|
Beirut–Rafic Hariri International Airport
Beirut–Rafic Hariri International Airport (Arabic: مطار رفيق الحريري الدولي بيروت, (previously known as Beirut International Airport) () is the only operational commercial airport in Lebanon, which is located in the Southern Suburbs of Beirut, Lebanon, from the city center. It is the hub for Lebanon's national carrier, Middle East Airlines (MEA) and was the hub for the Lebanese cargo carrier TMA cargo and Wings of Lebanon before their respective collapses. The airport is named after former Lebanese Prime Minister Rafic Hariri in 2005, who was assassinated earlier that year. It is the main port of entry into the country along with the Port of Beirut. The airport is managed and operated by the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA), which operates within the Ministry of Public Works and Transport. The DGCA is also responsible for operating the air traffic control (ATC) at the airport as well as controlling Lebanon's airspace. DGCA duties i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle East Airlines
Middle East Airlines – Air Liban S.A.L. ( ar, طيران الشرق الأوسط ـ الخطوط الجوية اللبنانية ''Ṭayyarān al-Sharq al-Awsaṭ – al-Khuṭūṭ al-jawiyyah al-lubnāniyyah''), more commonly known as Middle East Airlines (MEA) ( ar, links=no, طيران الشرق الأوسط ''Ṭayyarān al-Sharq al-Awsaṭ''), is the national flag-carrier airline of Lebanon, with its head office in Beirut, near Beirut–Rafic Hariri International Airport. It operates scheduled international flights to Asia, Europe, the Middle East, and Africa from its base at Rafic Hariri International Airport. Middle East Airlines (MEA) is a member of the SkyTeam airline alliance. MEA expressed its interest in becoming a SkyTeam associate member in early 2006 at a press conference in New York. On 28 February 2011, the airline signed the partnership agreement with SkyTeam at a ceremony in Beirut, and officially joined the alliance on 28 June 2012, becoming its 17th memb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lebanese International Airways
Lebanese International Airways was a Lebanese airline based in Beirut.Lebanese International Airways Al Mashriq. Retrieved 5 September 2014. Formed with help from Pan Am,Profile for: Lebanese International Airways Aero Transport. Retrieved 5 September 2014. it began scheduled flights in January 1956, and by 1958 had expanded its network through agreements with of Belgium. By the mid-1960s, LIA's destinations included |
2006 Lebanon War
The 2006 Lebanon War, also called the 2006 Israel–Hezbollah War and known in Lebanon as the July War ( ar, حرب تموز, ''Ḥarb Tammūz'') and in Israel as the Second Lebanon War ( he, מלחמת לבנון השנייה, ''Milhemet Levanon HaShniya''), was a 34-day war, military conflict in Lebanon, Northern Israel and the Golan Heights. The principal parties were Hezbollah paramilitary forces and the Israel Defense Forces (IDF). The conflict started on 12 July 2006, and continued until a United Nations-brokered ceasefire went into effect in the morning on 14 August 2006, though it formally ended on 8 September 2006 when Israel lifted its naval blockade of Lebanon. Due to unprecedented Iranian military support to Hezbollah before and during the war, some consider it the first round of the Iran–Israel proxy conflict, rather than a continuation of the Arab–Israeli conflict. The conflict was precipitated by the 2006 Hezbollah cross-border raid. On 12 July 2006, Hezbolla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israeli Air Force
The Israeli Air Force (IAF; he, זְרוֹעַ הָאֲוִיר וְהֶחָלָל, Zroa HaAvir VeHahalal, tl, "Air and Space Arm", commonly known as , ''Kheil HaAvir'', "Air Corps") operates as the aerial warfare branch of the Israel Defense Forces. It was founded on May 28, 1948, shortly after the Israeli Declaration of Independence. , Aluf Tomer Bar has been serving as the Air Force commander. The Israeli Air Force was established using commandeered or donated civilian aircraft and obsolete and surplus World War II combat aircraft. Eventually, more aircraft were procured, including Boeing B-17s, Bristol Beaufighters, de Havilland Mosquitoes and P-51D Mustangs. The Israeli Air Force played an important part in Operation Kadesh, Israel's part in the 1956 Suez Crisis, dropping paratroopers at the Mitla Pass. On June 5, 1967, the first day of the Six-Day War, the Israeli Air Force performed Operation Focus, debilitating the opposing Arab air forces and attaining air suprema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed-base Operator
A fixed-base operator (FBO) is an organization granted the right by an airport to operate at the airport and provide aeronautical services such as fueling, hangaring, tie-down and parking, aircraft rental, aircraft maintenance, flight instruction, and similar services. In common practice, an FBO is the primary provider of support services to general aviation operators at a public-use airport and is on land leased from the airport, or, in rare cases, adjacent property as a "through the fence operation". In many smaller airports serving general aviation in remote or modest communities, the town itself may provide fuel services and operate a basic FBO facility. Most FBOs doing business at airports of high to moderate traffic volume are non-governmental organizations, either privately or publicly held companies. Though the term ''fixed-base operator'' originated in the United States, the term has become more common in the international aviation industry as business and corporate aviati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
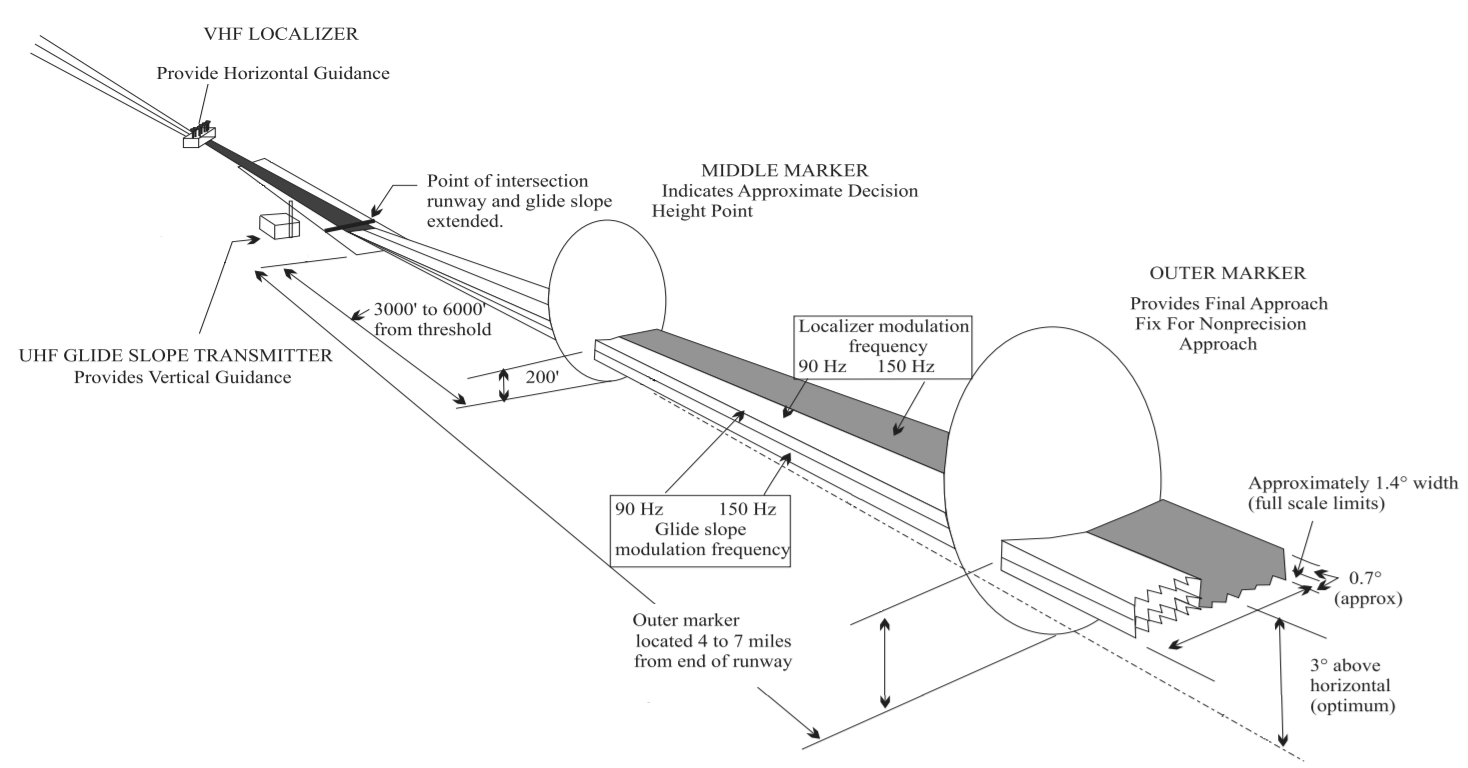
Instrument Landing System
In aviation, the instrument landing system (ILS) is a precision radio navigation system that provides short-range guidance to aircraft to allow them to approach a runway at night or in bad weather. In its original form, it allows an aircraft to approach until it is over the ground, within a of the runway. At that point the runway should be visible to the pilot; if it is not, they perform a missed approach. Bringing the aircraft this close to the runway dramatically increases the range of weather conditions in which a safe landing can be made. Other versions of the system, or "categories", have further reduced the minimum altitudes, runway visual ranges (RVRs), and transmitter and monitoring configurations designed depending on the normal expected weather patterns and airport safety requirements. ILS uses two directional radio signals, the ''localizer'' (108 to 112 MHz frequency), which provides horizontal guidance, and the ''glideslope'' (329.15 to 335 MHz frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxiway
A taxiway is a path for aircraft at an airport connecting runways with aprons, hangars, terminals and other facilities. They mostly have a hard surface such as asphalt or concrete, although smaller general aviation airports sometimes use gravel or grass. Most airports do not have a specific speed limit for taxiing (though some do). There is a general rule on safe speed based on obstacles. Operators and aircraft manufacturers might have limits. Typical taxi speeds are 20–30 knots (37–56 km/h; 23–35 mph). High-speed exit Busy airports typically construct high-speed or rapid-exit taxiways to allow aircraft to leave the runway at higher speeds. This allows the aircraft to vacate the runway quicker, permitting another to land or take off in a shorter interval of time. This is accomplished by reducing the angle the exiting taxiway intercepts the runway at to 30 degrees, instead of 90 degrees, thus increasing the speed at which the aircraft can exit the runway onto the taxiway. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Noise
Aircraft noise pollution refers to noise produced by aircraft in flight that has been associated with several negative stress-mediated health effects, from sleep disorders to cardiovascular ones. Governments have enacted extensive controls that apply to aircraft designers, manufacturers, and operators, resulting in improved procedures and cuts in pollution. Sound production is divided into three categories: * Mechanical noise—rotation of the engine parts, most noticeable when fan blades reach supersonic speeds. * Aerodynamic noise—from the airflow around the surfaces of the aircraft, especially when flying low at high speeds. * Noise from aircraft systems—cockpit and cabin pressurization and conditioning systems, and Auxiliary Power units. Mechanisms of sound production Aircraft noise is noise pollution produced by an aircraft or its components, whether on the ground while parked such as auxiliary power units, while taxiing, on run-up from propeller and jet exhaust, duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parking Garage
A multistorey car park (British and Singapore English) or parking garage (American English), also called a multistory, parking building, parking structure, parkade (mainly Canadian), parking ramp, parking deck or indoor parking, is a building designed for car, motorcycle & bicycle parking and where there are a number of floors or levels on which parking takes place. It is essentially an indoor, stacked car park. The first known multistory facility was built in London in 1901, and the first underground parking was built in Barcelona in 1904. (See History, below.) The term multistory is almost never used in the US, since parking structures are almost all multiple levels. Parking structures may be heated if they are enclosed. Design of parking structures can add considerable cost for planning new developments, and can be mandated by cities in new building parking requirements. Some cities such as London have abolished previously enacted minimum parking requirements. Minimum p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1983 Beirut Barracks Bombing
Early on a Sunday morning, October 23, 1983, two truck bombs struck buildings in Beirut, Lebanon, housing American and French service members of the Multinational Force in Lebanon (MNF), a military peacekeeping operation during the Lebanese Civil War. The attack killed 307 people: 241 U.S. and 58 French military personnel, six civilians, and two attackers. The first suicide bomber detonated a truck bomb at the building serving as a barracks for the 1st Battalion 8th Marines (Battalion Landing Team – BLT 1/8) of the 2nd Marine Division, killing 220 marines, 18 sailors and three soldiers, making this incident the deadliest single-day death toll for the United States Marine Corps since the Battle of Iwo Jima in World War II and the deadliest single-day death toll for the United States Armed Forces since the first day of the Tet Offensive in the Vietnam War. Another 128 Americans were wounded in the blast; 13 later died of their injuries, and they are counted among the number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lebanese Civil War
The Lebanese Civil War ( ar, الحرب الأهلية اللبنانية, translit=Al-Ḥarb al-Ahliyyah al-Libnāniyyah) was a multifaceted armed conflict that took place from 1975 to 1990. It resulted in an estimated 120,000 fatalities and an exodus of almost one million people from Lebanon. The diversity of the Lebanese population played a notable role in the lead-up to and during the conflict: Sunni Muslims and Christians comprised the majority in the coastal cities; Shia Muslims were primarily based in the south and the Beqaa Valley in the east; and Druze and Christians populated the country's mountainous areas. The Lebanese government had been run under the significant influence of elites within the Maronite Christian community. The link between politics and religion had been reinforced under the French Mandate from 1920 to 1943, and the country's parliamentary structure favoured a leading position for its Christian-majority population. However, the country had a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)