|
Belmeken (peak)
Belmeken ( bg, Белмекен) is a summit in the northeastern part of the Rila Mountain in southwestern Bulgaria with a height of 2,626 m. It is built up of granite. Its northern slopes are steep and rise over the Kutlinite cirque. The southern and southeastern slopes are oblique. To the southeast at an altitude of 1,923 m is situated the Belmeken Dam which fuels some of Bulgaria's largest hydro power plants — Chaira Pumped Storage Hydro Power Plant (864 MW), Belmeken Pumped Storage Hydro Power Plant (375 MW), Sestrimo Hydro Power Plant (240 MW) and Momina Klisura Hydroelectric Power Station (120 MW). Close to the summit is the Belmeken High Mountain Sports Complex at an altitude of 2,050 m, used for training, medical and biological research by athletes. The main starting points for climbing are the villages of Yundola and Sestrimo. In clear days, there is visibility to many of Bulgaria's major mountain ranges, including Pirin, Slavyanka, Vitosha, Bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. Bulgaria covers a territory of , and is the sixteenth-largest country in Europe. Sofia is the nation's capital and largest city; other major cities are Plovdiv, Varna and Burgas. One of the earliest societies in the lands of modern-day Bulgaria was the Neolithic Karanovo culture, which dates back to 6,500 BC. In the 6th to 3rd century BC the region was a battleground for ancient Thracians, Persians, Celts and Macedonians; stability came when the Roman Empire conquered the region in AD 45. After the Roman state splintered, tribal invasions in the region resumed. Around the 6th century, these territories were settled by the early Slavs. The Bulgars, led by Asp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
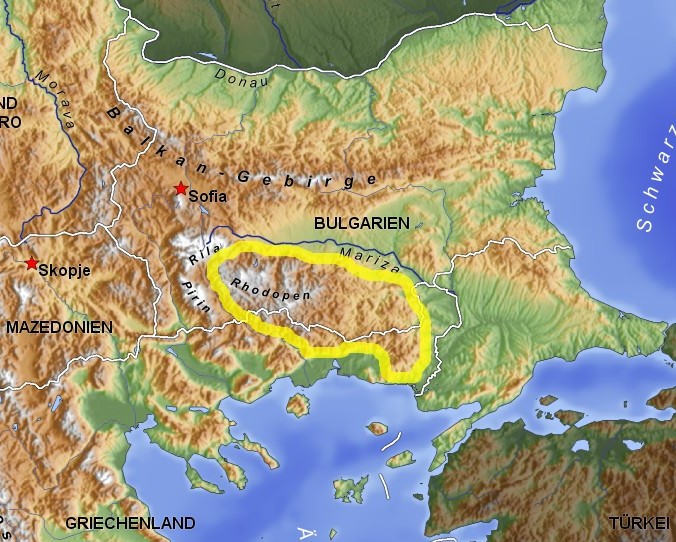
Rhodope Mountains
The Rhodopes (; bg, Родопи, ; el, Ροδόπη, ''Rodopi''; tr, Rodoplar) are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, and the largest by area in Bulgaria, with over 83% of its area in the southern part of the country and the remainder in Greece. Golyam Perelik is its highest peak at . The mountain range gives its name to the terrestrial ecoregion Rodope montane mixed forests that belongs in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome and the Palearctic realm. The region is particularly notable for its karst areas with their deep river gorges, large caves and specific sculptured forms, such as the Trigrad Gorge. A significant part of Bulgaria's hydropower resources are located in the western areas of the range. There are a number of hydro-cascades and dams used for electricity production, irrigation, and as tourist destinations. In Greece, there are also the hydroelectric power plants of Thisavros and Platanovrysi. The Rhodopes have a rich cultural heritage including a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Pazardzhik Province
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, stratification, rock exposure and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, mounds, hills, ridges, cliffs, valleys, rivers, peninsulas, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodies and sub-surface features. Mountains, hills, plateaux, and plains are the fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Blagoevgrad Province
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, stratification, rock exposure and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, mounds, hills, ridges, cliffs, valleys, rivers, peninsulas, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodies and sub-surface features. Mountains, hills, plateaux, and plains are the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Rila
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and has many mineral springs, such as the Sofia Central Mineral Baths. It has a humid continental climate. Being in the centre of the Balkans, it is midway between the Black Sea and the Adriatic Sea, and closest to the Aegean Sea. Known as Serdica in Antiquity and Sredets in the Middle Ages, Sofia has been an area of human habitation since at least 7000 BC. The recorded history of the city begins with the attestation of the conquest of Serdica by the Roman Republic in 29 BC from the Celtic tribe Serdi. During the decline of the Roman Empire, the city was raided by Huns, Visigoths, Avars and Slavs. In 809, Serdica was incorporated into the Bulgarian Empire by Khan Krum and became known as Sredets. In 1018, the Byzantines ended Bulgarian rule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasian Crag Martin
The Eurasian crag martin or just crag martin (''Ptyonoprogne rupestris'') is a small passerine bird in the swallow family. It is about long with ash-brown upperparts and paler underparts, and a short, square tail that has distinctive white patches on most of its feathers. It breeds in the mountains of southern Europe, northwestern Africa and across the Palearctic. It can be confused with the three other species in its genus, but is larger with brighter tail spots and different plumage tone. Many European birds are resident, but some northern populations and most Asian breeders are bird migration, migratory, wintering in northern Africa, the Middle East or India. The Eurasian crag martin builds a nest adherent to the rock under a cliff overhang or increasingly onto a man-made structure. It makes a neat half-cup mud nest with an inner soft lining of feathers and dry grass. Nests are often solitary, although a few pairs may breed relatively close together at good locations. Two to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Raven
The common raven (''Corvus corax'') is a large all-black passerine bird. It is the most widely distributed of all corvids, found across the Northern Hemisphere. It is a raven known by many names at the subspecies level; there are at least eight subspecies with little variation in appearance, although recent research has demonstrated significant genetic differences among populations from various regions. It is one of the two largest corvids, alongside the thick-billed raven, and is possibly the heaviest passerine bird; at maturity, the common raven averages in length and in mass. Although their typical lifespan is considerably shorter, common ravens can live more than 23 years in the wild. Young birds may travel in flocks but later mate for life, with each mated pair defending a territory. Common ravens have coexisted with humans for thousands of years and in some areas have been so numerous that people have regarded them as pests. Part of their success as a species is due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peregrine Falcon
The peregrine falcon (''Falco peregrinus''), also known as the peregrine, and historically as the duck hawk in North America, is a Cosmopolitan distribution, cosmopolitan bird of prey (Bird of prey, raptor) in the family (biology), family Falconidae. A large, Corvus (genus), crow-sized falcon, it has a blue-grey back, barred white underparts, and a black head. The peregrine is renowned for its speed, reaching over during its characteristic hunting stoop (high-speed dive), making it the fastest bird in the world, as well as the Fastest animals, fastest member of the animal kingdom. According to a ''National Geographic (U.S. TV channel), National Geographic'' TV program, the highest measured speed of a peregrine falcon is . As is typical for avivore, bird-eating raptors, peregrine falcons are Sexual dimorphism, sexually dimorphic, with females being considerably larger than males. The peregrine's breeding range includes land regions from the Arctic tundra to the tropics. It can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Ground Squirrel
The European ground squirrel (''Spermophilus citellus''), also known as the European souslik, is a species from the squirrel family, Sciuridae. It is among the few European species in the genus ''Spermophilus''. Like all squirrels, it is a member of the rodent order. It is to be found in eastern Europe from southern Ukraine, to Asia Minor, Austria, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Serbia, Greece, Romania, Bulgaria, North Macedonia and north as far as Poland but the range is divided in two parts by the Carpathian Mountains. The European ground squirrel grows to a length of approximately and a weight of approximately . It is a diurnal animal, living in colonies of individual burrows in pastures or grassy embankments. The squirrels emerge during the day to feed upon seeds, plant shoots and roots or flightless invertebrates. The colonies maintain sentinels who whistle at the sight of a predator, bringing the pack scurrying back to safety. Breeding takes place in early summer when a sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batak Reservoir
The Batak Reservoir ( bg, езеро Батак) is located in the Rhodope Mountains and is the third largest in Bulgaria. It attracts many tourists and fishermen, and the resort Tsigov Chark was built on its shore. The lake is situated around 8 km away from the historic town of Batak from which it took its name. Additionally, in close proximity are the cities of Rakitivo (14 km) and Velingrad (24 km). ( bg, Официален туристически портал на България) The Batak reservoir is located in the Batak municipality and within the . The dam is positioned at around 1,100 m above the sea level. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iskar Reservoir
The Iskar Reservoir (язовир „Искър“) is the largest reservoir in Bulgaria. It is situated on the Iskar River and provides 2/3 of the water for the capital Sofia, also being used for producing hydroelectricity. The reservoir has a total volume of 673 million m3, of which 580 million are in use and the rest is reserve. The reservoir has a drainage basin of 1,046 km² and is 25 km long. It is situated at 820 m above sea level, its dam being 204 m long and 76 m high. History The initial plans for the construction of a dam on the Iskar date to as early as 1900-1901, immediately after the building of the Pancharevo Hydroelectric Power Plant. In 1921, the idea was once again brought up, but its accomplishment failed due to the municipality's inability to indemnify the residents of the neighbouring villages of Gorni Pasarel, Shishmanovo and Kalkovo. Topographic photographs and a geological assessment regarding the dam were made and observations of the Iskar's w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



