|
Begin Road (Tel Aviv)
Begin Road is a major thoroughfare in Tel Aviv, Israel. It begins at Allenby Street and runs to its northern end which is at Arlozorov Interchange on Ayalon Highway. There is one interchange along Begin Road, Kaplan Interchange, located near Azrieli Center and Tel Aviv HaShalom railway station, with two lanes in each direction passing under Kaplan Street. Another interchange, Ma'ariv Bridge, was demolished on August 21, 2015, as part of the works to build the Carlebach station of Tel Aviv Light Rail. Begin Road is a section of the ancient road from Jaffa Clock Tower to Nablus in Samaria. On the Survey of Palestine map from 1944, the whole section north of the old Tel Aviv central bus station is named Petah Tikva Road. In 2001, its part within the city boundaries of Tel Aviv-Yafo, i.e. west of Ayalon Highway, was renamed after Menachem Begin. The rest of the former Petah Tikva Road, lying in the cities of Ramat Gan Ramat Gan ( he, רָמַת גַּן or , ) is a city i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaffa Clock Tower
The Jaffa Clock Tower ( he, מגדל השעון יפו, ''Migdal haShaon Yafo'', ar, يافا برج الساعة, tr, Yafa Saat Kulesi) stands in the middle of the north end of Yefet Street in Jaffa, Tel Aviv. The tower, built of limestone, incorporates two clocks and a plaque commemorating the Israelis killed in the battle for the town in the 1948 Arab–Israeli War. It is one of seven clock towers built in Ottoman Palestine. The others are located in Safed, Acre, Nazareth (though that one is significantly smaller), Haifa, Nablus. Jerusalem also had a clock tower built during the Ottoman period, but the British Field Marshal Sir Edmund Allenby, demanded its destruction as he would not see such a clear Ottoman symbol resting on the city wall of Jerusalem, for which he had much emotions. History The construction of the tower was initiated by Joseph Bey Moyal, a prominent Jewish businessman from Jaffa, who was also the mind behind the Jaffa–Jerusalem railway. The constructio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramat Gan
Ramat Gan ( he, רָמַת גַּן or , ) is a city in the Tel Aviv District of Israel, located east of the municipality of Tel Aviv and part of the Tel Aviv metropolitan area. It is home to one of the world's major diamond exchanges, and many high-tech industries. Ramat Gan was established in 1921 as a moshav shitufi, a communal farming settlement. In it had a population of . History Ramat Gan was established by the ''Ir Ganim'' association in 1921 as a satellite town of Tel Aviv. The first plots of land were purchased between 1914 and 1918. It stood just south of the Arab village of Jarisha. The settlement was initially a moshava, a Zionist agricultural colony that grew wheat, barley and watermelons. The name of the settlement was changed to Ramat Gan (lit: ''Garden Height'') in 1923. The settlement continued to operate as a moshava until 1933, although it achieved local council status in 1926. At this time it had 450 residents. In the 1940s, Ramat Gan became a battlegr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menachem Begin
Menachem Begin ( ''Menaḥem Begin'' (); pl, Menachem Begin (Polish documents, 1931–1937); ''Menakhem Volfovich Begin''; 16 August 1913 – 9 March 1992) was an Israeli politician, founder of Likud and the sixth Prime Minister of Israel. Before the creation of the state of Israel, he was the leader of the Zionist militant group Irgun, the Revisionist breakaway from the larger Jewish paramilitary organization Haganah. He proclaimed a revolt, on 1 February 1944, against the British mandatory government, which was initially opposed by the Jewish Agency. Later, the Irgun fought the Arabs during the 1947–48 Civil War in Mandatory Palestine. Begin was elected to the first Knesset, as head of Herut, the party he founded, and was at first on the political fringe, embodying the opposition to the Mapai-led government and Israeli establishment. He remained in opposition in the eight consecutive elections (except for a national unity government around the Six-Day War), but bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petah Tikva
Petah Tikva ( he, פֶּתַח תִּקְוָה, , ), also known as ''Em HaMoshavot'' (), is a city in the Central District (Israel), Central District of Israel, east of Tel Aviv. It was founded in 1878, mainly by Haredi Judaism, Haredi Jews of the Old Yishuv, and became a permanent settlement in 1883 with the financial help of Edmond James de Rothschild, Baron Edmond de Rothschild. In , the city had a population of . Its population density is approximately . Its jurisdiction covers 35,868 dunams (~35.9 km2 or 15 sq mi). Petah Tikva is part of the Tel Aviv Metropolitan Area. Etymology Petah Tikva takes its name (meaning "Door of Hope") from the biblical allusion in Hosea 2:15: "... and make the valley of Achor a door of hope." The Achor Valley, near Jericho, was the original proposed location for the town. The city and its inhabitants are sometimes known by the nickname "Mlabes" after the Arab village preceding the town. (See "Ottoman era" under "History" below.) Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Tel Aviv Central Bus Station
The Old Tel Aviv central bus station was the main bus station of Tel Aviv from 1941 until 1993. The station served intercity bus routes as well as local city and suburban buses. On August 18, 1993, Tel Aviv's New central bus station became the city's new transportation hub. The old station was demolished in July 2009. History When the station opened in 1941, it was intended to serve 60,000 passengers a day. It had six departure platforms linked by underground passages and another platform for arrivals. Soon after its opening, it was found to be inadequate and poorly planned. The canopies over the platforms were too narrow to protect passengers from rain and sun, and interfered with loading of baggage onto the roofs of the buses. During the 1948 Arab–Israeli War the station was bombed by Egyptian planes, killing 42 persons, including four members of the Dan cooperative, and wounding 100. On November 6, 1970, two bombs exploded in Tel Aviv at the central bus station killing one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Survey Of Palestine
The Survey of Palestine was the government department responsible for the Cartography of Palestine, survey and mapping of Palestine during the Mandatory Palestine, British mandate period. The survey department was established in 1920 in Jaffa, and moved to the outskirts of Tel Aviv in 1931. It established the Palestine grid. In early 1948, the British Mandate appointed a temporary Director General of the Survey Department for the impending Jewish State; this was to became the Survey of Israel. The maps produced by the survey have been widely used in "Palestinian refugee cartography" by scholars documenting the 1948 Palestinian exodus; notably in Salman Abu Sitta's ''Atlas of Palestine'' and Walid Khalidi's ''All That Remains''. In 2019 the maps were used as the basis for ''Palestine Open Maps'', supported by the Bassel Khartabil Free Culture Fellowship. History Prior to the beginning of the Mandate for Palestine, the British had carried out two significant surveys of the reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samaria
Samaria (; he, שֹׁמְרוֹן, translit=Šōmrōn, ar, السامرة, translit=as-Sāmirah) is the historic and biblical name used for the central region of Palestine, bordered by Judea to the south and Galilee to the north. The first-century historian Josephus set the Mediterranean Sea as its limit to the west, and the Jordan River as its limit to the east. Its territory largely corresponds to the biblical allotments of the tribe of Ephraim and the western half of Manasseh. It includes most of the region of the ancient Kingdom of Israel, which was north of the Kingdom of Judah. The border between Samaria and Judea is set at the latitude of Ramallah. The name "Samaria" is derived from the ancient city of Samaria, capital of the northern Kingdom of Israel. The name Samaria likely began being used for the entire kingdom not long after the town of Samaria had become Israel's capital, but it is first documented after its conquest by Sargon II of Assyria, who turned the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nablus
Nablus ( ; ar, نابلس, Nābulus ; he, שכם, Šəḵem, ISO 259-3: ; Samaritan Hebrew: , romanized: ; el, Νεάπολις, Νeápolis) is a Palestinian city in the West Bank, located approximately north of Jerusalem, with a population of 126,132.PCBS02007 Locality Population Statistics. Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS). Located between Mount Ebal and Mount Gerizim, it is the capital of the Nablus Governorate and a commercial and cultural centre of the State of Palestine, home to An-Najah National University, one of the largest Palestinian institutions of higher learning, and the Palestine Stock Exchange.Amahl Bishara, ‘Weapons, Passports and News: Palestinian Perceptions of U.S. Power as a Mediator of War,’ in John D. Kelly, Beatrice Jauregui, Sean T. Mitchell, Jeremy Walton (eds.''Anthropology and Global Counterinsurgency,''pp.125-136 p.126. Nablus is under the administration of the Palestinian National Authority as part of Area A of the West Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
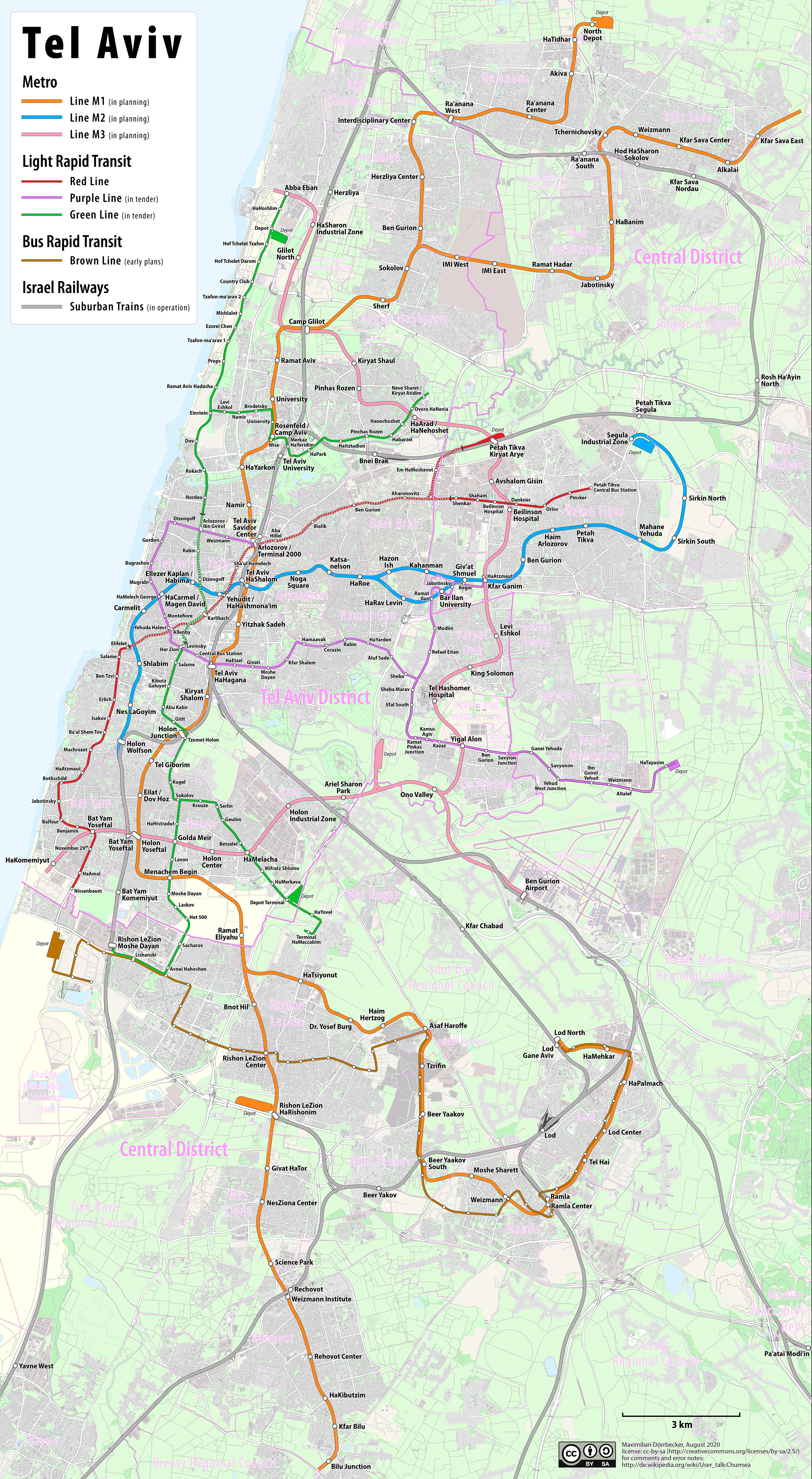
Tel Aviv Light Rail
Dankal ( he, דנקל, commonly known as the Tel Aviv Light Rail) is a planned mass transit system for the Tel Aviv metropolitan area in central Israel. The system will include different modes of mass transit, including rapid transit (metro), light rail transit (LRT), and bus rapid transit (BRT). Overseen by the government agency NTA, the project will complement the intercity and suburban rail network operated by Israel Railways. As of 2021, three LRT lines are under construction. Work on the Red Line, the first in the project, started on September 21, 2011, following years of preparatory works, and is expected to be completed in late 2022 after numerous delays. Construction of the Purple Line started in December 2018; work on the Green Line began in January 2019. The network was originally planned to be called "MetroTLV" but was changed to "Dankal". History The first proposals for a tramway in the area were made by the Lebanese engineer George Franjieh in November 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlebach Station
Carlebach is the family name of a notable Jewish family originally from Germany that now lives all over the world, it can refer to: *People: ** Elisheva Carlebach Jofen, American scholar of early modern Jewish history ** Emil Carlebach (1914–2001), German writer and journalist ** Ephraim Carlebach (1879–1936), German-born Orthodox rabbi ** Ezriel Carlebach (1909–1956), Israeli journalist and editorial writer ** Felix Carlebach (1911–2008), Rabbi in Manchester, England ** Hartwig Naftali Carlebach (1889–1967), founder of the Carlebach Shul, father of Rabbi Shlomo Carlebach ** Joseph Carlebach (1883–1942), German Orthodox rabbi, scholar and scientist ** Julius Carlebach, (1922–2001), German-British Rabbi and scholar ** Naftoli Carlebach (1916–2005), Orthodox rabbi and accountant ** Neshama Carlebach, singer ** Shlomo Carlebach (1925–1994), rabbi, religious teacher, composer, and singer ** Shlomo Carlebach (1925–2022), German-born American Haredi rabbi and scholar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |