|
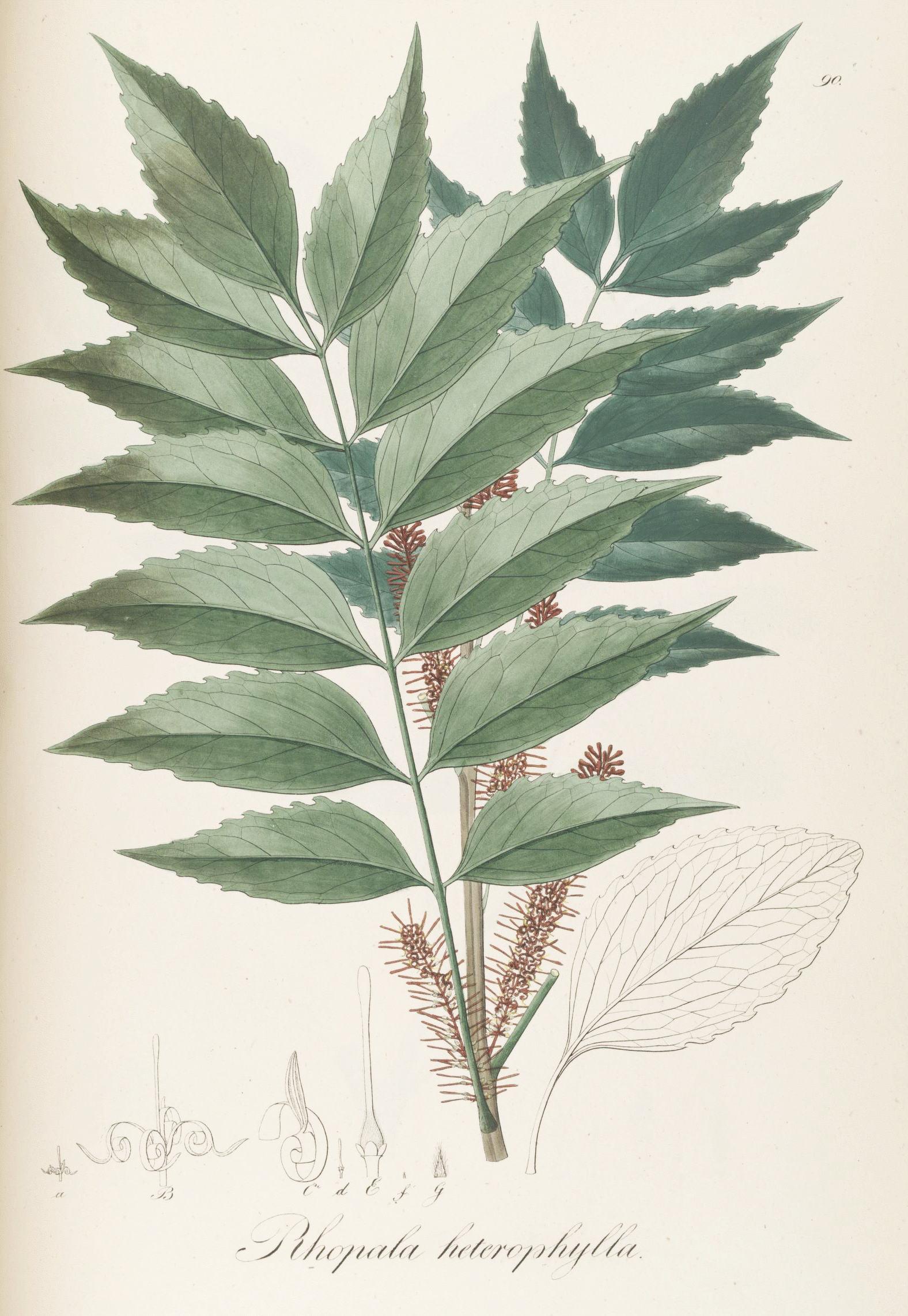
Beauprea Spathulaefolia
''Beauprea spathulaefolia'' is a species of flowering plants in the family Proteaceae. It is found in New Caledonia. References External links ''Beauprea spathulaefolia''at The Plant List The Plant List was a list of botanical names of species of plants created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and the Missouri Botanical Garden and launched in 2010. It was intended to be a comprehensive record of all known names of plant species ... ''Beauprea spathulaefolia''at Tropicos spathulaefolia Plants described in 1871 Flora of New Caledonia Taxa named by Adolphe-Théodore Brongniart Taxa named by Jean Antoine Arthur Gris {{proteaceae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolphe-Théodore Brongniart
Adolphe-Théodore Brongniart () Royal Society, FRS FRSE FGS (14 January 1801 – 18 February 1876) was a French botany, botanist. He was the son of the geologist Alexandre Brongniart and grandson of the architect, Alexandre-Théodore Brongniart. Brongniart's pioneering work on the relationships between extinct and existing plants has earned him the title of father of paleobotany. His major work on plant fossils was his ' (1828–37). He wrote his dissertation on the Buckthorn family (Rhamnaceae), an extant family of flowering plants, and worked at the Muséum national d'Histoire naturelle in Paris until his death. In 1851, he was elected a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. This botanist is denoted by the List of botanists by author abbreviation, author abbreviation Brongn. when Author citation (botany), citing a botanical name. Brongniart's works Brongniart was an indefatigable investigator and a prolific writer of books and memoirs. As early as 1822 h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Antoine Arthur Gris
Jean Antoine Arthur Gris (11 December 1829 – 19 August 1872) was a French botanist who was a native of Châtillon-sur-Seine, in the department of Côte-d'Or. Beginning in 1855 he worked in the laboratory of Adolphe-Théodore Brongniart (1801-1876) at the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle in Paris. In 1859 he received his PhD with a dissertation involving microscopic studies of chlorophyll. He was the author of 80 scientific articles, the majority of them being published in the '' Bulletin de la Société botanique de France'' and the ''Annales des sciences naturelles''. In 1865, Brongniart named the genus ''Grisia'' (synonym: ''Bikkia'', family: Rubiaceae) in his honor. Grisia Brongn. Jean Gris died in Paris on 19 August 1872 at the age of 42. He is buried in the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flowering Plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants that produce their seeds enclosed within a fruit. They are by far the most diverse group of land plants with 64 orders, 416 families, approximately 13,000 known genera and 300,000 known species. Angiosperms were formerly called Magnoliophyta (). Like gymnosperms, angiosperms are seed-producing plants. They are distinguished from gymnosperms by characteristics including flowers, endosperm within their seeds, and the production of fruits that contain the seeds. The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from the common ancestor of all living gymnosperms before the end of the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. The closest fossil relatives of flowering plants are uncertain and contentious. The earliest angiosperm fossils ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteaceae
The Proteaceae form a family of flowering plants predominantly distributed in the Southern Hemisphere. The family comprises 83 genera with about 1,660 known species. Together with the Platanaceae and Nelumbonaceae, they make up the order Proteales. Well-known genera include ''Protea'', ''Banksia'', ''Embothrium'', ''Grevillea'', ''Hakea'' and ''Macadamia''. Species such as the New South Wales waratah (''Telopea speciosissima''), king protea (''Protea cynaroides''), and various species of ''Banksia'', ''soman'', and ''Leucadendron'' are popular cut flowers. The nuts of ''Macadamia integrifolia'' are widely grown commercially and consumed, as are those of Gevuina avellana on a smaller scale. Australia and South Africa have the greatest concentrations of diversity. Etymology The name Proteaceae was adapted by Robert Brown from the name Proteae coined in 1789 for the family by Antoine Laurent de Jussieu, based on the genus ''Protea'', which in 1767 Carl Linnaeus derived from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Plant List
The Plant List was a list of botanical names of species of plants created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and the Missouri Botanical Garden and launched in 2010. It was intended to be a comprehensive record of all known names of plant species over time, and was produced in response to Target 1 of the 2002-2010 Global Strategy for Plant Conservation (GSP C), to produce "An online flora of all known plants.” It has not been updated since 2013, and has been superseded by World Flora Online. World Flora Online In October 2012, the follow-up project World Flora Online was launched with the aim to publish an online flora of all known plants by 2020. This is a project of the United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity, with the aim of halting the loss of plant species worldwide by 2020. It is developed by a collaborative group of institutions around the world response to the 2011-2020 GSPC's updated Target 1. This aims to achieve an online Flora of all known plants by 2020. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropicos
Tropicos is an online botanical database containing taxonomic information on plants, mainly from the Neotropical realm (Central, and South America). It is maintained by the Missouri Botanical Garden and was established over 25 years ago. The database contains images and taxonomical and bibliographical data on more than 4.2 million herbarium A herbarium (plural: herbaria) is a collection of preserved plant specimens and associated data used for scientific study. The specimens may be whole plants or plant parts; these will usually be in dried form mounted on a sheet of paper (called ... specimens. In addition, it contains data on over 49,000 scientific publications. The database can be queried in English, French, and Spanish. The oldest records in the database go back to 1703. References External links * Online botany databases Online taxonomy databases Missouri Botanical Garden {{database-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beauprea
''Beauprea'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Proteaceae. Its 13 extant species are endemic to New Caledonia, though closely related forms have been found in the fossil records of Australia and New Zealand. Its closest extant relatives are the African ''Protea'' and ''Faurea ''Faurea'' is a genus containing 16 species of flowering plants in the protea family which occur in the summer rainfall area of southern Africa, extending to tropical Africa and Madagascar. The name honours South African soldier and botanist W ...''. Species Described species include: *'' Beauprea asplenioides'' Schltr. *'' Beauprea balansae'' Brongn. & Gris *'' Beauprea comptonii'' S.Moore *'' Beauprea congesta'' Virot *'' Beauprea crassifolia'' Virot *'' Beauprea filipes'' Schltr. *'' Beauprea gracilis'' Brongn. & Gris *'' Beauprea montana'' (Brongn. & Gris) Virot *'' Beauprea montis-fontium'' Guillaumin *'' Beauprea neglecta'' Virot *'' Beauprea pancheri'' Brongn. & Gris *'' Beauprea penar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plants Described In 1871
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude the fungi and some algae, as well as the prokaryotes (the archaea and bacteria). By one definition, plants form the clade Viridiplantae (Latin name for "green plants") which is sister of the Glaucophyta, and consists of the green algae and Embryophyta (land plants). The latter includes the flowering plants, conifers and other gymnosperms, ferns and their allies, hornworts, liverworts, and mosses. Most plants are multicellular organisms. Green plants obtain most of their energy from sunlight via photosynthesis by primary chloroplasts that are derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria. Their chloroplasts contain chlorophylls a and b, which gives them their green color. Some plants are parasitic or mycotrophic and have lost the ability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of New Caledonia
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous (ecology), indigenous) native plant, native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms ''gut flora'' or ''skin flora''. Etymology The word "flora" comes from the Latin name of Flora (mythology), Flora, the goddess of plants, flowers, and fertility in Roman mythology. The technical term "flora" is then derived from a metonymy of this goddess at the end of the sixteenth century. It was first used in poetry to denote the natural vegetation of an area, but soon also assumed the meaning of a work cataloguing such vegetation. Moreover, "Flora" was used to refer to the flowers of an artificial garden in the seventeenth century. The distinction between vegetation (the general appearance of a community) and flora (the taxonomic composition of a community) was first made by Jules Thurmann (1849). Prior to this, the two terms were used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Adolphe-Théodore Brongniart
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |