|
Beihai Kingdom
Beihai Commandery ( zh, 北海郡) was a historical commandery (China), commandery of China, located in present-day northern Shandong province. Beihai was created during Emperor Jing of Han's reign. According to Zhou Zhenhe, Beihai was likely established on six counties from Jiaoxi Kingdom, and gradually expanded its borders over the rest of Western Han as marquessates from neighboring kingdoms were added to the commandery. In late Western Han, it covered 26 counties and marquessates: Yingling (營陵), Jukui (劇魁), Anqiu (安丘), Zhi (瓡), Chunyu (淳于), Yi (益), Pingshou (平壽), Ju (劇), Duchang (都昌), Pingwang (平望), Pingdi (平的), Liuquan (柳泉), Shouguang (壽光), Lewang (樂望), Rao (饒), Zhen (斟), Sangdu (桑犢), Pingcheng (平城), Mixiang (密鄉), Yangshi (羊石), Ledu (樂都), Shixiang (石鄉), Shangxiang (上鄉), Xincheng (新成), Chengxiang (成鄉) and Jiaoyang (膠陽). The population in 2 AD was 593,159, or 127,000 households. In earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commandery (China)
A jùn (郡) was a historical administrative division of China from the Eastern Zhou (c. 7th century BCE) until the early Tang dynasty (c. 7th century CE). It is usually translated as a commandery. Countries around China have adopted administrative divisions based on or named after the ''jùn''. History and development China Eastern Zhou During the Eastern Zhou's Spring and Autumn period from the 8th to 5th centuries BCE, the larger and more powerful of the Zhou's vassal states—including Qin, Jin and Wei—began annexing their smaller rivals. These new lands were not part of their original fiefs and were instead organized into counties (''xiàn''). Eventually, jun were developed as marchlands between the major realms. Despite having smaller populations and ranking lower on the official hierarchies, the jun were larger and boasted greater military strength than the counties. As each state's territory gradually took shape in the 5th- to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Song
Song, known as Liu Song (), Former Song (前宋) or Song of (the) Southern Dynasty (南朝宋) in historiography, was an imperial dynasty of China and the first of the four Southern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties period. It succeeded the Eastern Jin dynasty and preceded the Southern Qi dynasty. The dynasty was founded by Liu Yu (Emperor Wu; 363–422 CE), whose surname together with "Song" forms the common name for the dynasty, the Liu Song. This appellation is used to distinguish it from a later dynasty of the same name, the Song dynasty (960–1279 CE, ruled by the House of Zhao). Although the Liu Song has also at times been referred to as the "Southern Song", the name is now mainly used to refer to the Song dynasty after 1127 CE. The Liu Song was a time when there was much internal turmoil. A number of emperors were incompetent and/or tyrannical, which at least partially led to many military revolts. These rulers include Liu Shao, Emperor Xiaowu, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commanderies Of The Jin Dynasty (266–420)
In the Middle Ages, a commandery (rarely commandry) was the smallest administrative division of the European landed estate, landed properties of a Military order (religious society), military order. It was also the name of the house where the knights of the commandery lived.Anthony Luttrell and Greg O'Malley (eds.), ''The Countryside Of Hospitaller Rhodes 1306–1423: Original Texts And English Summaries'' (Routledge, 2019), p. 27. The word is also applied to the emoluments granted to a commander. They were the equivalent for those orders to a monastic grange. The knight in charge of a commandery was a commander (order), commander. Etymology The word derives from French ''commanderie'' or ''commenderie'', from mediaeval Latin ''commendaria'' or ''commenda'', meaning "a trust or charge", originally one held ''in commendam''. "commandery , commandry, n." OED Online, Oxford University Press, December 2018, https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/36962. Accessed 9 December 2018. Originally, co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commanderies Of The Han Dynasty
In the Middle Ages, a commandery (rarely commandry) was the smallest administrative division of the European landed properties of a military order. It was also the name of the house where the knights of the commandery lived.Anthony Luttrell and Greg O'Malley (eds.), ''The Countryside Of Hospitaller Rhodes 1306–1423: Original Texts And English Summaries'' (Routledge, 2019), p. 27. The word is also applied to the emoluments granted to a commander. They were the equivalent for those orders to a monastic grange. The knight in charge of a commandery was a commander. Etymology The word derives from French ''commanderie'' or ''commenderie'', from mediaeval Latin ''commendaria'' or ''commenda'', meaning "a trust or charge", originally one held ''in commendam''. "commandery , commandry, n." OED Online, Oxford University Press, December 2018, https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/36962. Accessed 9 December 2018. Originally, commandries were benefices, particularly in the Church, held ''in comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Book Of Tang
The ''New Book of Tang'', generally translated as the "New History of the Tang" or "New Tang History", is a work of official history covering the Tang dynasty in ten volumes and 225 chapters. The work was compiled by a team of scholars of the Song dynasty, led by Ouyang Xiu and Song Qi. It was originally simply called the ''Tangshu'' (Book of Tang) until the 18th century. History In Chinese history, it was customary for dynasties to compile histories of their immediate predecessor as a means of cementing their own legitimacy. As a result, during the Later Jin dynasty of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, a history of the preceding Tang dynasty, the '' Old Book of Tang'' () had already been compiled. In 1044, however, Emperor Renzong of Song ordered a new compilation of Tang history, based on his belief that the original ''Old Book of Tang'' lacked organization and clarity. The process took 17 years, being finally completed in 1060. Contents The ''New Book of Tang' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
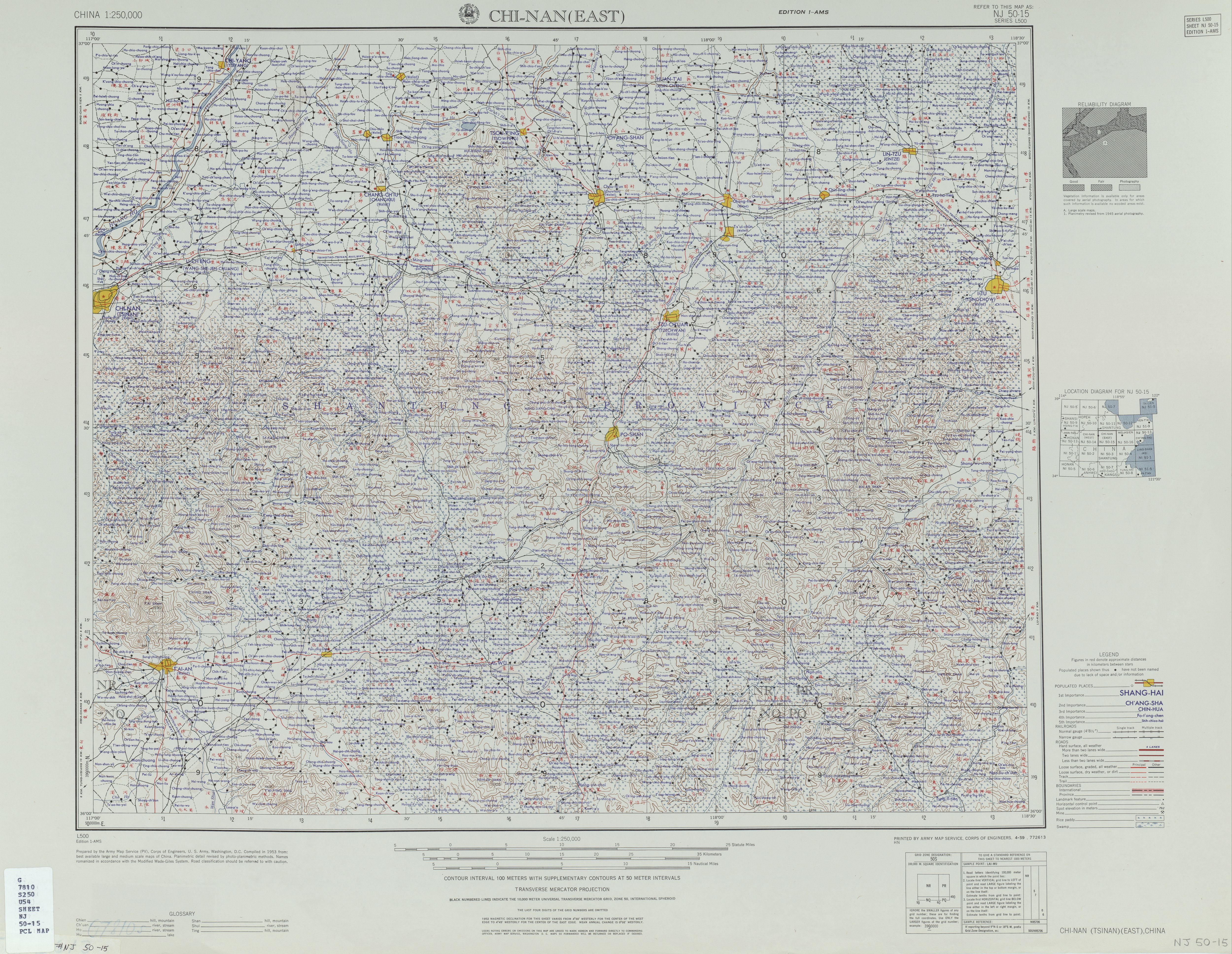
Linqu County
Linqu County () is a county, originally known as "Pianyi", located in the southwest of Weifang and the middle of Shandong Peninsula, Shandong Province, China. Linqu also has the name Zhuxu County. It covers an area of and governs 937 villages which were grouped into eight townships and two subdistricts . Linqu has a population of 926 thousand(2020). With a long history of over 2000 years since its establishment in the West Han Dynasty, Linqu is well known for its beautiful sceneries and rich cultures, such as traditional operas, brush paintings and calligraphy, rare rock arts, Mount Yi National Forest Park, Shanwang National Geography Park, Old Dragon Spring and Shimenfang Park. Its over 210 archeology sites include Dawenkou culture and Longshan culture relics. It was also the site of the Battle of Linqu in 409 Geography There are many mountains in the county, such as Mountain Yi and Mountain Song. The River Mi originated from the foothills of Mountain Yi. It is the first wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linzi District
Linzi District () is a district of the prefecture-level city of Zibo, in central Shandong province, China. Located near the Shengli Oil Field, Linzi's economy is driven by petro-chemical refinery. Wheat, corn and cotton are cultivated in the rural areas surrounding the urban center. The ruins of Ancient Linzi located in the northwest of the district, was the site of the ancient State of Qi's capital. Linzi is one of the most highly developed industrial districts in north China with the highest GDP in Shandong Province. Administrative divisions As 2012, this District is divided to 5 subdistricts, 7 towns and 1 township. ;Subdistricts ;Towns ;Townships * Bianhe Township () Climate People from Linzi #Zuo Si, poet of the Western Jin #Zuo Fen, poet of the Western Jin Western may refer to: Places *Western, Nebraska, a village in the US *Western, New York, a town in the US *Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia *Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qingzhou
Qingzhou () Wade–Giles: Tsing-chou, sometimes written as Ching-chow-fu, formerly Yidu County (Yitu) (), is a county-level city, which is located in the west of the prefecture-level city of Weifang, in the central part of Shandong Province, China. Qingzhou is a dynamic industry city, and also grows a great number of farm products. The local government holds an open policy of introduction of foreign capital, and has established strong business relationships with more than fifty countries and regions. History Qingzhou is named after one of the nine provinces that appear in the ''Yu Gong'' geography chapter of the classic ''Book of Documents'' composed during the Warring States period of Chinese history (403 BC - 221 BC). The history of this centuries old city dates back to ancient times twenty two centuries ago when it was part of the Dongyi area. Administrative divisions As 2012, this city is divided to 3 subdistricts and 9 towns. ;Subdistricts *Wangfu Subdistrict () *Yidu S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Prefecture (Shandong)
Qingzhou is a county-level city in Shandong, China. Qingzhou may also refer to: *Qingzhou Bridge, a bridge over the Min River in Fuzhou, Fujian, China Towns and townships *Qingzhou, Fujian, a town in Shaxian District, Sanming, Fujian, China * Qingzhou, Guangdong, a town in Heping County, Guangdong, China * Qingzhou, Hebei, a town in Qing County, Hebei, China * Qingzhou Township, a township in Jiajiang County, Sichuan, China Historical locations *Qing Province (青州), one of the Nine Provinces in ancient China * Qīng Prefecture (青州), a prefecture in modern Shandong, China between the 6th and 11th centuries, named after the ancient province *Qìng Prefecture (慶州), a prefecture in modern Gansu, China between the 6th and 11th centuries See also * Ching Chau (other) — Cantonese equivalent *Qing (other) *Cheongju, a city in North Chungcheong, South Korea, known as "Qingzhou" in Chinese *Gyeongju Gyeongju ( ko, 경주, ), historically known as ''Seora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilization, and a Golden age (metaphor), golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivaled that of the Han dynasty. The House of Li, Lǐ family () founded the dynasty, seizing power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire and inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Zhou dynasty (690–705), Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The devast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sui Dynasty
The Sui dynasty (, ) was a short-lived imperial dynasty of China that lasted from 581 to 618. The Sui unified the Northern and Southern dynasties, thus ending the long period of division following the fall of the Western Jin dynasty, and laying the foundations for the much longer lasting Tang dynasty. Founded by Emperor Wen of Sui, the Sui dynasty capital was Chang'an (which was renamed Daxing, modern Xi'an, Shaanxi) from 581–605 and later Luoyang (605–18). Emperors Wen and his successor Yang undertook various centralized reforms, most notably the equal-field system, intended to reduce economic inequality and improve agricultural productivity; the institution of the Five Departments and Six Board (五省六曹 or 五省六部) system, which is a predecessor of Three Departments and Six Ministries system; and the standardization and re-unification of the coinage. They also spread and encouraged Buddhism throughout the empire. By the middle of the dynasty, the newly unifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Song
The ''Book of Song'' (''Sòng Shū'') is a historical text of the Liu Song Dynasty of the Southern Dynasties of China. It covers history from 420 to 479, and is one of the Twenty-Four Histories, a traditional collection of historical records. It was written in 492–493 by Shen Yue from the Southern Qi dynasty (479–502). The work contained 100 volumes at the time that it was written, but some volumes were already missing by the time of the Song Dynasty. Later editors reconstructed those volumes by taking material from the ''History of the Southern Dynasties'', plus a few works such as the ''Historiette of Gao'' by Gao Jun, though many of those volumes were no longer in their original condition. History The ''Book of Song'' was based on records compiled beginning in the Liu Song. He Chentian 何承天 (370-447) was commissioned by the imperial court of the time in 439. He compiled biographies and also treatises on astronomy and music. Compilation was later continued by Shan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |