|
Bechuana
The Tswana ( tn, Batswana, singular ''Motswana'') are a Bantu-speaking ethnic group native to Southern Africa. The Tswana language is a principal member of the Sotho-Tswana language group. Ethnic Tswana made up approximately 85% of the population of Botswana in 2011. Batswana are the native people of south and eastern Botswana, and the Gauteng, North West, Northern Cape and Free State provinces of South Africa, where the majority of Batswana are located. History Early history of Batswana The Batswana are descended mainly from Bantu-speaking tribes along with the Khoi-San. Tswana tribe migrated southward to Africa around 600 CE, living in tribal enclaves as farmers and herders. Several Iron Age cultures flourished around the 900 CE, including the Toutswemogala Hill Iron Age settlement. The Toutswe were in the eastern region of what is now Botswana, relying on Tswana cattle breed held in kraals as their source of wealth. The arrival of the ancestors of the Tswana-speaker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botswana
Botswana (, ), officially the Republic of Botswana ( tn, Lefatshe la Botswana, label=Setswana, ), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. Botswana is topographically flat, with approximately 70 percent of its territory being the Kalahari Desert. It is bordered by South Africa to the south and southeast, Namibia to the west and north, and Zimbabwe to the northeast. It is connected to Zambia across the short Zambezi River border by the Kazungula Bridge. A country of slightly over 2.3 million people, Botswana is one of the most sparsely populated countries in the world. About 11.6 percent of the population lives in the capital and largest city, Gaborone. Formerly one of the world's poorest countries—with a GDP per capita of about US$70 per year in the late 1960s—it has since transformed itself into an upper-middle-income country, with one of the world's fastest-growing economies. Modern-day humans first inhabited the country over 200,000 years ago. The Tswana ethnic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khama III
Khama III (1837?–1923), referred to by missionaries as Khama the Good also called Khama the Great, was the ''Kgosi'' (meaning king) of the Bangwato people. Ancestry and Youth Malope a chief of the Bakwena, led his people from the Transvaal region of South Africa into the southeast territory of Botswana. Malope had three sons – Kwena, Ngwato, and Ngwaketse – each of whom would eventually break away from their father (as well as from each other) and form new communities in neighboring territories. This type of familial break between father and sons (and then between sons) was historically how ethnic communities proliferated throughout the southern African region. In this particular instance, the break between Malope and sons was precipitated by a series of events – the death of Malope, Kwena's subsequent assumption of the Bakwena chieftainship, and ultimately a dispute between Kwena and Ngwato over a lost cow. Shortly after the lost-cow incident, Ngwato and his followers s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Matabele War
The First Matabele War was fought between 1893 and 1894 in modern-day Zimbabwe. It pitted the British South Africa Company against the Ndebele (Matabele) Kingdom. Lobengula, king of the Ndebele, had tried to avoid outright war with the company's pioneers because he and his advisors were mindful of the destructive power of European-produced weapons on traditional Matabele impis (units of warriors) attacking in massed ranks. Lobengula reportedly could muster 80,000 spearmen and 20,000 riflemen, armed with Martini-Henry rifles, which were modern arms at that time. However, poor training meant that these were not used effectively. The British South Africa Company had no more than 750 troops in the British South Africa Company's Police, with an undetermined number of possible colonial volunteers and an additional 700 Tswana (Bechuana) allies. Cecil Rhodes, who was Prime Minister of the Cape Colony and Leander Starr Jameson, the Administrator of Mashonaland also tried to avoid war ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
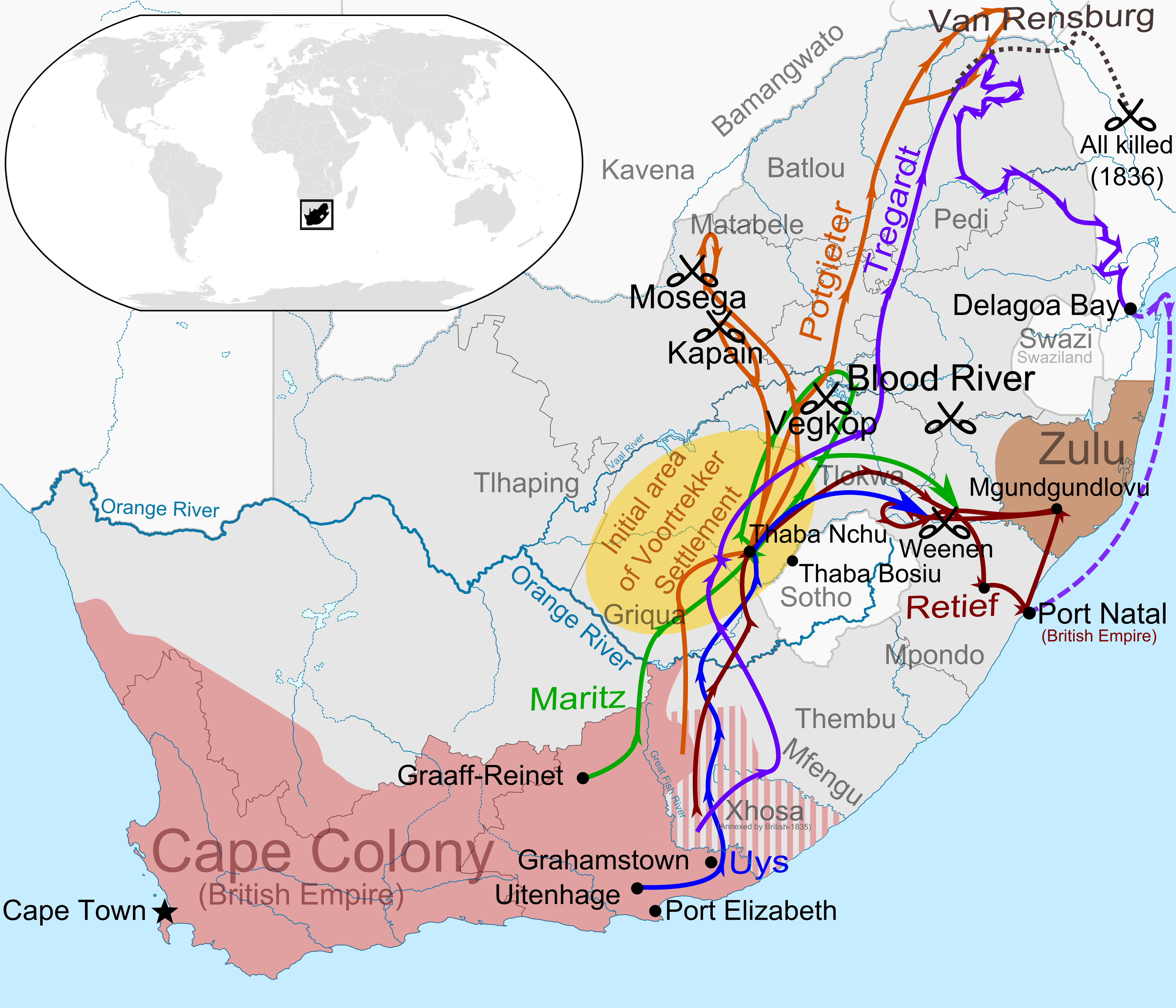
Paul Kruger
Stephanus Johannes Paulus Kruger (; 10 October 1825 – 14 July 1904) was a South African politician. He was one of the dominant political and military figures in 19th-century South Africa, and President of the South African Republic (or Transvaal) from 1883 to 1900. Nicknamed ''Oom Paul'' ("Uncle Paul"), he came to international prominence as the face of the Boer cause—that of the Transvaal and its neighbour the Orange Free State—against Britain during the Second Boer War of 1899–1902. He has been called a personification of Afrikanerdom, and remains a controversial figure; admirers venerate him as a tragic folk hero. Born near the eastern edge of the Cape Colony, Kruger took part in the Great Trek as a child during the late 1830s. He had almost no education apart from the Bible. A protégé of the Voortrekker leader Andries Pretorius, he witnessed the signing of the Sand River Convention with Britain in 1852 and over the next decade played a prominent role in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sechele Gustav Fritsch 1865
Sechele I a Motswasele "Rra Mokonopi" (1812–1892), also known as Setshele, was the ruler of the Kwêna people of Botswana. He was converted to Christianity by David Livingstone and in his role as ruler served as a missionary among his own and other African peoples. According to Livingstone biographer Stephen Tomkins, Sechele was Livingstone's only African convert to Christianity, even though Livingstone himself came to regard Sechele as a "backslider". Sechele led a coalition of Batswana (Bakwêna, Bakaa, Balete, Batlokwa) in the Battle of Dimawe in 1852. Early life Sechele was born in 1812, the son of the chief of the Kwêna tribe of Tswana people of what is modern-day Botswana. When Sechele was ten years old, his father was killed and the leadership of the tribe was divided between his two uncles. Sechele and some of his supporters fled into the desert. He spent some years among the Ngwato people and married Mokgokong, a daughter of Chief Kgari. In about 1831 he succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tswana Language
Tswana, also known by its Endonym and exonym, native name , and previously spelled Sechuana in English, is a Bantu language spoken in Southern Africa by about 8.2 million people. It belongs to the Bantu languages, Bantu language family within the Sotho-Tswana languages, Sotho-Tswana branch of Guthrie classification of Bantu languages#Zone S, Zone S (S.30), and is closely related to the Northern Sotho language, Northern Sotho and Sotho language, Southern Sotho languages, as well as the Kgalagadi language and the Lozi language. Setswana is an official language of Botswana and South Africa. It is a lingua franca in Botswana and parts of South Africa, particularly North West Province. Tswana tribes are found in more than two provinces of South Africa, primarily in the North West (South African province), North West, where about four million people speak the language. An urbanised variety, which is part slang and not the formal Setswana, is known as Pretoria Sotho, and is the prin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Dimawe
The Battle of Dimawe was fought between several Batswana tribes and the Boers in August 1852. Under the command of Kgosi Setshele I of the Bakwena tribe, the Batswana were victorious at Dimawe Hill. Background According to Paul Kruger, a chief called Moselele the chief of Bakgatla-ba-ga mmanana had committed several murders in the South African Republic and then fled to Sechele I, who refused to hand him over to the Boers, saying "Who wants Moselele can come and fetch him out of my stomach". He meant to convey that Moselele was as safely hidden with him as the food which he had eaten. When the Boers arrived Sechele I send a messenger to Commandant Scholtz to say that he would do nothing to him on the morrow, as that was a Sunday, but that he would duly settle the account on the Monday. At the same time he demanded coffee and sugar, probably in return for his amiability in "letting the Boers off" for Sunday. Commandant Scholtz send back word that he had coffee and sugar, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-colonial Indigenous South African Rondavel
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their religion, language, economics, and other cultural practices. The foreign administrators rule the territory in pursuit of their interests, seeking to benefit from the colonised region's people and resources. It is associated with but distinct from imperialism. Though colonialism has existed since ancient times, the concept is most strongly associated with the European colonial period starting with the 15th century when some European states established colonising empires. At first, European colonising countries followed policies of mercantilism, aiming to strengthen the home-country economy, so agreements usually restricted the colony to trading only with the metropole (mother country). By the mid-19th century, the British Empire gave up merc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(14796270283).jpg)