|
Beiting Protectorate
The Beiting Protectorate-General, initially the Beiting Protectorate, was a Chinese protectorate established by the Tang dynasty in 702 to control the Beiting region north of Gaochang in contemporary Xinjiang. Wu Zetian set up the Beiting Protectorate in Ting Prefecture (Jimsar County) and granted it governorship over Yi Prefecture (Hami) and Xi Prefecture (Gaochang). The Beiting Protectorate ended in 790 when Tingzhou was conquered by the Tibetan Empire. The ruins, along with other sites along the Silk Road, were inscribed in 2014 on the UNESCO World Heritage List as the Silk Roads: the Routes Network of Chang'an-Tianshan Corridor World Heritage Site. History In 702 Wu Zetian set up the Beiting Protectorate in Ting Prefecture (Jimsar County) and granted it governorship over Yi Prefecture (Hami) and Xi Prefecture (Gaochang). In 715 the Tibetan Empire attacked the Beiting Protectorate. In 735 the Türgesh attacked Ting Prefecture. In 755 the An Lushan Rebellion occurred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunhuang Zhang Yichao Army
Dunhuang () is a county-level city in Northwestern Gansu Province, Western China. According to the 2010 Chinese census, the city has a population of 186,027, though 2019 estimates put the city's population at about 191,800. Dunhuang was a major stop on the ancient Silk Road and is best known for the nearby Mogao Caves. Dunhuang is situated in an oasis containing Crescent Lake and Mingsha Shan (, meaning "Singing-Sand Mountain"), named after the sound of the wind whipping off the dunes, the singing sand phenomenon. Dunhuang commands a strategic position at the crossroads of the ancient Southern Silk Route and the main road leading from India via Lhasa to Mongolia and Southern Siberia, and also controls the entrance to the narrow Hexi Corridor, which leads straight to the heart of the north Chinese plains and the ancient capitals of Chang'an (today known as Xi'an) and Luoyang. Administratively, the county-level city of Dunhuang is part of the prefecture-level city of Jiuquan. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Dezong Of Tang
Emperor Dezong of Tang (27 May 742According to Li Kuo's biography in the ''Old Book of Tang'', he was born on the ''guisi'' day in the 4th month of the 1st year of the Tianbao era of Tang Xuanzong's reign. This date corresponds to 27 May 742 in the Gregorian calendar.(「天宝元年四月癸巳,生于长安大内之东宫。」) ''Old Book of Tang'', vol. 12. – 25 February 805),According to Li Kuo's biography in the ''Old Book of Tang'', he died on the ''guisi'' day in the 1st month of the 21st year of the Zhenyuan era of his reign, at the age of 64 (by East Asian reckoning). This date corresponds to 25 Feb 805 in the Gregorian calendar.「(贞元)二十一年春正月...癸巳,....。是日,上崩于会宁殿,享寿六十四。」) ''Old Book of Tang'', vol. 13. personal name Li Kuo, was an emperor of the Chinese Tang Dynasty and the oldest son of Emperor Daizong. His reign of 26 years was the third longest in the Tang dynasty (surpassed only by Emperor Xuanzong an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horses In East Asian Warfare
Horses in East Asian warfare are inextricably linked with the strategic and tactical evolution of armed conflict. A warrior on horseback or horse-drawn chariot changed the balance of power between civilizations. When people with horses clashed with those without, horses provided a huge advantage. When both sides had horses, battles turned on the strength and strategy of their mounted horsemen, or cavalry. Military tactics were refined in terms of the use of horses (cavalry tactics). As in most cultures, a war horse in East Asia was trained to be controlled with limited use of reins, responding primarily to the rider's legs and weight. Horses were significant factors in the Han–Xiongnu War and Five Barbarians incursions into the Central Plain, and the Mongol conquest of much of Eurasia and into Europe; and they played a part in military conflicts on a smaller, more localized scale. Horse warfare in national contexts China Japan Most Japanese horses are descended from C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military History Of China Before 1911
The recorded military history of China extends from about 2200 BC to the present day. Chinese pioneered the use of crossbows, advanced metallurgical standardization for arms and armor, early gunpowder weapons, and other advanced weapons, but also adopted nomadic cavalry and Western military technology.Frederic E. Wakeman: ''The Great Enterprise: The Manchu Reconstruction of Imperial Order in Seventeenth-century China'', Vol. 1 (1985), , p. 77 China's armies also benefited from an advanced logistics system as well as a rich strategic tradition, beginning with Sun Tzu's ''The Art of War'', that deeply influenced military thought. History of military organization The military history of China stretches from roughly 2200 BC to the present day. Chinese armies were advanced and powerful, especially after the Warring States period. These armies were tasked with the twofold goal of defending China and her subject peoples from foreign intruders, and with expanding China's territory and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protectorate General To Pacify The East
The Protectorate-General to Pacify the East () was an administrative division of the Chinese Tang dynasty in Manchuria and the northern part of the Korean Peninsula. It was established after the Tang dynasty defeated Goguryeo and annexed its territories. In the place of Baekje and Goguryeo, the Tang dynasty created the Protectorate General to Pacify the East and the Ungjin Commandery. A proposal to set up the Great Commandery of Gyerim by the Emperor Gaozong of Tang to King Munmu of Silla was refused. History After the Tang dynasty conquered Goguryeo in 668, the Protectorate General to Pacify the East, otherwise known as the Andong Protectorate, was created in Pyongyang and supposedly stationed with 200,000 soldiers. The protectorate was divided into 9 commanderies, 42 prefectures, and 100 counties. In 669 the people of Goguryeo revolted in response to Tang governance. In response the Tang forcibly deported 78,000 households and resettled them in empty areas south of the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protectorate General To Pacify The North
The Protectorate General to Pacify the North or Grand Protectorate General to Pacify the North (647–784) was a Chinese military government established by the Tang dynasty in 647 to pacify the former territory of Xueyantuo, which extended from Lake Baikal to the north, the Gobi Desert to the south, the Khingan Mountains to the east, and the Altay Mountains to the west. It controlled the Mongolian Plateau from 647 to 682. It was first established as Yanran at Shanyu Tai, southwest of present-day Urat Middle Banner, the northern slope of Lang Shan. This was later shifted to Hanhai, around the bank of the Orkhon River, and named from its namesakes for a short period before it was changed to Anbei. The seat of governance remained there until the year 687. History In 646 the Tang dynasty conquered the Xuyantuo and on 9 January 647, thirteen Tiele and Uyghur tribes surrendered to the Tang. Tang Taizong organized them into six commanderies and seven tributary prefectures under the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protectorate General To Pacify The West
The Protectorate General to Pacify the West (Anxi Grand Protectorate), initially the Protectorate to Pacify the West (Anxi Protectorate), was a protectorate (640 – ) established by the Chinese Tang dynasty in 640 to control the Tarim Basin. The head office was first established at the prefecture of Xi, now known as Turpan, but was later shifted to Qiuci (Kucha) and situated there for most of the period. The Four Garrisons of Anxi in Kucha, Khotan, Kashgar, and Karashahr were installed between 648 and 658 as garrisons under the western protectorate. In 659, Sogdia, Ferghana, Tashkent, Bukhara, Samarkand, Balkh, Herat, Kashmir, the Pamirs, Tokharistan, and Kabul all submitted to the protectorate under Emperor Gaozong of Tang. After the An Lushan Rebellion (755–763) was suppressed, the office of Protector General was given to Guo Xin, who defended the area and the four garrisons even after communication had been cut off from Chang'an by the Tibetan Empire. The last five years o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
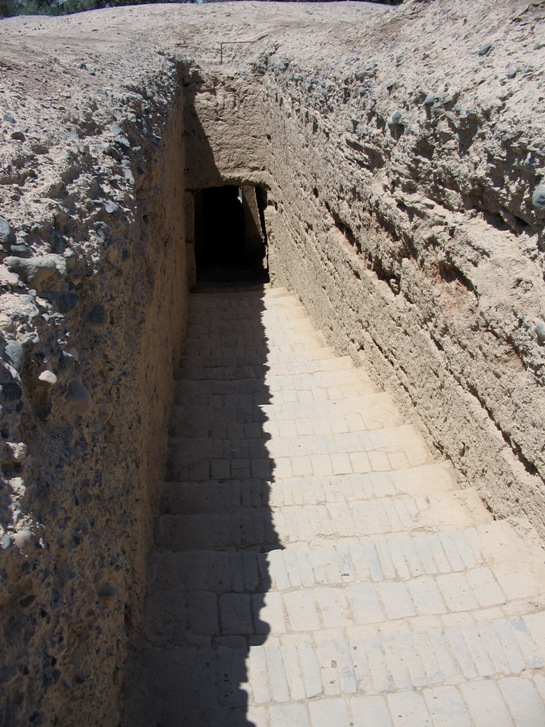
Astana Graves
The Astana Cemetery () is an ancient cemetery southeast of Turpan, in Xinjiang, China, from the ancient city of Gaochang. It served mainly as the cemetery for the descendants of Chinese settlers in Gaochang from the 4th century to the first half of the 8th century. The complex covers and contains over 1,000 tombs. Due to the arid environment many important artifacts have been well preserved at the tombs, including natural mummies. Description of the tombs The tombs consist of sloping passageways leading downwards for 4 or 5m to a rockcut entrance, about a meter wide and over a meter high. A step then leads into a brick-lined chamber, square or oblong and measuring between two and four meters wide, three to four meters long and up to two meters high. Some tombs contain one or two narrow antechambers in which there are niches on either side for guardian beasts in effigy. These figures show a variety of animal features and some have human faces. In their exuberance they resemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Qocho
Qocho (), also known as Idiqut, ("holy wealth"; "glory"; "lord of fortune") was a Uyghur kingdom created in 843, with strong Chinese Buddhist and Tocharian influences. It was founded by Uyghur refugees fleeing the destruction of the Uyghur Khaganate after being driven out by the Yenisei Kirghiz. They made their summer capital in Qocho (also called ''Gaochang'' or ''Qara-Khoja'', near modern Turpan) and winter capital in Beshbalik (modern Jimsar County, also known as Tingzhou). Its population is referred to as the "Xizhou Uyghurs" after the old Tang Chinese name for Gaochang, the Qocho Uyghurs after their capital, the Kucha Uyghurs after another city they controlled, or the Arslan (lion) Uyghurs after their king's title. Timeline In 843 a group of Uyghurs migrated southward under the leadership of Pangtele and occupied Karasahr and Kucha, taking them from the Tibetan Empire. In 856, this group of Uyghurs received royal recognition from the Tang dynasty. At this time their c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
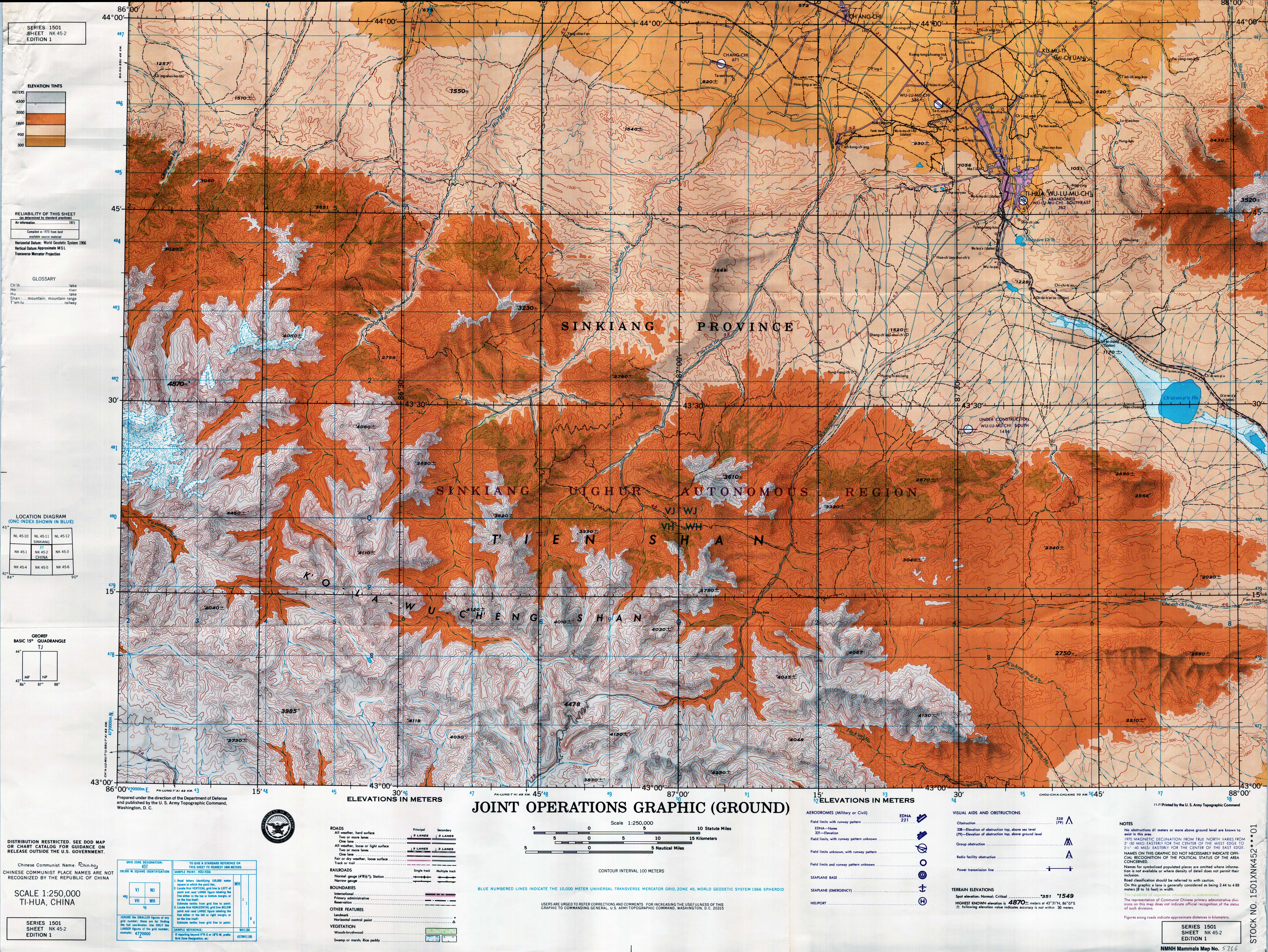
Ürümqi
Ürümqi ( ; also spelled Ürümchi or without umlauts), formerly known as Dihua (also spelled Tihwa), is the capital of the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in the far northwest of the People's Republic of China. Ürümqi developed its reputation as a leading cultural and commercial center during the Qing dynasty in the 19th century. With a census population of 4 million in 2020, Ürümqi is the second-largest city in China's northwestern interior after Xi'an as well as the largest in Central Asia in terms of population. According to the ''Guinness Book of Records'', Ürümqi is the most remote city from any sea in the world. Ürümqi has seen significant economic development since the 1990s and currently serves as a regional transport node and a cultural, political and commercial center. Ürümqi is one of the top 500 cities in the world by scientific research output, as tracked by the Nature Index. The city is also home to Xinjiang University, a comprehensive univer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunhuang
Dunhuang () is a county-level city in Northwestern Gansu Province, Western China. According to the 2010 Chinese census, the city has a population of 186,027, though 2019 estimates put the city's population at about 191,800. Dunhuang was a major stop on the ancient Silk Road and is best known for the nearby Mogao Caves. Dunhuang is situated in an oasis containing Crescent Lake and Mingsha Shan (, meaning "Singing-Sand Mountain"), named after the sound of the wind whipping off the dunes, the singing sand phenomenon. Dunhuang commands a strategic position at the crossroads of the ancient Southern Silk Route and the main road leading from India via Lhasa to Mongolia and Southern Siberia, and also controls the entrance to the narrow Hexi Corridor, which leads straight to the heart of the north Chinese plains and the ancient capitals of Chang'an (today known as Xi'an) and Luoyang. Administratively, the county-level city of Dunhuang is part of the prefecture-level city of Jiuquan. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_in_番客入朝圖_(937-976_CE).jpg)