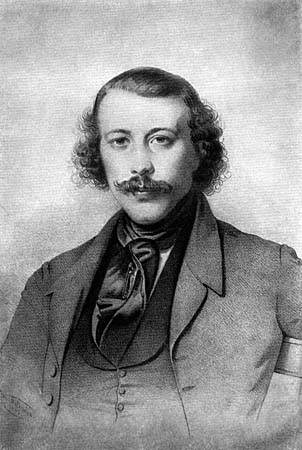|
Benalup-Casas Viejas
Casas Viejas is a city located in the province of Cádiz, Spain. According to the 2005 census, the city has a population of 6,754 inhabitants. Casas Viejas is located in the '' Ruta del Toro''. Main sights * Cueva del Tajo de las Figuras *Iglesia de Nuestra Señora del Socorro Economy *Agriculture *Rural tourism Benalup-Casas Viejas revolution The anarchist movement which spread across Spain in the late 19th and early 20th centuries was based on the ideas of Bakunin and propagated by Giuseppi Fanelli. It urged oppressed workers to unite and organize against their oppressors, namely the State, the latifundista landowners, and the Church. It quickly took a hold amongst the long-exploited agricultural workers in Andalusia, who joined the CNT union or the more radical FAI and had some limited success in improving wages and working conditions. The establishment's attempts to stamp out such revolutionary zeal came to a tragic head in 1933 at Casas Viejas, now Benalup-Casas Vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipalities Of Spain
The municipality ( es, municipio, , ca, municipi, gl, concello, eu, udalerria, ast, conceyu)In other languages of Spain: * Catalan/Valencian (), sing. ''municipi''. * Galician () or (), sing. ''municipio''/''bisbarra''. *Basque (), sing. ''udalerria''. * Asturian (), sing. ''conceyu''. is the basic local administrative division in Spain together with the province. Organisation Each municipality forms part of a province which in turn forms part or the whole of an autonomous community (17 in total plus Ceuta and Melilla): some autonomous communities also group municipalities into entities known as ''comarcas'' (districts) or ''mancomunidades'' (commonwealths). There are a total of 8,131 municipalities in Spain, including the autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla. In the Principality of Asturias, municipalities are officially named ''concejos'' (councils). The average population of a municipality is about 5,300, but this figure masks a huge range: the most populo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruta Del Toro
The Route of the Bull (in Spanish, ''Ruta del Toro'') is a tourist trail in the province of Cádiz, Spain, that traverses the areas where fighting bulls are raised. These bulls, used in bullfights (corridas) throughout Spain, are of a breed native to Spain, a breed also appreciated for its beef. The Route of the Bull is meant to direct tourists through landscapes where it is possible to observe these totemic animals in their natural habitat, but the scenic beauty of the countryside, and the myriad points of historical and cultural interest along the way, make following the route worthwhile even for the visitor who finds the very notion of the bullfight off-putting. The trail runs between Jerez de la Frontera and Tarifa, and it passes through the municipalities of San José del Valle, Paterna de Rivera, Medina Sidonia, Benalup-Casas Viejas, Alcalá de los Gazules, Jimena de la Frontera, Castellar de la Frontera, San Roque and Los Barrios. Another tourist trail of this sort is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niceto Alcalá-Zamora
Niceto Alcalá-Zamora y Torres (6 July 1877 – 18 February 1949) was a Spanish lawyer and politician who served, briefly, as the first prime minister of the Second Spanish Republic, and then—from 1931 to 1936—as its president. Early life Alcalá-Zamora was born on 6 July 1877 in Priego de Cordoba, son of Manuel Alcalá-Zamora y Caracuel and Francisca Torres y del Castillo. His mother died when Niceto was three years old. A lawyer by profession, from a very young age, he was active in the Liberal Party. Chosen as a deputy, he quickly gained fame for his eloquent interventions in the Congress of Deputies, becoming Minister of Public Works in 1917 and of War in 1922, and it comprised part of the governments of concentration presided over by García Prieto. He was also Spain's representative in the League of Nations. Second Republic Disappointed by the acceptance on the part of King Alfonso XIII of the ''coup d'état'' by General Miguel Primo de Rivera on 13 September 1923, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Spanish Republic
The Spanish Republic (), commonly known as the Second Spanish Republic (), was the form of government in Spain from 1931 to 1939. The Republic was proclaimed on 14 April 1931, after the deposition of Alfonso XIII, King Alfonso XIII, and was dissolved on 1 April 1939 after surrendering in the Spanish Civil War to the Nationalist faction (Spanish Civil War), Nationalists led by General Francisco Franco. After the proclamation of the Republic, Provisional Government of the Second Spanish Republic, a provisional government was established until December 1931, at which time the Spanish Constitution of 1931, 1931 Constitution was approved. During this time and the subsequent two years of constitutional government, known as the First Biennium, Reformist Biennium, Manuel Azaña's executive initiated numerous reforms to what in their view would modernize the country. In 1932 the Jesuits, who were in charge of the best schools throughout the country, were banned and had all their propert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federación Anarquista Ibérica
The Iberian Anarchist Federation ( es, Federación Anarquista Ibérica, FAI) is a Spanish organization of anarchist militants active within affinity groups in the Confederación Nacional del Trabajo (CNT) anarcho-syndicalist union. It is often abbreviated as CNT-FAI because of the close relationship between the two organizations. The FAI publishes the periodical '' Tierra y Libertad''. The '' Iberian'' part of its name alludes to the purpose of unifying Spanish and Portuguese anarchists in a Pan-Iberian organization. The FAI meetings were initially attended by members of the Portuguese anarchist organizations União Anarquista Portuguesa and Confederação Geral do Trabalho , including the Zaragoza Congress of the CNT in 1936. However, it later ceased to have Portuguese participation and become an entirely Spanish organization. It is still in operation today and aligns itself with the International of Anarchist Federations (IAF-IFA). History It was founded in Valencia i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confederación Nacional Del Trabajo
The Confederación Nacional del Trabajo ( en, National Confederation of Labor; CNT) is a Spanish confederation of anarcho-syndicalist labor unions, which was long affiliated with the International Workers' Association (AIT). When working with the latter group it was also known as CNT-AIT. Historically, the CNT has also been affiliated with the Federación Anarquista Ibérica ( en, Iberian Anarchist Federation); thus, it has also been referred to as the CNT-FAI. Throughout its history, it has played a major role in the Spanish labor movement. Founded in 1910 in Barcelona from groups brought together by the trade union ''Solidaridad Obrera'', it significantly expanded the role of anarchism in Spain, which can be traced to the creation of the Spanish chapter of the IWA in 1870 and its successor organization, the Federation of Workers of the Spanish Region. Despite several decades when the organization was illegal in Spain, today the CNT continues to participate in the Spanis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latifundista
A ''latifundium'' (Latin: ''latus'', "spacious" and ''fundus'', "farm, estate") is a very extensive parcel of privately owned land. The latifundia of Roman history were great landed estates specializing in agriculture destined for export: grain, olive oil, or wine. They were characteristic of Magna Graecia and Sicily, Egypt, Northwest Africa and Hispania Baetica. The ''latifundia'' were the closest approximation to industrialized agriculture in Antiquity, and their economics depended upon slavery. During the modern colonial period, the European monarchies often rewarded services with extensive land grants in their empires. The forced recruitment of local labourers allowed by colonial law made these land grants particularly lucrative for their owners. These grants, ''fazendas'' (in Portuguese) or ''haciendas'' (in Spanish), were also borrowed as loanwords, Portuguese ''latifúndios'' and Spanish ''latifundios'' or simply ''fundos''. Agrarian reforms aimed at ending the dominan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giuseppi Fanelli
Giuseppe Fanelli (13 October 1827 – 5 January 1877) was an Italian revolutionary anarchist, best known for his tour of Spain 1868, introducing the anarchist ideas of Mikhail Bakunin. Life and revolutionary path Fanelli was born in Naples, Italy on 13 October 1827. At the age of 18, he enrolled in Giovine Italia, a political movement with the goal to create a united Italian republic. He was active in the insurrectionary, united Italian republic Young Italy movement and fought in the Milan insurrection of the 1848 revolution. He went on to fight alongside Garibaldi's Redshirts in the ''Expedition of the Thousand'' in Sicily in 1860; he also fought in the Polish uprising in 1863. He was elected to Italian Parliament in November 1865 and fought against the Austrians in 1866. Fanelli met Bakunin at Ischia in 1866. In October 1868 Bakunin sponsored Fanelli to travel to Barcelona to share his libertarian visions and recruit revolutionists to the International Workingmen's Associ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Bakunin
Mikhail Alexandrovich Bakunin (; 1814–1876) was a Russian revolutionary anarchist, socialist and founder of collectivist anarchism. He is considered among the most influential figures of anarchism and a major founder of the revolutionary socialist and social anarchist tradition. Bakunin's prestige as a revolutionary also made him one of the most famous ideologues in Europe, gaining substantial influence among radicals throughout Russia and Europe. Bakunin grew up in Pryamukhino, a family estate in Tver Governorate. From 1840, he studied in Moscow, then in Berlin hoping to enter academia. Later in Paris, he met Karl Marx and Pierre-Joseph Proudhon, who deeply influenced him. Bakunin's increasing radicalism ended hopes of a professorial career. He was expelled from France for opposing The Russian Empire's occupation of Poland. In 1849, he was arrested in Dresden for his participation in the Czech rebellion of 1848 and deported to Russian Empire, where he was imprisoned fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anarchism In Spain
Anarchism in Spain has historically gained some support and influence, especially before Francisco Franco's victory in the Spanish Civil War of 1936–1939, when it played an active political role and is considered the end of the golden age of classical anarchism. There were several variants of anarchism in Spain, namely expropriative anarchism in the period leading up to the conflict, the peasant anarchism in the countryside of Andalusia; urban anarcho-syndicalism in Catalonia, particularly its capital Barcelona; and what is sometimes called "pure" anarchism in other cities such as Zaragoza. However, these were complementary trajectories and had many ideological similarities. Early on, the success of the anarchist movement was sporadic. Anarchists would organize a strike and ranks would swell. Usually, repression by police reduced the numbers again, but at the same time further radicalized many strikers. This cycle helped lead to an era of mutual violence at the beginning of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rural Tourism
Rural tourism is a tourism that focuses on actively participating in a rural lifestyle. It can be a variant of ecotourism. Many villages can facilitate tourism because many villagers are hospitable and eager to welcome or host visitors. Agriculture has become more mechanized and requires less manual labor. This trend is causing economic pressure on some villages, which in turn causes young people to move to urban areas. There is however, a segment of the urban population that is interested in visiting the rural areas and understanding the lifestyle. Principles * Minimize impact of rapid urban development. * Build environmental and cultural awareness and respect * Provide positive experiences for both visitors and hosts * Provide direct financial benefit for conservation * Provide financial benefits and empowerment for local people * Raise sensitivity to host countries' political, environmental, and social climate. Benefits Rural tourism allows the creation of a replacement source ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |