|
Belarusian History In The Russian Empire
The Belarusian history within the Russian Empire is associated with the history of Belarus from the Partitions of Poland, Partitions of the PolishŌĆōLithuanian Commonwealth to the October Revolution when the present-day Belarus' lands were made part of the Russian Empire. Territorial growth The First Partition of Poland (1772) awarded only some parts of the Belarusian lands, northern part of the Polotsk Voivodeship, entire Mstsislaw Voivodeship and Vitebsk Voivodeship, and southeastern part of the Minsk Voivodeship, which became parts of the Pskov Governorate, Pskov and the Mogilev Governorate, Mogilev ''guberniyas'' (governorates). In 1776, the Polotsk Governorate was created after separating from the original Russian lands of the Pskov Governorate. The Second Partition of Poland, second partition (1793) added more (the remaining part of Minsk Voivodeship, Brac┼éaw Voivodeship and Vilnius Voivodeship and Brest Litovsk Voivodeship). After the Third Partition of Poland, thir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Belarus
This article describes the history of Belarus. The Belarusians, Belarusian ethnos is traced at least as far in time as other East Slavs. Belarus is a successor of some Rus' people, Ruthenian principalities (Principality of Polotsk, Polotsk, Principality of Turov, Turov, Principality of Novogrudok, Novogrudok, etc.), the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, the PolishŌĆōLithuanian Commonwealth, Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth (with Lithuania, Republic of Lithuania and Poland), the Belarusian People's Republic, BPR, the Lithuanian-Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, LBSR, and the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, BSSR. After an initial period of independent feudal consolidation, Belarusian lands were incorporated into the Kingdom of Lithuania, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, the PolishŌĆōLithuanian Commonwealth, the Russian Empire and eventually the Soviet Union. Apart from a brief attempt at independence, known as the Belarusian People's Republic, following the political vacuum create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
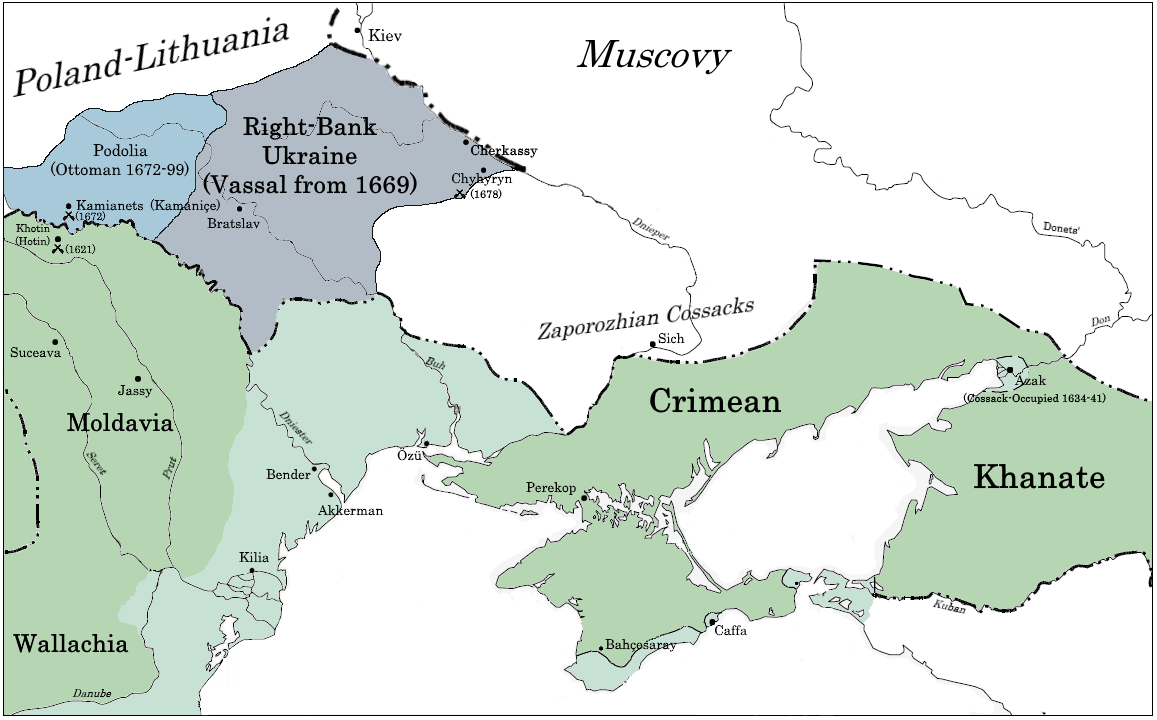
Bracław Voivodeship
The Brac┼éaw Voivodeship ( la, Palatinatus Braclaviensis; ; uk, ąæčĆą░čåą╗ą░ą▓čüčīą║ąĄ ą▓ąŠčöą▓ąŠą┤čüčéą▓ąŠ, ''Braclav┼øke vojevodstvo'') was a unit of administrative division of the PolishŌĆōLithuanian Commonwealth. Created in 1566 as part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, it was passed to the Crown of Poland in 1569 following the Union of Lublin. After partitions of Poland in 1793 the voivodeship was taken by the Russian Empire and replaced with the Bratslav Viceroyalty. In 1648-57 the territory of voivodeship was a part of Cossack Hetmanate following the Khmelnytsky Uprising and Truce of Andrusovo, while in 1672-99 it became part of Ottoman Ukraine which was a vassal Ottoman Empire (see: Treaty of Buchach and Treaty of Karlowitz). Overview Together with the Podole Voivodeship it formed the historical province of Podolia and part of a bigger Lesser Poland Province of the Polish Crown. Officially, the capital of the voivodeship was in Braclaw (today Bratslav), but local voi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Semashko
Joseph Semashko ( uk, ąÖąŠčüąĖčä ąĪąĄą╝ą░čłą║ąŠ; pl, J├│zef Siemaszko; russian: ąśąŠčüąĖčä ąĪąĄą╝ą░čłą║ąŠ; 25 December 1798 – 23 November 1868) was an Eastern Catholic priest and bishop who played a central role in the highly controversial conversion of the Ruthenian Uniate Church of the western provinces of the Russian Empire to Russian Orthodoxy in 1837ŌĆō1839. Subsequently, he became an archbishop in the Russian Orthodox hierarchy, elevated to the Metropolitan bishop of Vilnius and Lithuania in 1852. Early life and education Semashko was born and raised in right-bank Ukraine, in Pavlivka near Illintsi in the Kiev Governorate (now in Vinnytsia Oblast of Ukraine). His father Yosyf (1776ŌĆō1856) was originally a farmer and trader, then became a Uniate clergyman in 1811. As there were almost no Catholic churches in the region, Semashko attended Orthodox services more often than Catholic in his childhood. His mother tongue was Ruthenian and he acquired Polish at school. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Orthodoxy
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism. Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "canonical") Eastern Orthodox Church is organised into autocephalous churches independent from each other. In the 21st century, the number of mainstream autocephalous churches is seventeen; there also exist autocephalous churches unrecognized by those mainstream ones. Autocephalous churches choose their own primate. Autocephalous churches can have jurisdiction (authority) over other churches, some of which have the status of "autonomous" which means they have more autonomy than simple eparchies. Many of these jurisdictions correspond to the territories of one or more modern states; the Patriarchate of Moscow, for example, corresponds to Russia and some of the other post-Soviet states. They can also include metropolises, bishoprics, parishes, monas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synod Of Polotsk
The Synod of Polotsk was a local synod held on February 12, 1839 by the clergy of the Ruthenian Greek Catholic Church in the city of Polotsk for reunification with the Russian Orthodox Church. Polotsk was the center of the Greek Catholic Archeparchy of Polotsk-Vitebsk, the metropolitan seat of all Greek Catholics after the partition of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. The Synod of Polotsk was the culmination of the plans for reunification with the Russian Orthodox Church starting from to-be Metropolitan Joseph (Semashko), a Russophile Greek Catholic protopresbyter, who presented a document to Emperor Nicholas I of Russia with a draft ("About the situation of the Uniate Church in Russia and the means to return it to the bosom of the Orthodox Church") outlining the gradual rejoining of the Greek Catholic Church within the Russian Empire to the Russian Orthodox Church on January 17, 1828. The resolution of the Synod of Polotsk led to the Russian Orthodox Church immedia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belarusian Greek Catholic Church
The Belarusian Greek Catholic Church ( be, ąæąĄą╗ą░čĆčāčüą║ą░čÅ ą│čĆ菹║ą░-ą║ą░čéą░ą╗č¢čåą║ą░čÅ čåą░čĆą║ą▓ą░, ''Bielaruskaja hreka-katalickaja carkva'' BHKC; la, Ecclesiae Graecae Catholico Belarusica) sometimes called in reference to its Byzantine Rite liturgy the Belarusian Byzantine Catholic Church, is one of the 23 Eastern Catholic ''sui iuris'' particular churches in full communion with the Catholic Church and the Pope of Rome. It is the heir within Belarus to the Union of Brest and Ruthenian Uniate Church. History The Christians who, through the Union of Brest (1595ŌĆō96), entered full communion with the See of Rome while keeping their Byzantine liturgy in the Church Slavonic language, were at first mainly Belarusian. Even after further Ukrainians joined the Union around 1700, Belarusians still formed about half of the group. According to the historian Anatol Taras, by 1795, around 80% of Christians in Belarus were Greek Catholics, with 14% being Latin Catholics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas I Of Russia
, house = Romanov-Holstein-Gottorp , father = Paul I of Russia , mother = Maria Feodorovna (Sophie Dorothea of W├╝rttemberg) , birth_date = , birth_place = Gatchina Palace, Gatchina, Russian Empire , death_date = , death_place = Winter Palace, Saint Petersburg, Russian Empire , burial_place = Peter and Paul Cathedral, St. Petersburg, Russian Empire , religion = Russian Orthodox , signature = Signatur Nikolaus I. (Russland).PNG Nicholas I , group=pron ( ŌĆō ) was Emperor of Russia, King of Congress Poland and Grand Duke of Finland. He was the third son of Paul I and younger brother of his predecessor, Alexander I. Nicholas inherited his brother's throne despite the failed Decembrist revolt against him. He is mainly remembered in history as a reactionary whose controversial reign was marked by geographical expansion, economic growth, and massive industrialisation on the one hand, and centralisation of administrative policies an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
November Uprising
The November Uprising (1830ŌĆō31), also known as the PolishŌĆōRussian War 1830ŌĆō31 or the Cadet Revolution, was an armed rebellion in the heartland of partitioned Poland against the Russian Empire. The uprising began on 29 November 1830 in Warsaw when young Polish officers from the military academy of the Army of Congress Poland revolted, led by Lieutenant Piotr Wysocki. Large segments of the peoples of Lithuania, Belarus, and the Right-bank Ukraine soon joined the uprising. Although the insurgents achieved local successes, a numerically superior Imperial Russian Army under Ivan Paskevich eventually crushed the uprising. "Polish Uprising of 1830ŌĆō31." ''The Great Soviet Encyclopedia'', 3rd Edition (1970ŌĆō1979) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right-bank Ukraine
Right-bank Ukraine ( uk , ą¤čĆą░ą▓ąŠą▒ąĄčĆąĄąČąĮą░ ąŻą║čĆą░茹Įą░, ''Pravoberezhna Ukrayina''; russian: ą¤čĆą░ą▓ąŠą▒ąĄčĆąĄąČąĮą░čÅ ąŻą║čĆą░ąĖąĮą░, ''Pravoberezhnaya Ukraina''; pl, Prawobrze┼╝na Ukraina, sk, Pravobre┼Šn├Ī Ukrajina, hu, Jobb parti Ukrajna) is a historical and territorial name for a part of modern Ukraine on the right (west) bank of the Dnieper River, corresponding to the modern-day oblasts of Vinnytsia, Zhytomyr, Kirovohrad, as well as the western parts of Kyiv and Cherkasy. It was separated from the left bank during the Ruin. Right-bank Ukraine is bordered by the historical regions of Volhynia and Podolia to the west, Moldavia to the southwest, Yedisan and Zaporizhzhia to the south, left-bank Ukraine to the east, and Polesia to the north. Main cities of the region include Cherkasy, Kropyvnytskyi, Bila Tserkva, Zhytomyr and Oleksandriia. History The history of right- and left-bank Ukraine is closely associated with the Khmelnytsky Uprising of 1648ŌĆō57. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Szlachta
The ''szlachta'' (Polish: endonym, Lithuanian: ┼Īl─Śkta) were the noble estate of the realm in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the PolishŌĆōLithuanian Commonwealth who, as a class, had the dominating position in the state, exercising extensive political rights and power. Szlachta as a class differed significantly from the feudal nobility of Western Europe. The estate was officially abolished in 1921 by the March Constitution."Szlachta. Szlachta w Polsce" ''Encyklopedia PWN'' The origins of the ''szlachta'' are obscure and the subject of several theories. Traditionally, its members owned land (allods), [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Litvin
Litvin ( be, ą╗č¢čåčīą▓č¢ąĮ, ą╗č¢čéą▓č¢ąĮ, li─ćvin, litvin; lt, litvinas; pl, Litwin; russian: ą╗ąĖčéą▓ąĖąĮ, litvin; uk, ą╗ąĖčéą▓ąĖąĮ, lytvyn) is a Slavic word for residents of Lithuania, which was used no earlier than the 16th century mostly by the East Slavs. Currently, Litvin or its cognates are used internationally for Lithuanians (; ; ; ). Meanings Grand Duchy of Lithuania In the 16ŌĆō18th centuries, the term "Litvin" was mostly used by East Slavs to refer to all inhabitants of Lithuania, i.e. Grand Duchy of Lithuania. ąÆčÅčćą░čüą╗ą░č× ąØą░čüąĄą▓č¢čćąøč¢čéą▓č¢ąĮčŗ // ąÆčÅą╗č¢ą║ą░ąĄ ą║ąĮčÅčüčéą▓ą░ ąøč¢č鹊č×čüą║ą░ąĄ: ąŁąĮčåčŗą║ą╗ą░ą┐ąĄą┤čŗčÅ. ąŻ 2 čé. / čĆ菹┤. ąō. ą¤. ą¤ą░čłą║ąŠč× č¢ č¢ąĮčł.ąó. 2: ąÜą░ą┤čŹčåą║č¢ ą║ąŠčĆą┐čāčü ŌĆö ą»čåą║ąĄą▓č¢čć. ŌĆö ą£č¢ąĮčüą║: ąæąĄą╗ą░čĆčāčüą║ą░čÅ ąŁąĮčåčŗą║ą╗ą░ą┐ąĄą┤čŗčÅ, 2005. ąĪ. 206ŌĆö208. Several authentic sources, surviving from the Middle Ages, with expressed opinion of the Grand Dukes of Lithuania themselves proves that the Lit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwestern Krai
Northwestern Krai (russian: links=no, ąĪąĄą▓ąĄčĆąŠ-ąŚą░ą┐ą░ą┤ąĮčŗą╣ ą║čĆą░ą╣) was a ''krai'' of the Russian Empire (unofficial subdivision) in the territories of the former Grand Duchy of Lithuania (present-day Belarus and Lithuania). The administrative center was in Vilna (Vilnius). Northwestern Krai together with the Southwestern Krai, which was composed of the territories formerly belonging to the Polish Crown (in present-day Ukraine), formed the Western Krai. It included six : *Governorate-General of Vilna: ** Vilna Governorate **Kovno Governorate **Grodno Governorate *Minsk Governorate *Mogilev Governorate *Vitebsk Governorate See also * Southwestern Krai *Western Krai Western Krai (russian: ąŚą░ą┐ą░ą┤ąĮčŗą╣ ą║čĆą░ą╣, literally ''Western Land'') was an unofficial name for the westernmost parts of the Russian Empire, excluding the territory of Congress Poland (which was sometimes referred to as Vistula Krai). T ... References * ą©ą░čäą░čĆąĖą║, ą¤.ąś.br>ąĪą╗ą░ą▓čÅą ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)