Kuskokwim The Kuskokwim River or Kusko River (Yup'ik: ''Kusquqvak''; Deg Xinag: ''Digenegh''; Upper Kuskokwim: ''Dichinanek' ''; russian: Кускоквим (''Kuskokvim'')) is a river, long, in Southwest Alaska in the United States. It is the ninth la ... may have shaped in part the heads of these canyons. At the shelf break, it is approximately wide. References Submarine canyons of the Bering Sea {{marine-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalweg
In geography and fluvial geomorphology, a thalweg or talweg () is the line of lowest elevation within a valley or watercourse. Under international law, a thalweg is the middle of the primary navigable channel of a waterway that defines the boundary line between states. Also under international law, thalwegs can acquire special significance because disputed river borders are often deemed to run along the river's thalweg. Etymology The word ''thalweg'' is of 19th-century German origin. The German word (modern spelling ) is a compound noun that is built from the German elements (since Duden's orthography reform of 1901 written ) meaning ''valley'' (cognate with ''dale'' in English), and , meaning ''way.'' It literally means "valley way" and is used, with its modern spelling , in daily German to describe a path or road that follows the bottom of a valley, or in geography with the more technical meaning also adopted by English. Hydrology In hydrological and fluvial landforms, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleutian Basin
The Aleutian Basin is an oceanic basin under the southwestern Bering Sea. While the northeastern half of the Bering Sea overlies the North American Plate in relatively shallow water, the Aleutian Basin consists of oceanic plate—the remnant of the Kula Plate that was mostly subducted under the North American Plate. Subduction of the Kula Plate ceased after the creation of the Aleutian Trench to its south. What remained of the Kula Plate attached to the North American Plate. This former subduction zone is now the Beringian Margin, which now hosts sixteen submarine canyons, including Zhemchug Canyon, the world's largest. The deep-water part of the Bering Sea is separated into the Commander Basin and Bowers basins by the submarine Shirshov Ridge and Bowers Ridge. The Commander Basin occupies the western part of the Bering Sea, with the Shirshov Ridge on its eastern border. The Shirshov Ridge extends 750 km southward from the Russian Olyutorskii Peninsula to connect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |