|
Beer Chemistry
The chemical compounds in beer give it a distinctive taste, smell and appearance. The majority of compounds in beer come from the metabolic activities of plants and yeast and so are covered by the fields of biochemistry and organic chemistry. The main exception is that beer contains over 90% water and the mineral ions in the water (hardness) can have a significant effect upon the taste. Four main ingredients Four main ingredients are used for making beer in the process of brewing: carbohydrates (from malt), hops, yeast, and water. Carbohydrates (from malt) The carbohydrate source is an essential part of the beer because unicellular yeast organisms convert carbohydrates into energy to live. Yeast metabolize the carbohydrate source to form a number of compounds including ethanol. The process of brewing beer starts with malting and mashing, which breaks down the long carbohydrates in the barley grain into more simple sugars. This is important because yeast can only metabo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12-hopfenwiegen
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley production is used as animal fodder, while 30% as a source of fermentable material for beer and certain distilled beverages, and as a component of various foods. It is used in soups and stews, and in barley bread of various cultures. Barley grains are commonly made into malt in a traditional and ancient method of preparation. In 2017, barley was ranked fourth among grains in quantity produced () behind maize, rice and wheat. Etymology The Old English word for barley was ', which traces back to Proto-Indo-European and is cognate to the Latin word ' "flour" (''see corresponding entries''). The direct ancestor of modern English ''barley'' in Old English was the derived adjective ''bærlic'', meaning "of barley". The first citation of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lupulone
Lupulone is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C26 H38 O4 and an appearance of a yellow powder which was historically used in beer brewing. However, recent studies have revealed numerous antibacterial and anti-cancer abilities of lupulone. History Since lupulone is found as a component of hops, the history of the compound can be traced back to 736 AD in southern Germany where hops plant were first cultivated. The commercial production of using lupulone in brewing was not until 1079 AD. The reason that lupulone was not utilized in beer brewing earlier on may be due to the fact that the hops plants has a bitter taste. However, brewers began to realize that beta acids of hops provided very little bitterness to the beer. Eventually, hops brewing with the use of lupulone made its way to the United States about 6 centuries later in 1629 after England introduced it. Synthesis A synthesis pathway of lupulone involves the alkenylation of 2-acylcyclohexane-1, 3, 5-tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humulone
Humulone (α-lupulic acid), a vinylogous type of organic acid, is a bitter-tasting chemical compound found in the resin of mature hops (''Humulus lupulus''). Humulone is a prevalent member of the class of compounds known as alpha acids, which collectively give hopped beer its characteristic bitter flavor. Chemistry In terms of structure, humulone is a phloroglucinol derivative with three isoprenoid side-chains. Two side-chains are prenyl groups and one is an isovaleryl group. The acidity of the ring enol moieties that give rise to its designation as an acid lie in their vinylogous relationship with the ring and side chain carbonyl functional groups. Isohumulone During the brewing process, humulone degrades to ''cis-'' and ''trans-''isohumulone. These “alpha acids” survive the boiling process, although numerous oxidized derivatives are produced. The iso-alpha acids are significantly more soluble than humulone at the pH levels typically present in the brewing process. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humulus Lupulus
''Humulus lupulus'', the common hop or hops, is a species of flowering plant in the hemp family Cannabinaceae, native to Europe, western Asia and North America. It is a perennial, herbaceous climbing plant which sends up new shoots in early spring and dies back to a cold-hardy rhizome in autumn. It is dioecious (having separate male and female plants). As the female cone-shaped flowers (hops) are used to preserve and flavor beer, the species is widely cultivated by the brewing industry. Description ''Humulus lupulus'' is a perennial herbaceous plant up to tall, living up to 20 years. It has simple leaves with 3–5 deep lobes that can be opposite or alternate. The species is triggered by the longer summer days to flower, usually around July or August. The plant is dioecious, with male and female flowers on separate plants. The fragrant flowers are wind-pollinated. The staminate (male) flowers do not have petals, while the pistillate (female) flowers have petals enveloping th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dextrin Skeletal
Dextrins are a group of low-molecular-weight carbohydrates produced by the hydrolysis of starch and glycogen. Dextrins are mixtures of polymers of D-glucose units linked by α-(1→4) or α-(1→6) glycosidic bonds. Dextrins can be produced from starch using enzymes like amylases, as during digestion in the human body and during Malt#Malting, malting and mashing, or by applying dry heat under acidic conditions (pyrolysis or roasting). This procedure was first discovered in 1811 by Edme-Jean Baptiste Bouillon-Lagrange. The latter process is used industrially, and also occurs on the surface of bread during the baking process, contributing to flavor, color and crispness. Dextrins produced by heat are also known as pyrodextrins. Starch hydrolyses during roasting under acidic conditions, and short-chained starch parts partially rebranch with α-(1,6) bonds to the degraded starch molecule. See also Maillard reaction. Dextrins are white, yellow, or brown powder that are partially or full ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the substance and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Site
In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site consists of amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate (binding site) and residues that catalyse a reaction of that substrate (catalytic site). Although the active site occupies only ~10–20% of the volume of an enzyme, it is the most important part as it directly catalyzes the chemical reaction. It usually consists of three to four amino acids, while other amino acids within the protein are required to maintain the tertiary structure of the enzymes. Each active site is evolved to be optimised to bind a particular substrate and catalyse a particular reaction, resulting in high specificity. This specificity is determined by the arrangement of amino acids within the active site and the structure of the substrates. Sometimes enzymes also need to bind with some cofactors to fulfil their function. The active si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amylase
An amylase () is an enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of starch (Latin ') into sugars. Amylase is present in the saliva of humans and some other mammals, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Foods that contain large amounts of starch but little sugar, such as rice and potatoes, may acquire a slightly sweet taste as they are chewed because amylase degrades some of their starch into sugar. The pancreas and salivary gland make amylase (alpha amylase) to hydrolyse dietary starch into disaccharides and trisaccharides which are converted by other enzymes to glucose to supply the body with energy. Plants and some bacteria also produce amylase. Specific amylase proteins are designated by different Greek letters. All amylases are glycoside hydrolases and act on α-1,4-glycosidic bonds. Classification α-Amylase The α-amylases () ( CAS 9014-71-5) (alternative names: 1,4-α-D-glucan glucanohydrolase; glycogenase) are calcium metalloenzymes. By acting at random loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight, where it is used to make cellulose in cell walls, the most abundant carbohydrate in the world. In energy metabolism, glucose is the most important source of energy in all organisms. Glucose for metabolism is stored as a polymer, in plants mainly as starch and amylopectin, and in animals as glycogen. Glucose circulates in the blood of animals as blood sugar. The naturally occurring form of glucose is -glucose, while -glucose is produced synthetically in comparatively small amounts and is less biologically active. Glucose is a monosaccharide containing six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group, and is therefore an aldohexose. The glucose molecule can exist in an open-chain (acyclic) as well as ring (cyclic) form. Gluco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
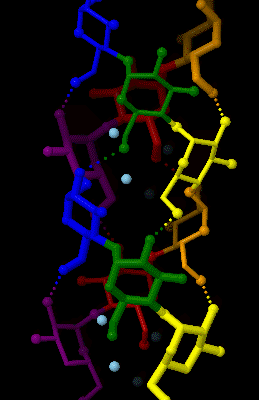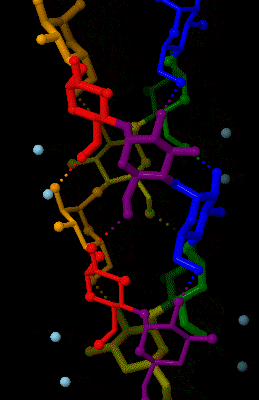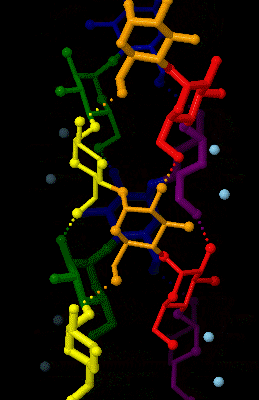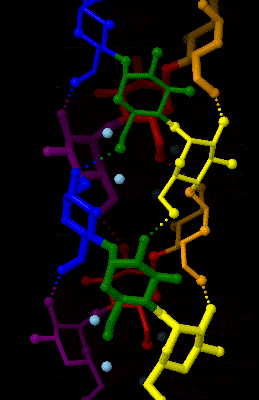
Amylose
Amylose is a polysaccharide made of α-D-glucose units, bonded to each other through α(1→4) glycosidic bonds. It is one of the two components of starch, making up approximately 20–30%. Because of its tightly packed helical structure, amylose is more resistant to digestion than other starch molecules and is therefore an important form of resistant starch. Structure Amylose is made up of α(1→4) bound glucose molecules. The carbon atoms on glucose are numbered, starting at the aldehyde (C=O) carbon, so, in amylose, the 1-carbon on one glucose molecule is linked to the 4-carbon on the next glucose molecule (α(1→4) bonds). The structural formula of amylose is pictured at right. The number of repeated glucose subunits (n) is usually in the range of 300 to 3000, but can be many thousands. There are three main forms of amylose chains can take. It can exist in a disordered amorphous conformation or two different helical forms. It can bind with itself in a double helix (A or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



-2017-Ystad.jpg)